JOURNAL 2391
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2023 Issue: 1 January-February
p.125 - 144
Viewed 3645 times.
-
Michaella Yosephine

-
Isa Anshori

-
Muhammad Miftah Jauhar

-
Putri Hawa Syaifie

-
Adzani Gaisani Arda

-
Azza Hanif Harisna

-
Dwi Wahyu Nugroho

-
Etik Mardliyati

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
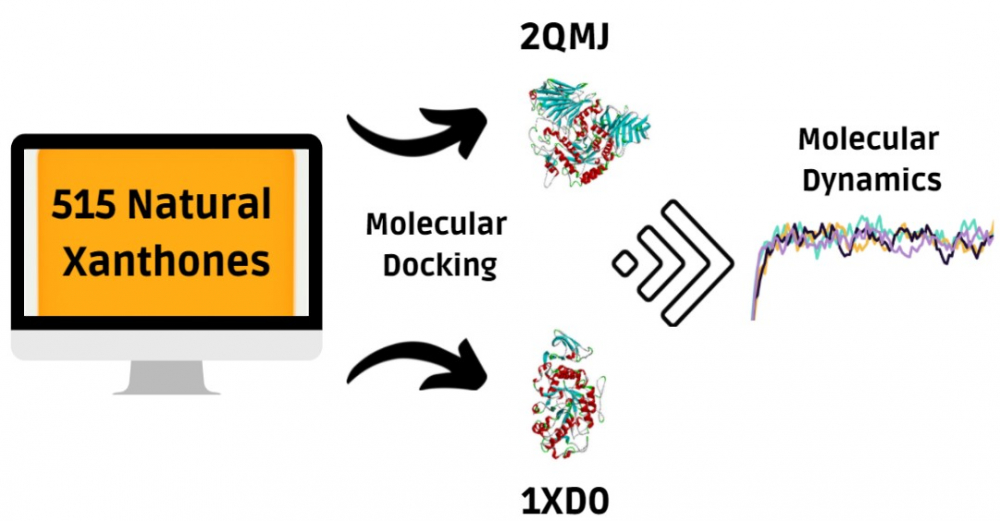
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a disease caused by insulin resistance. Many types of oral medications exist, but the effectiveness and side effects differ from patient to patient, so alternative drugs are still required. One compound group receiving much scientific interest regarding its antidiabetic potential is xanthones as potential alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase inhibitors. This study performed molecular docking simulations on all 515 natural xanthones with alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase as the protein targets. We found 31 unique ligands that comply, and the three best ligands per protein target were filtered based on how many active site residues the ligands interacted with the targets. The three best alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are 3,4,5,8-tetrahydroxy-1,2-diisoprenylxanthone, Polygalaxanthone V, and Polygalaxanthone VII. As for alpha-amylase, we found 1-O-primeverosyl-3,8-dihydroxy-5-methoxyxanthone, Garcimangosone C, and Mangostinone as the best inhibitors. The six chosen and standard ligands underwent 2 ns molecular dynamics simulations. Both standard ligands had the highest interaction energies, followed by complexes with glycosylated xanthones, and prenylated xanthones. We also found that the prenylated xanthones could retain their initial protein-ligand interactions. Therefore, this is the first study that revealed prenylated xanthones have a good potential as anti-type 2 diabetes mellitus agents among other xanthones groups through in silico method.
KEYWORDS- Molecular docking
- molecular dynamics
- xanthone
- alpha-amylase inhibitor
- alpha-glucosidase inhibitor