Records of Natural Products
A scientific open access journal in the field of natural products.LATEST ARTICLES
LC-MS/MS characterization of phenolic compounds and in vitro assessment of antioxidant, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, and anti-Alzheimer activities of Echium creticum L.
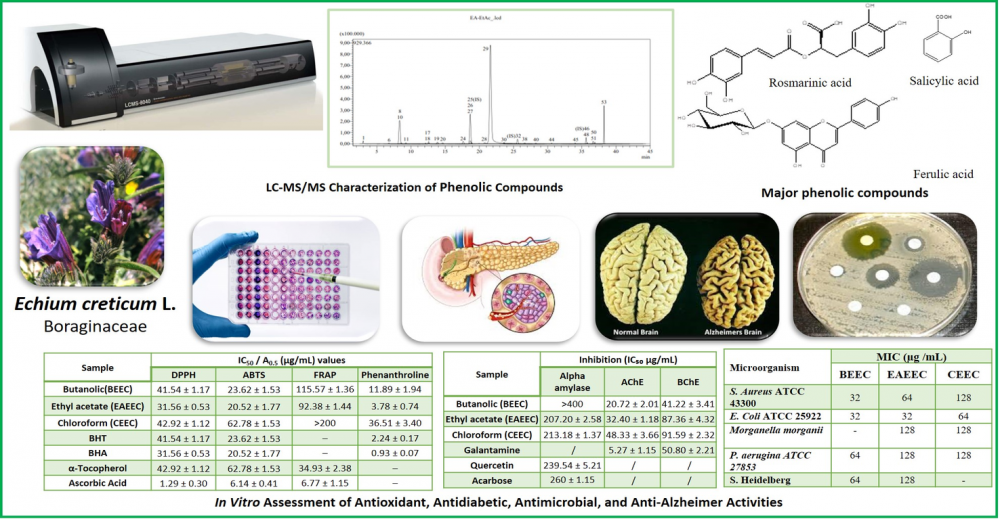
The present work provides the first comprehensive LC–MS/MS phytochemical profiling and pharmacological investigation of Echium creticum L., Boraginaceae, native to the Mediterranean region, used in folk medicine, The aerial parts were sequentially extracted using petroleum ether (PEEEC), chloroform (CEEC), ethyl acetate (EAEEC), and n-butanol (BEEC). LC-MS/MS profiling of the polar extracts identified 25, 22, and 24 bioactive compounds, with rosmarinic acid, ferulic acid, salicylic acid, and gentisic acid as major phenolics. Several flavonoid glycosides (cosmosiin, nicotiflorin, genistin) are reported for the first time in the Echium genus. Antioxidant activity was evaluated using DPPH, ABTS FRAP, and Fe³⁺-phenanthroline assays, was strongest in the ethyl acetate fraction. Antidiabetic potential was confirmed via α-amylase inhibition, where EAEEC demonstrated effective inhibition (IC₅₀ = 207.20 ± 2.58 µg/mL), comparable to quercetin and Acarbose. The antibacterial activity was also evaluated through the disc diffusion methods and MIC tests against a panel of 10 gram-positive (+) and gram-negative (-) bacterial strains (references and isolates multi-drug resistant bacteria) (MIC 32- 80 μg/mL). The n-butanol extract (BEEC) displayed the strongest anticholinesterase activity (IC₅₀ = 68.98 ± 1.33 µg/mL), consistent with its flavonoid glycoside enrichment. Altogether, these results highlight E. creticum as an underexplored source of phenolic compounds with multi-target in vitro bioactivities and expand the phytochemical diversity of the Echium genus.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2508.3611 Keywords Echium creticum LC–MS/MS phenolic compounds antioxidant anti-diabetic anticholinesterase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and application of Clitoria ternatea L.: a review
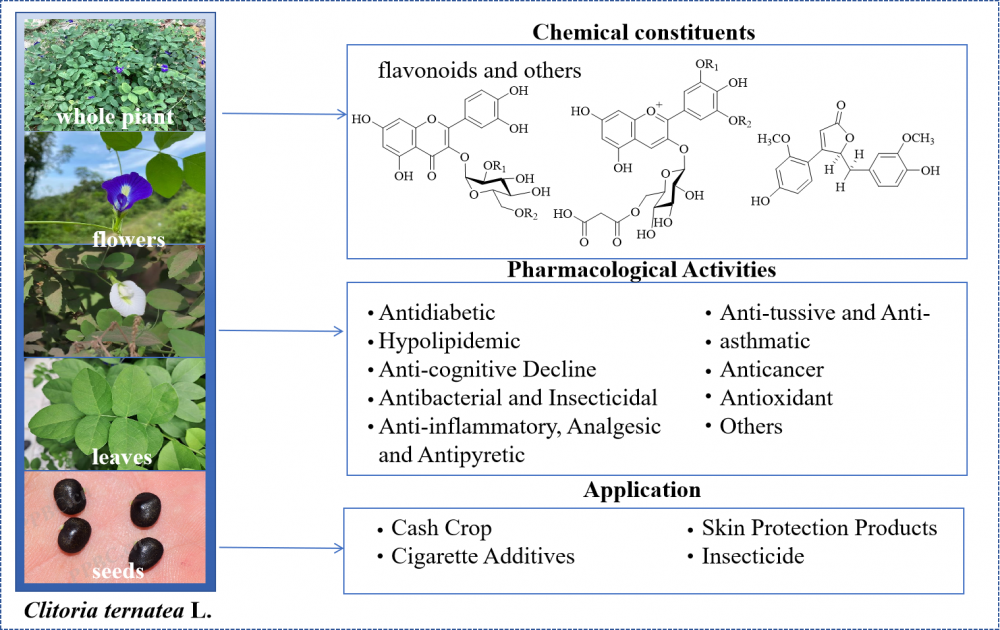
Clitoria ternatea L. (Fabaceae) is a leguminous plant with a long history of medicinal use and multifaceted applications, widely distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Oceania. In traditional medicine, particularly within the Ayurvedic system, C. ternatea has been employed to treat various ailments such as diabetes, cognitive impairment, and respiratory disorders. With advancing research into its chemical composition and pharmacological activity, C. ternatea has been found to possess a rich array of bioactive constituents, including flavonoids, anthocyanins, lignans, and triterpenoids. It exhibits diverse pharmacological effects such as hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic properties, memory enhancement, antibacterial and insecticidal action, anti-inflammatory effects, cough suppression, and antitumor activity. Moreover, C. ternatea demonstrates broad application prospects across agriculture, cosmetics, food additives, and pesticides. This article aims to provide a systematic review of the plant's botanical characteristics, chemical constituents, pharmacological activities, and practical applications, thereby offering a reference framework for subsequent in-depth research and comprehensive development.