JOURNAL 3165
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2024 Issue: 3 May-June
p.339 - 346
Viewed 2136 times.
-
Shihao Zhang

-
Minghua Ma

-
Sicheng Liu

-
Guoce Jin

-
Wencong Li

-
Yu Zhao

-
Yanyu Li

-
Xueyan Li

-
Zixuan Zhu

-
Chengxiong Liu

-
Zhaoxia Liu

-
Xiaocong Li

-
Kun Zou

GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
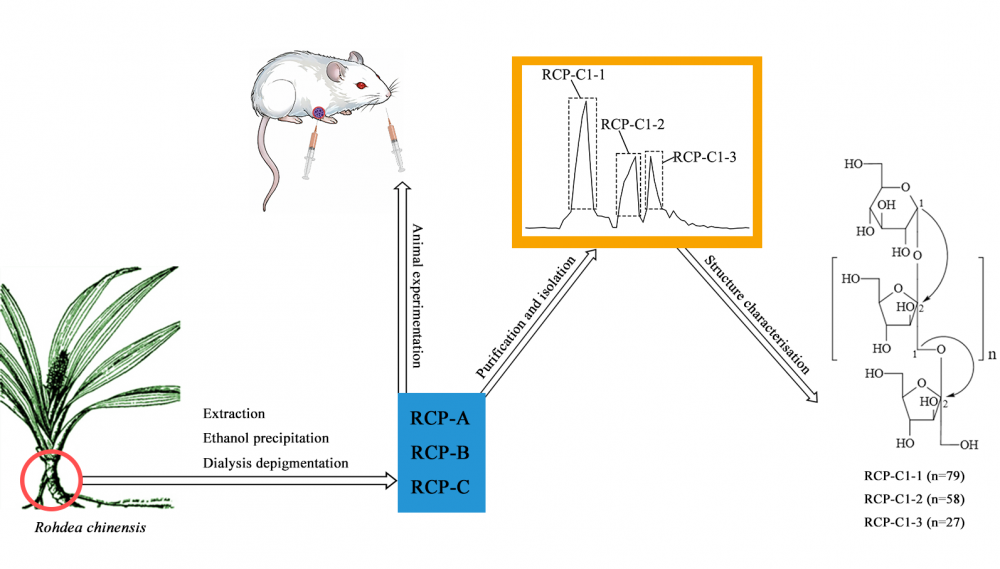
Three crude polysaccharides of RCP-A, B, and C were derived from the rhizome of Rohdea chinensis by means of hot water extraction, gradient ethanol precipitation and dialysis. Three different polysaccharides of RCP-C1-1, RCP-C1-2, and RCP-C1-3 were isolated using cellulose DEAE-52 and Sephadex G-200 chromatography from RCP-C. The average molecular weights of RCP-C1-1, RCP-C1-2, and RCP-C1-3 were measured as 1.51×104, 1.06×104, and 4.86×103 by means of MALDI-TOF MS and UHPGC, respectively. All three polysaccharides were found to consist of D-fructose and D-glucose following hydrolysis and comparison with literature data. Based on FT-IR and NMR analysis, the polysaccharides were identified as inulin-type fructans, with their backbone composed of α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-(β-D-fructofuranosyl)n-(1→2)-β-D-fructofuranoside (nRCP-C1-1=79, nRCP-C1-2=58, nRCP-C1-3=27). The anti-tumor activity of the polysaccharides (RCP-A, B, and C) was evaluated in H22 tumor-bearing mice. The results suggested that the polysaccharides (RCP-A, RCP-B, and RCP-C) inhibited the growth of H22 hepatocellular. Further, the treated groups of RCP-A, RCP-B, and RCP-C exhibited improvements in body weight as well as spleen/thymus indexes in H22 tumor-bearing mice.
KEYWORDS- Rohdea chinensis
- polysaccharides
- anti-tumor activity
- inulin-type fructans