JOURNAL 3374
Organic Communications
Year: 2024 Issue: 4 October-December
p.218 - 240
Viewed 1435 times.
-
Aiyagala M.M. Mallikarjunasawamy

-
Kuruvalli Gouthami

-
Subhasish Maity

-
Vaddi Damodara Reddy

-
Lakshmi Basavegowda

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
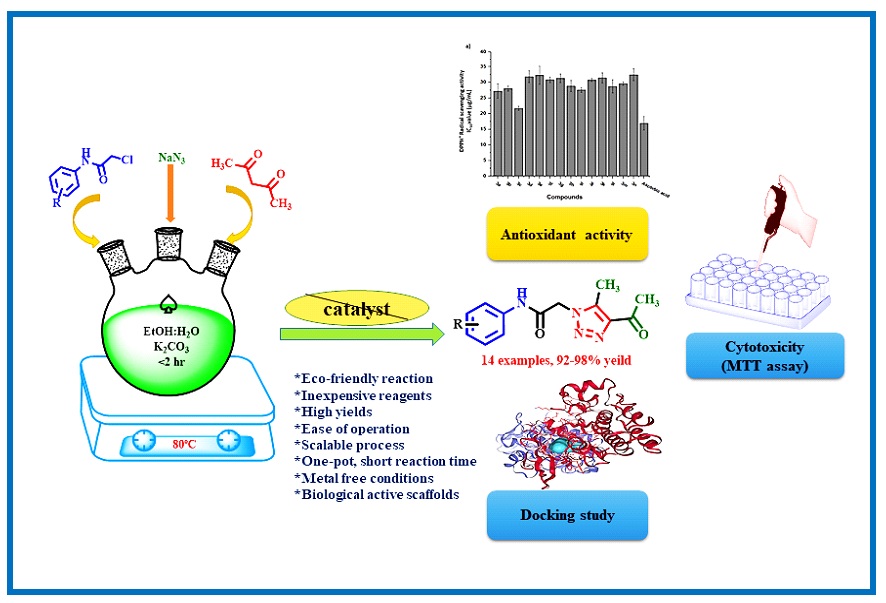
Cancer has been a widespread disease for decades in various of types for decades, and the search for effective treatments continues. Researchers are exploring various new drugs, including natural compounds and small organic molecules, for their potential to combat cancer. One promising approach involves hybrid structures that combine different pharmacophore units with known biological activities. These structures have gained popularity due to their encouraging results. In this study, we synthesized several new hybrid compounds containing 1,2,3-triazole units. We confirmed the structures of these compounds using methods like ¹H NMR, ¹³C NMR, and LC-MS. We then evaluated their antioxidant properties and in vitro anticancer activities. The results showed that these new compounds demonstrated having good radical scavenging activity and potential agents for anticancer activity. Notably, compounds 3b, 3d, 3a, 3m, and 3i exhibited low concentrations of IC50 values (14.08±0.6, 14.3±0.8, 15.82±0.4, 18.12±0.86 and 19.7±0.88 μg/mL, respectively) when compared to the standard drug Cisplatin (IC50: 21.13±1.6 µg/mL). Computational analysis has been performed like ADMET evaluation and Molecular docking studies revealed the compounds having good binding affinity with cancer target proteins like HIF-1α ranging from -8.1 kcal/mol to -7.0 kcal/mol and HER2 ranging from -10.0 kcal/mol to -8.8 kcal/mol respectively when compared with standard drug Cisplatin showed binding affinity ranging from -4.2 kcal/mol to -3.9 kcal/mol.
KEYWORDS- Nucleophilic substitution
- 2-chloro-N-arylacetamide
- 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition
- 1,2,3-triazoles
- MTT assay