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2509.3634 Keywords Clitoria ternatea L. Fabaceae phytochemistry pharmacology applications DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.A Novel Monoterpenoid Derivative Isolated from Chloranthus serratus Roots with Anti-inflammatory Activity

Eight compounds were isolated from the 95% ethanol extract of Chloranthus serratus roots, including two monoterpenoid derivatives (1, 2), one pimarane-type diterpenoid (3), and five labdane-type diterpenoids (4-8). Compound 1 was identified as a previously undescribed camphene derivative, while compound 3 was a new natural product. Their structures and relative configurations were elucidated using HR-MS, NMR and ECD calculations. Compounds 1, 2, 5 significantly inhibited nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 cells, with IC50 values of 17.47±1.24, 14.92±1.17, and 30.48±1.48 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.542.2506.3558 Keywords Chloranthus serratus monoterpenoid anti-inflammatory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.Windienoic acid, a new compound from themedicinal plant Wikstroemia indica

A phytochemical investigation of the roots of the medicinal plant Wikstroemia indica (Linn.) C. A. Mey led to the isolation of five compounds (1–5), comprising one previously undescribed metabolite (1), named windienoic acid, and four reported compounds (2–5). The structural elucidation of these compounds was accomplished through comprehensive analysis of spectroscopic data, including 1D (¹H and ¹³C NMR) and 2D NMR techniques (HSQC, COSY, and HMBC). Compounds 2–5 were identified as the monoterpene 6,7-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenoic acid (2), the dibenzylbutyrolactone-type lignans (-)-nortrachelogenin (3) and (-)-trachelogenin (4), and the furofuran-type lignan pinoresinol (5) by comparing with literature data. Notably, the structure of compound 1 incorporated an extended conjugated system comprising a dienone moiety linked to a carboxylic acid group, which is rarely in acyclic compound, its structure was confirmed by 13C NMR calculation. The NMR assignment of dihydroxy-3,7-dimethyl-2-octenoic acid (2) is reported herein for the first time in methanol-d4. The cytotoxic screening assay against the A549 human lung cancer cell line of all compounds revealed that compound 3 exhibited weak activity with an IC₅₀ value of 42.3 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2508.3621 Keywords Wikstroemia indica windienoic acid cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2026 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
