JOURNAL 2001
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 3 May-June
p.212 - 224
Viewed 3238 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
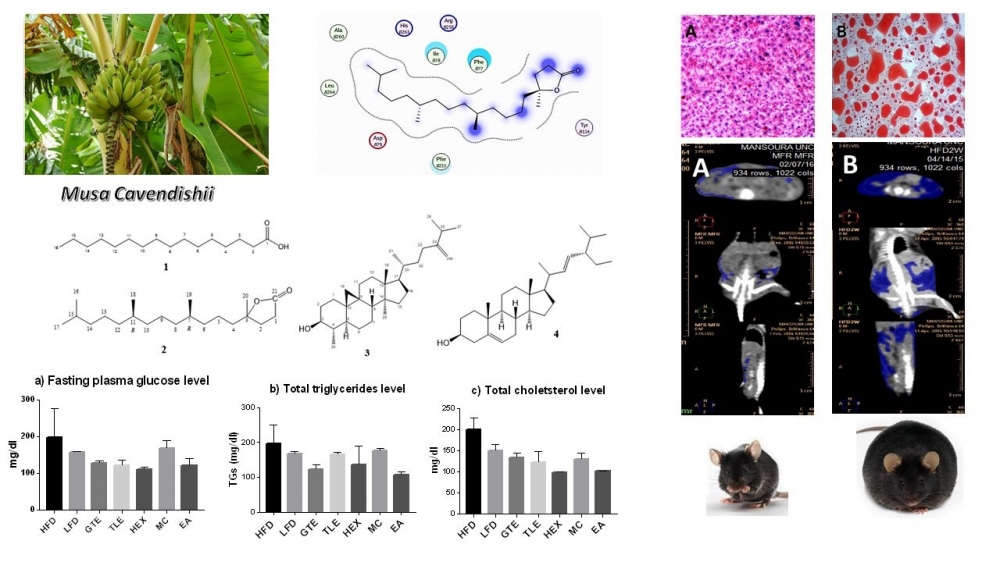
ABSTRACT
Obesity is a major risk factor in many health problems. This study explored the anti-obesity and antihyperlipidemic effects of Musa cavendishii Lamb. leaves. Doses of 1200 mg/kg of M. cavendishii methanol extract, or 300 mg/kg of fractions, were given to C57BL/6J mice fed with a high-fat diet (HFD) for 7 weeks. The reduction in fat volume was determined using CT scan and histopathological examination of mice livers. The results showed that the n-hexane and the EtOAc fractions reduced the body fat volume to 2.0% and 2.2% respectively, compared to 20.1% in the HFD group. Also, treated groups showed almost normal liver architecture with no fat vacuoles compared to the HFD group. Moreover, the treated groups showed a reduction in the levels of some obesity-related biochemical parameters, including plasma glucose, cholesterol, and triglycerides levels. Chromatographic fractionation of the bioactive n-hexane extract afforded four known compounds viz., palmitic acid (1), 5-methyl-5-(4,8,12-trimethyl-tridecyl)-dihydro-furan-2-one (2), cycloeucalenol (3), and stigmasterol (4). These compounds were in vitro and in silico studied for their pancreatic lipase (PL) inhibition. Compound 2 showed remarkable PL inhibition (89.8%) compared to orlistat (85.0%) at 200 µM, which was in full agreement with the docking scores (-7.19 and -4.05, respectively).
KEYWORDS- musa cavendishii
- anti-obesity
- antihyperlipidemic
- banana leaf
- anti-adipogenesis
- pancreatic lipase