JOURNAL 2920
Organic Communications
Year: 2023 Issue: 4 October-December
p.197 - 203
Viewed 2273 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
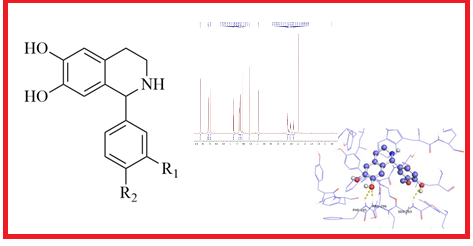
ABSTRACT
Phenolic aldehydes and their derivatives found in nature are well-known for their potential biological activity. In this study, four 1-substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines (THIQs) derived from phenolic aldehydes were synthesized by phosphate buffer mediated Pictet-Spengler reaction. All derivatives were chemically and structurally characterized by elemental CHN analysis and spectroscopic methods (IR, HR-ESI-MS, 1H- and 13C-NMR). 1-Substituted THIQs derived from 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde were described for the first time. In order to cover the diversity of the mechanistic approach, but also to establish the relationship between structure and activity, antioxidant activity was examined by five different in vitro methods, namely: neutralization and reduction of stable free radicals 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl and radical cation derived from [(2,2´-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)], ferric reducing antioxidant power, oxygen radical absorbance capacity, and ability to chelate Fe(II) ions. In vitro inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) was examined by the Ellman's colorimetric method, while computer-simulated docking was used to reveal the preferred binding site and major interaction between AChE and THIQs. Antibacterial testing was examined using the agar well method and results were presented in the form of zones of inhibition (mm).
KEYWORDS- Synthesis
- bioactivity
- 1-Substituted tetrahydroisoquinolines
- phenolic aldehydes