JOURNAL 3763
Records of Natural Products
Year: 2026 Issue: 3
p.5 - 5
Viewed 190 times.
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
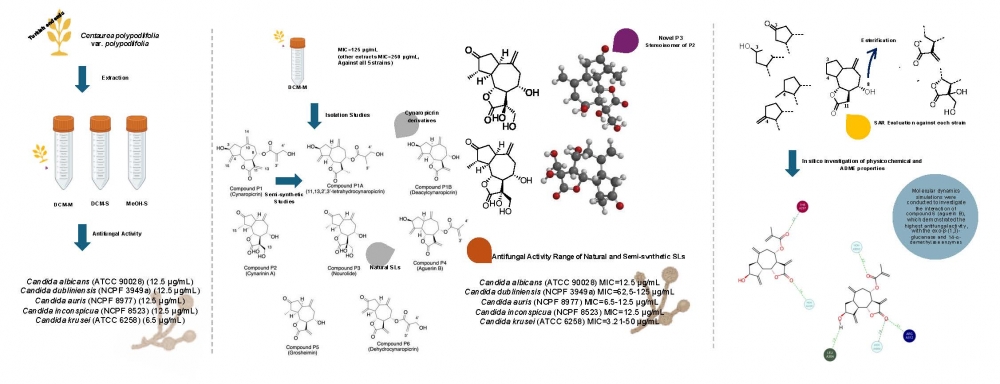
The emergence of multidrug-resistant Candida strains especially, Candida auris, C. dubliniensis, and C. inconspicua has accelerated the research on antifungal novel molecules. Sesquiterpene lactones, abundant in the Asteraceae family, have drawn attention with their antifungal activity. Therefore, three extracts obtained from the aerial part of Turkish endemic Centaurea polypodiifolia were investigated against Candida albicans (ATCC 90028), C. krusei (ATCC 6258), C. dubliniensis (NCPF 3949a), C. inconspicua (NCPF 8523), and C. auris (NCPF 8977) and gave MIC values between 6.25 and 12.5 µg/mL. Dichloromethane (DCM-M) extract yielded five known (cynaropicrin, cynarinin A, aguerin B, grosheimin, and dehydrocynaropicrin) and one novel (nourolide) guaianolide-type sesquiterpene lactones. Two semi-synthetic cynaropicrin derivatives were obtained to enhance the molecular diversity of the present study. 1D (1H and 13C APT) and 2D (COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY) NMR experiments were employed for structure elucidation. MIC values of the tested sesquiterpene lactones against the above-mentioned strains ranged between 3.12 and 50 µg/mL. Molecular dynamics simulations were conducted to investigate the interaction of 4 (aguerin B), which demonstrated the highest antifungal activity, with the exo-β-(1,3)-glucanase and 14-α-demethylase enzymes. These findings revealed stable binding interactions, suggesting that aguerin B has potential as a lead for further antifungal drug development.
KEYWORDS- antifungal
- Candida
- Centaurea
- sesquiterpene lactone
- fungal resistance