JOURNAL 1971
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Issue: 1 January-February
p.74 - 83
Viewed 2566 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
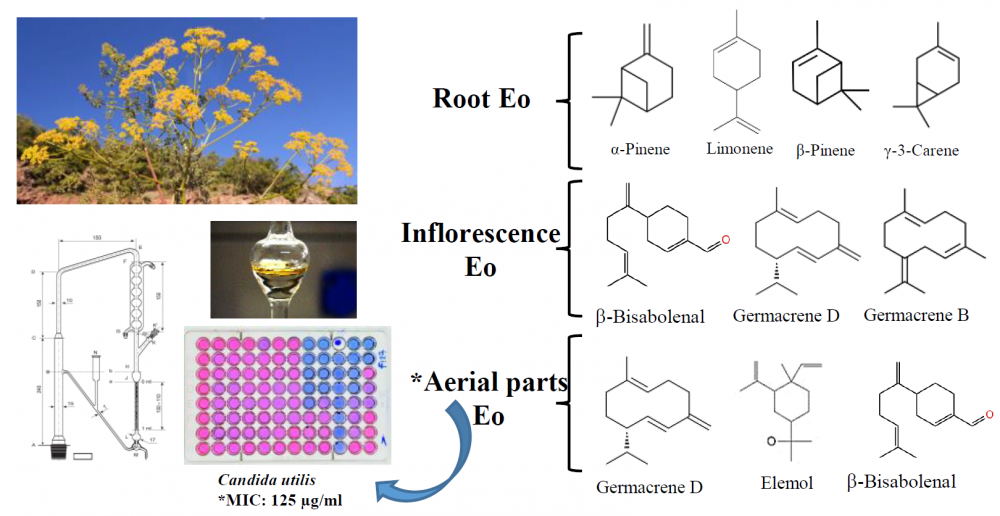
The chemical compositions and anticandidal activities of the essential oils from the aerial parts, inflorescence, and roots of the endemic P. heyniae H. Duman & M. F.Watson were evaluated. Hydrodistillation was used to isolate the essential oils and the chemical analyses were performed both by GC-FID and GC/MS, respectively. Forty-four compounds constituting 94.4% of aerial parts, thirty-nine compounds constituting 99.5% of inflorescence, and twenty-five compounds representing 100.0% of root essential oil were characterized. The main compounds of the aerial parts oil were elemol (36.2%), b-bisabolenal (14.1%), and germacrene D (12.7%). Main compounds of inflorescence oil were b-bisabolenal (21.6%) germacrene D (15.6%), and germacrene B (12.4%) while the roots oil were a-pinene (44.8%), limonene (15.3%), b-pinene (12.5%), and d-3-carene (10.2%), respectively. The in vitro anticandidal activity of the essential oils were evaluated against several Candida strains by using partly modified CLSI broth microdilution method M27-A2. The tested essential oil showed relatively weak effects against pathogenic Candida strains compared to standard antifungal agents.
KEYWORDS- Apiaceae
- essential oil
- GC/MS
- Prangos heyniae
- anticandidal activity