JOURNAL 3340
Organic Communications
Year: 2024 Issue: 4 October-December
p.178 - 192
Viewed 1533 times.
-
Aiyagala M.M. Mallikarjunasawamy

-
Praveen Naik

-
Momidi Bharath Kumar

-
Kuruvalli Gouthami

-
Vaddi Damodara Reddy

-
Vipin A. Nair

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
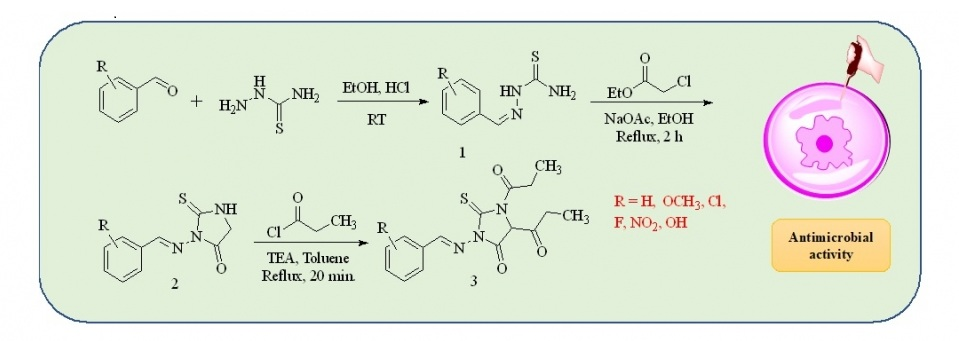
The infectious diseases caused by antimicrobial pathogens are often difficult to treat and thwarted by resistance to drugs. Therefore, designing new drugs to treat antimicrobial infections is a challenge in drug discovery research. A series of 2-thioxoimidazolidinone derivatives were synthesized in high yield from N'-arylideneamino-2-thioxoimidazolidin-4-ones using propionyl chloride and triethyl amine in toluene medium. The compounds were screened for the in vitro antifungal and antibacterial activities. The studies revealed that compounds (±)1,1'-(3-(((1E,2E)-3-(2-methoxyphenyl)allylidene)amino)-4-oxo-2-thioxoimidazolidine-1,5-diyl)-bis(propan-1-one) and (±)1,1'-(3-((2,4-dichlorobenzylidene)amino)-4-oxo-2-thioxoimidazolidine-1,5-diyl)bis-(propan-1-one) possess antifungal properties comparable to the reference drug ketoconazole. This study highlights the importance of substituted 2-thioxoimidazolidinone derivatives, and their potential as antimicrobial agents.
KEYWORDS- 2-Thioxoimidazolidinone
- in-vitro studies
- molecular docking
- nitrogen heterocycles
- antifungal agents