JOURNAL 3285
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2024 Issue: 5 September-October
p.499 - 507
Viewed 1768 times.
-
Abdulaziz S. Saeedan

-
Najeeb Ur Rehman

-
Faisal K. Alkholifi

-
Yousef A. Alanzi

-
Anzar Haque

-
Omar K.M. Al-Rahimi

-
Maged S. Abdel-Kader

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
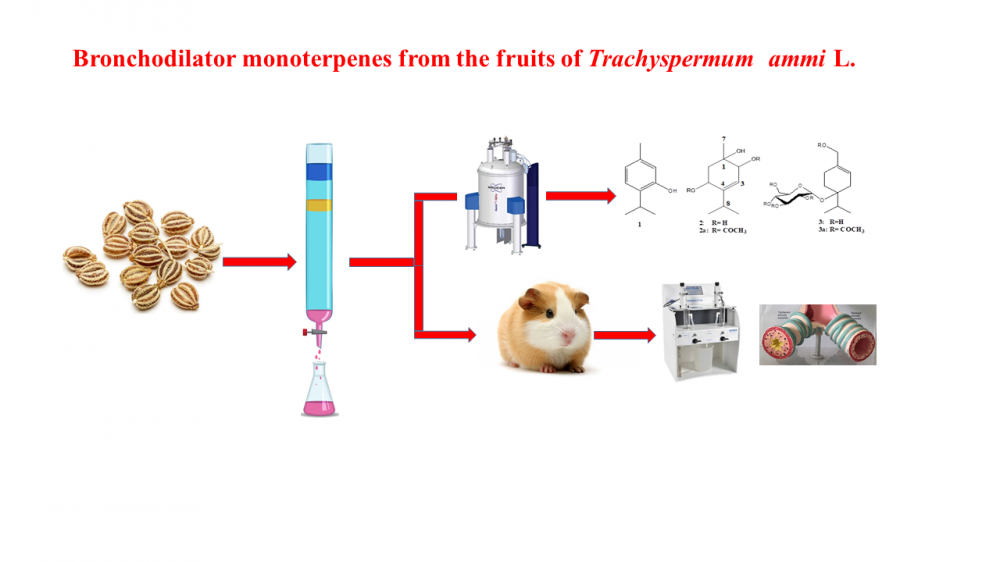
ABSTRACT
Trachyspermum ammi is widely used among the people in the Arabian Peninsula to treat general respiratory problems including bronchoconstriction. In this study, the fruit extracts and its fractions and purely isolated components obtained from the T. ammi were investigated for their possible bronchodilator potential in an ex vivo model using guinea pig trachea. It was observed that the ethanol extract (TAT) of the plant and its hexane (TAH) and chloroform (TAC) extract fractions completely inhibited carbachol (CCh, 1 µM)-induced contractions at a concentration of 1 mg/mL. As a result of the biological activity-guided purification studies of the chloroform extract (TAC), in which the highest activity was observed, eight sub-fractions were obtained between A-H. Of these, fractions A, D, G were found to have significant activity for tracheal relaxation with 100%, 55 ± 5% and 31 ± 3%, respectively, while the other five fractions were found not to have any activity. Three monoterpene compounds were isolated from the fractions with high activity and their structures were determined by 1D and 2D NMR and mass spectrometric techniques as well as by simple chemical derivatization. In this study, it was determined that the bronchodilator effect of compound 1 (thymol) was demonstrated by the activation of different subtypes of K+ channels. Reported data herein, demonstrated the scientific justification for the traditional use of T. amni species against asthma and bronchitis.
KEYWORDS- Trachyspermum ammi L.
- thymol
- bronchodilator
- K+ channel opener
- ex-vivo