JOURNAL 2270
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 5 September-October
p.443 - 453
Viewed 3718 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
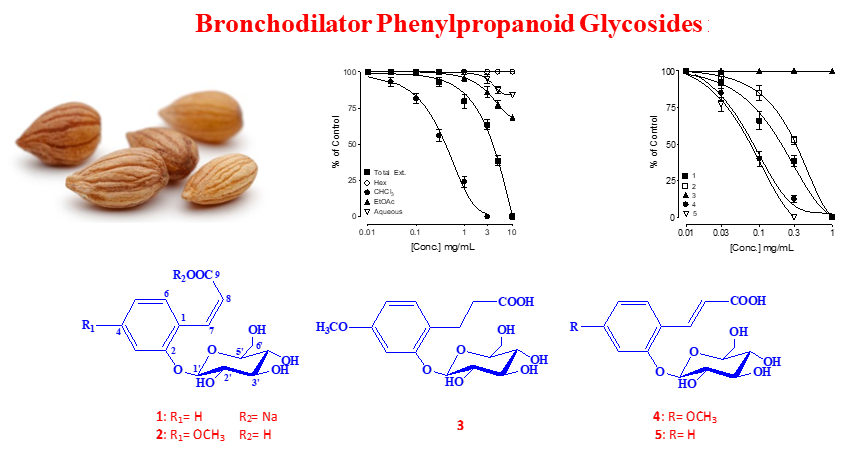
Prunus mahaleb seeds were selected for phytochemical study directed by ex-vivo bronchodilator effect based on the traditional use for the treatment of respiratory problems. From the active chloroform fraction, five known phenylpropanoid glycosides: cis-melilotoside sodium salt (1), cis-methoxy-melilotoside (2), 3-(2-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl-4-methoxyphenyl) propanoic acid (3), trans-methoxy-melilotoside (4) and trans-melilotoside (5) were identified for the first time from genus Prunus. Chemical structure of the compounds elucidated by spectroscopic techniques such as 1D, 2D NMR and HR-ESI/MS. Compounds 1, 2, 4, 5 showed promising bronchodilator effects against carbamylcholine (CCh) induced bronchospasm in isolated Guinea-pig trachea while 2 was found completely inactive. The mechanism(s) of action was studied using both CCh, low K+ (25 mM) and high K+ (80 mM)-mediated contractions and compound 2 was found distinctly more potent and efficacious against CCh compared to both types of K+-mediated contractions where partial efficacy was observed, hence showed dual inhibition of cholinergic receptors followed by Ca2+ channels. The anticholinergic and Ca2+ inhibitory activities of compound 2 were further confirmed when it deflected CCh concentration response curves (CRCs) without suppression, whereas its higher doses shifted Ca2+ CRCs similar to verapamil. The bronchodilator effect proved to be mediated via dual anticholinergic and Ca2+ channels blocking effects.
KEYWORDS- Prunus mahaleb L seeds
- bronchodilator
- phenylpropanoid glycosides
- anticholinergic
- calcium channel blocker