JOURNAL 3384
Organic Communications
Year: 2024 Issue: 4 October-December
p.249 - 264
Viewed 1692 times.
-
Meson Haji Basha

-
Ch. Subramanyam

-
C. Gladis Raja Malar

-
Katare Kiran Kumar

-
Mohan Seelam

-
Vedula Naga Lakshmi

-
Kammela Prasada Rao

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
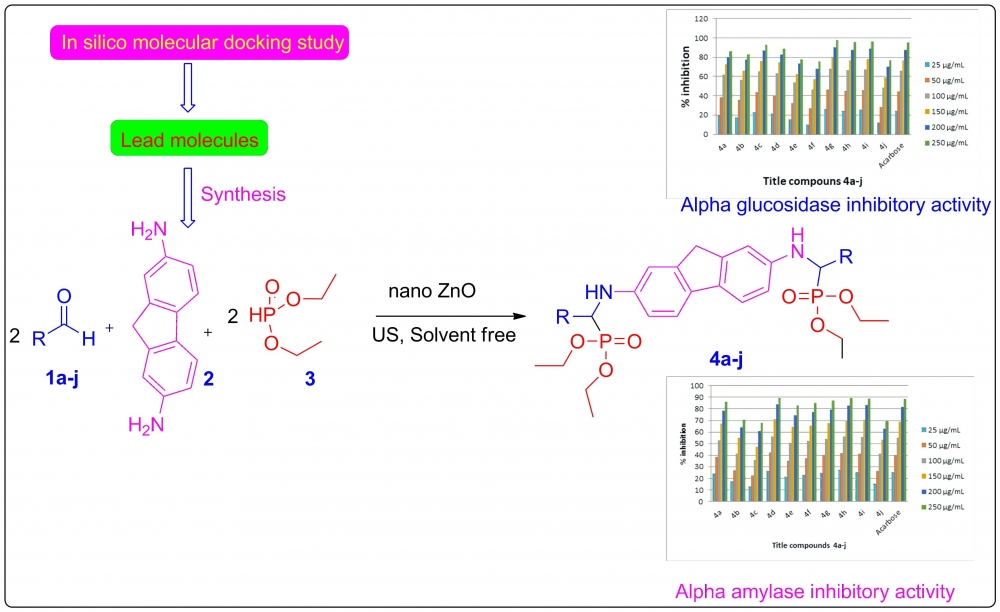
ABSTRACT
A more efficient and environmentally friendly way of synthesizing α-aminophosphonates is achieved by employing nano-ZnO to catalyze the Kabachnik-Fields reaction under ultrasonication within a solvent-free environment. Before synthesis, molecular docking and in silico ADME analysis were used to assess each molecule's drug-like characteristics and ability to inhibit α-amylase and α-glucosidase. The newly synthesized compounds' in vitro inhibitory effects on α-amylase and α-glucosidase were also evaluated, and their structure was confirmed using spectroscopic investigation. The target enzyme was effectively inhibited by most of the substances. In comparison to the reference drug, acarbose (IC50, 106.5±0.6 μg/mL), compounds 4d (IC50, 102.2±0.3 μg/mL), 4h (IC50, 102.9±0.4 μg/mL), which contained a 2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl moiety, and 4i (IC50, 103.9±0.5 μg/mL) showed the strongest inhibitory activity. The enzyme inhibition of the remaining compounds ranged from moderate to good.
KEYWORDS
- Kabachnik-Fields reaction
- α-aminophosphonates
- ADMET
- molecular docking
- α-amylase
- α-glucosidase