JOURNAL 2993
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2024 Issue: 2 March-April
p.251 - 272
Viewed 1777 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
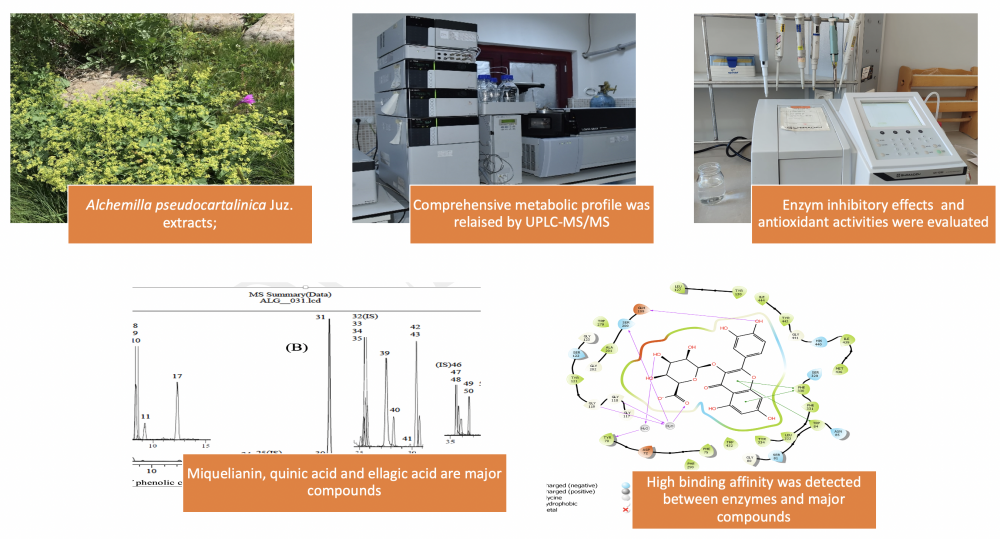
ABSTRACT
Alchemilla species (Rosaceae) are popularly known as ‘Lady’s Mantle, Lion’s claw’ and are used for medicinal purposes as diuretic, laxative, tonic, and wound healing agents. Bioactivities and phenolic content of Alchemilla pseudocartalinica Juz. species have yet to be investigated. Our research focused on assessing the antioxidant characteristics of A. pseudocartalinica methanol (MEAP) and water extracts (WEAP), as well as their inhibitory effects on acetylcholinesterase (AChE), α-glycosidase (α-gly), and human carbonic anhydrase II (hCA II) enzymes. Additionally, we conducted chemical characterization using UPLC-MS/MS and investigated the correlation between major phenolic compounds and enzymes through molecular docking analysis. To assess the antioxidant activities of the MEAP and WEAP, six test systems were employed, including DPPH, ABTS, DMPD, FRAP, CUPRAC, and Fe3+ reducing assays. The outcome showed that the methanol extract of the plant generally has stronger antioxidant activity. In addition, UPLC-MS/MS analysis indicated, miquelianin (44.095 mg/g), quinic acid (17.054 mg/g), and ellagic acid (6.492 mg/g) were significant in the methanol extract. A molecular docking study revealed a significant affinity for binding between the hCAII enzyme and quinic acid, miquelianin, and AChE/α-gly enzymes. A. pseudocatalinica methanol and water extracts have high antioxidant activity and good inhibition effect against AChE, α-glycosidase, and hCA II enzymes.
KEYWORDS- Alchemilla
- antioxidant activity
- enzyme inhibition
- UPLC-MS/MS
- molecular docking