JOURNAL 1913
Organic Communications
Year: 2020 Issue: 4 October-December
p.184 - 193
Viewed 2994 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
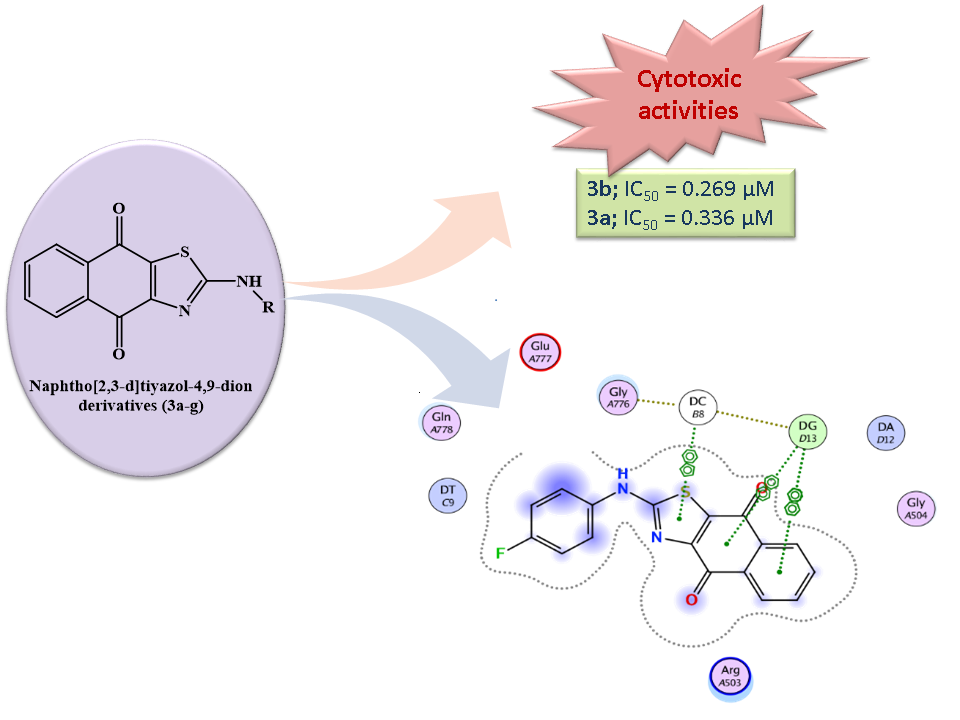
Quinones, especially 1,4-naphthoquinones, are one of the most significant and widely distributed phytochemical groups in nature. 1,4-Naphthoquinones and their synthetic derivatives are found to possess remarkable cytotoxic activities. In this study, a series of 2-aminonaphtho[2,3-d][1,3]thiazole-4,9-dione derivatives were synthesized and their structures were verified with spectral analysis. In vitro cytotoxic activities of the synthesized compounds were evaluated by using MTT assay against MKN-45 (Human Gastric cancer), MDA-MB-231 (Human Breast cancer) and HeLa (Human Cervical cancer) cell lines. Among the synthesized compounds, 3d inhibited MDA-MB-cell proliferation with an IC50 value of 0.276 µM. Compound 3a inhibited HeLa and MKN-45 cell proliferation with IC50 values of 0.336 µM and 8.769 µM, respectively. Compound 3b inhibited HELA cell proliferation with an IC50 value of 0.269 µM. Molecular docking results suggest that the ligands may bind to the hDNA TopoIIβ binding pocket and partially exert their effects. These results propose that 2-aminonaphtho[2,3-d]thiazole-4,9-dion core has important biological effects and further explorations are worthwhile.
KEYWORDS- 2-aminonaphtho[2,3-d][1,3]thiazole-4,9-dione
- naphthoquinones
- DNA topoisomerases
- anticancer activity