JOURNAL 2143
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 4 July-August
p.335 - 345
Viewed 3249 times.
-
Dušan Čulum

-
Amira Čopra-Janićijević

-
Edina Muratović

-
Sonja Siljak-Yakovlev

-
Milka Maksimović

-
Danijela Vidic

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
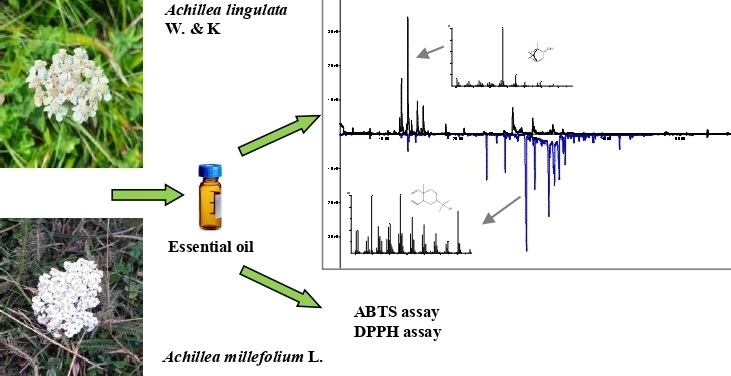
In this study, the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the hydrodistilled essential oil of Achillea lingulata, an endemic species of the Euro-Mediterranean region, originating from Bosnia and Herzegovina, was investigated for the first time. For comparison, an analysis of the essential oil of the widely distributed Achillea millefolium, which grows together in the same habitat, was made. Ninety-six components were identified in A. lingulata and A. millefolium oils comprising 97.8% and 85.8%, of the total oil, respectively. The oil of A. lingulata was characterized by a high content of oxygenated monoterpenes (76.8%). The main compounds were borneol (30.1%), trans-verbenol (15.5%), 2-tridecanone (12.2%), fragranol (8.3%), and myrtenol (7.9%). In contrast, essential oil of A. millefolium had oxygenated sesquiterpenes (60.8%) as the most abundant compounds, with elemol (32.9%) as the main constituent. In addition, γ-eudesmol (12.9%), caryophyllene oxide (7.7%), trans-caryophyllene (5.7%) and γ-muurolene (4.7%) were present in a significant percentage in A. millefolium oil. Antioxidant activity was tested by three methods, ABTS, DPPH and FRAP, and the obtained results showed low activity of both investigated oils.
KEYWORDS
- Achillea lingulata
- Achillea millefolium
- GC-MS
- essential oil
- terpenes
- antioxidant activity