JOURNAL 1985
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Issue: 6 November-December (Special Issue Dedicated to the Memory of Professor Ayhan Ulubelen)
p.537 - 546
Viewed 2394 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
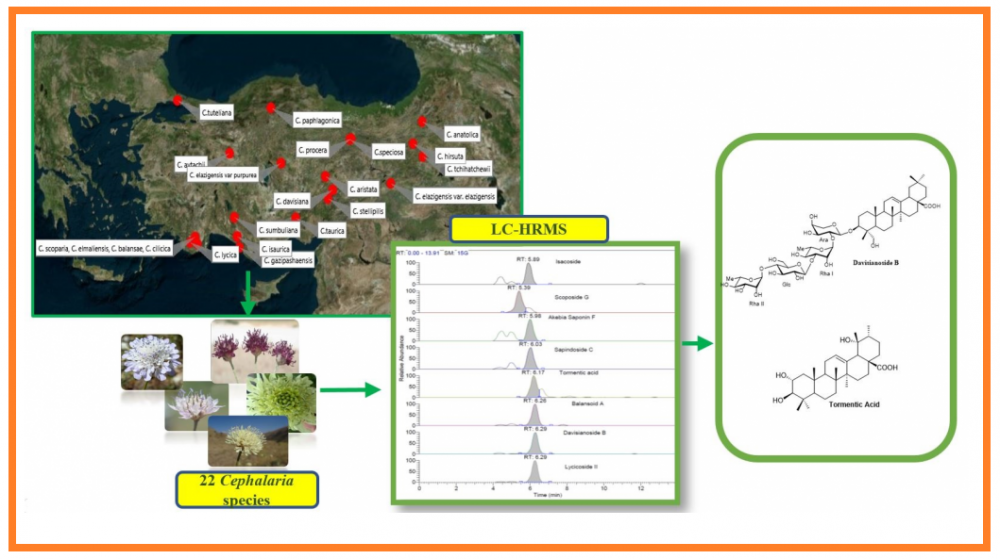
Saponins in the Cephalaria species have a broad spectrum of biological properties and application potentials. This research aimed to develop a novel method to tentatively identify and quantify triterpenes and saponins in 22 Cephalaria species by LC-HR/MS method. In this study, we provided a broad screening of important biologically active triterpenes and saponins with high separation ability, high sensitivity and high selectivity. This is the first report to prove that Cephalaria species can be a good source of tormentic acid which has many biological activities in literature. The main triterpene compound, tormentic acid was presented at the level between 74.02 mg/kg and 75702.0 mg/kg in n-butanol extract of Cephalaria species. The source of some biologically active saponins such as davisianoside B, aristatoside C, elmalienoside A, balansoide B and scoposide B were also determined with this study, for the first time. Therefore, due to the different activities and usages of the identified compounds, these findings may find application in a number of industries such as nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, medical and cosmetic industries.
KEYWORDS- Cephalaria
- Caprifoliaceae
- triterpene
- saponin
- validation
- LC-HR/MS