JOURNAL 2080
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 2 March-April
p.194 - 199
Viewed 2899 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
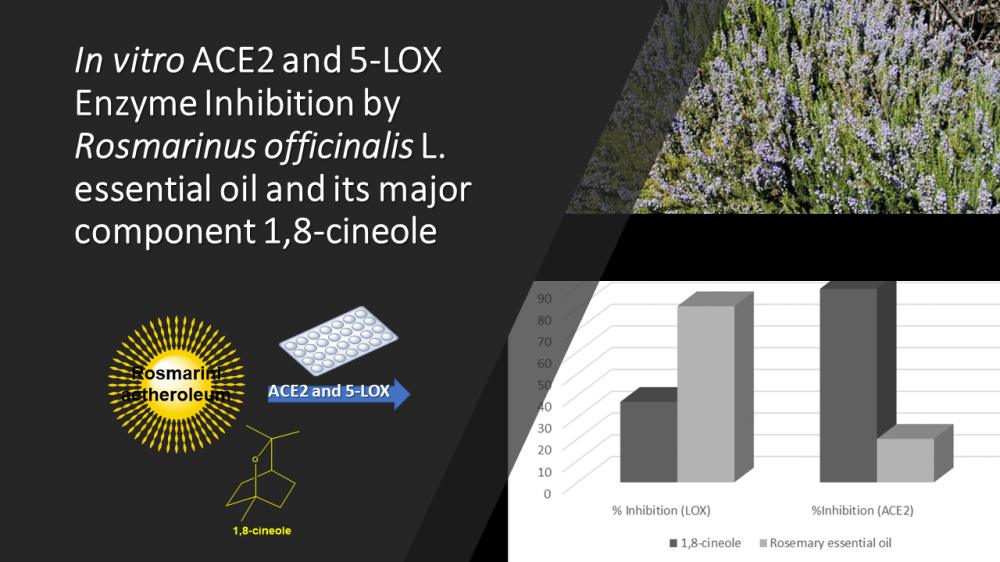
In this present study, Rosmarinus officinalis L. essential oil, and its major component 1,8-cineole was evaluated in vitro for angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), as well as for 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) enzyme inhibitory activity. The essential oil composition was confirmed both by GC-FID and GC/MS, where 1,8-cineole (62.7%), α-pinene (12.6 %), and camphor (8.3 %) were identified as the main constituents. Activity studies were performed at concentrations of 20 µg/mL for essential oil, and 5 µg/mL for the major compound 1,8-cineole, which were compared experimentally with standards. The essential oil was evaluated using a fluorometric multiplate based enzyme inhibition kit, where the ACE2 inhibition of Rosmarinus aetheroleum was 20%, while the 5-LOX inhibition was observed as 81.1%, respectively. In addition, the major constituent 1,8-cineole also showed remarkable ACE2 inhibition with 89.2%, and 5-LOX inhibition with 37.2%, respectively. As a result, the cineole chemotype rosemary essential oil, and its major constituent 1,8-cineol may have antiviral potential applications against coronaviruses due to ACE2 enzyme inhibition with anti-inflammatory effects. Further in vivo studies are needed to confirm the efficacy of essential oils and their constituents.
KEYWORDS- Rosmarinus officinalis L.
- essential oil
- ACE2
- 5-LOX
- 1,8-cineole