JOURNAL 2273
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 6 November-December
p.550 - 558
Viewed 3779 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
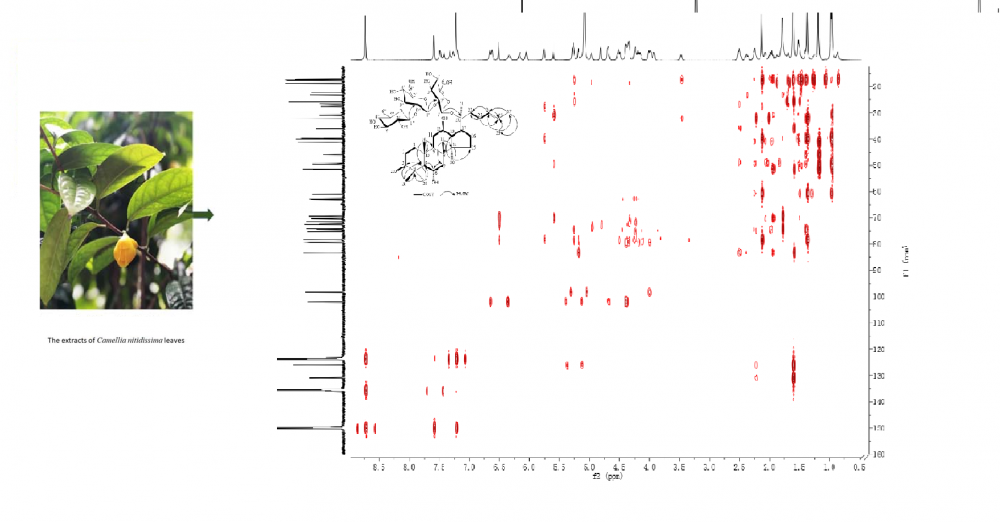
ABSTRACT
Camellia nitidissima is commonly used for making tea to prevent cancer in China, but its phytochemicals and bioactivity was insufficiently reported. In this work, the total content of saponins from leaves of C. nitidissima was investigated, and the high level of total saponins varied obviously with the augment of leafage. There are 12 triterpenes and saponins, i.e., β-daucosterol (1), α-spinasterol-β-D-glucoside (2), lupeol (3), 17,3β-acetoxy-20-lupanol (4), 3β,6α,13β-trihydroxyolean-7-one (5), oleanolic acid (6), oleanolic acid 3-acetate (7), ginsenoside Rg1 (8), ginsenoside F5 (9), ginsenoside F1 (10), ginsenoside Rd (11), and (3β,6α,12β)-3,6,12-trihydroxydammar-24-en-20-yl-2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(2→1)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(2→1)-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (12) from C. nitidissima leaves were isolated and identified. Specially, five dammarane tetracyclic triterpenoids derived from 20(S)-protopanaxatriols (compounds 8-12) obtained from C. nitidissima were the first reported, and compound 12 is a new dammarane triterpenoid. Based on scratch assay and cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, compound 12 and the extracts of C. nitidissima leaves showed potential cytotoxic activities against Bel-7402 and SMMC-7721 human liver cancer cells in vitro.
KEYWORDS- Camellia nitidissima
- triterpenes and saponins
- cytotoxic activities
- liver cancer