JOURNAL 3361
Organic Communications
Year: 2024 Issue: 4 October-December
p.205 - 217
Viewed 1610 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
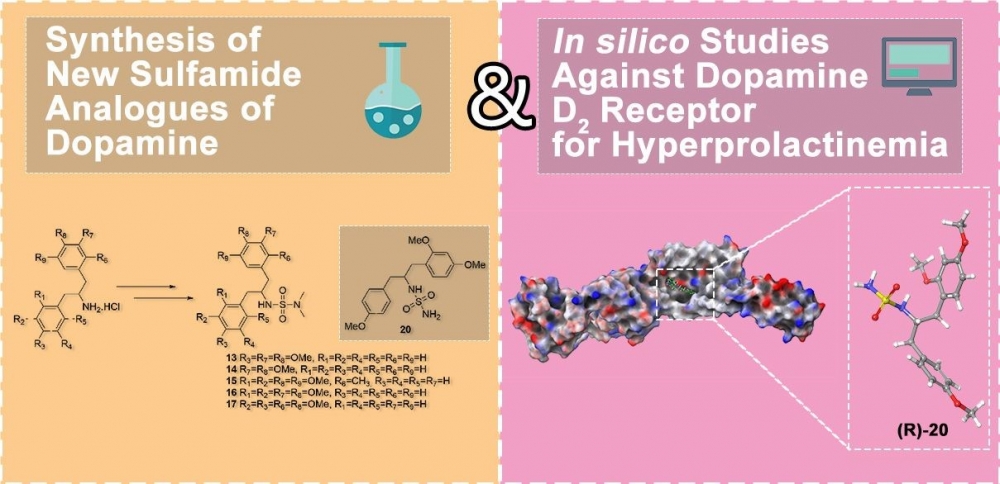
ABSTRACT
Because of the important biological properties of sulfamides, in the present work six novel sulfamides were synthesized from dopamine derivatives and their insilico studies were carried out against hyperprolactinemia. Five sulfamides were synthesized via the reaction of known dopamine derivatives with N,N-dimethyl sulfamoyl chloride in the presence of NEt3. For comparison of biological activity, a sulfamide without N-alkyl at the terminal nitrogen was also synthesized. For this synthesis, firstly benzyl alcohol was reacted with chlorosulfonyl isocyanate (CSI). Then, new sulfamoyl carbamate was obtained by the reaction of the formed carbamate derivative with a dopamine analogue in the presence of NEt3. As a result of the hydrogenolysis of the formed sulfamoyl carbamate under Pd-C catalyst, a new sulfamide was obtained. Molecular docking simulations and ADME predictions were employed to assess the binding affinity and drug-like properties of sulfamide derivatives at the dopamine D2 receptor, aiming to identify potential contributors to hyperprolactinemia. In the in silico docking studies, it was determined that the binding affinity of the R enantiomer of unsubstituted sulfamide 20 to the D2 receptor was higher than that of Cabergoline and Quinagolide used as standards and there was no deviation from the Lipinski rule of five in the ADME evaluation.
KEYWORDS- Dopamin derivatives
- dopaminergic
- hyperprolactinemia
- molecular docking
- sulfamides