Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Reports
Year: 2024 Volume: 7 Issue:2 July-December
1) The anti-pathogenic activity and DNA gyrase inhibition of freshwater crabs (Barytelphusa cunicularis) are related to their structure-activity relationship

For screening purposes, there has been interest in creating natural product scaffolds that closely resemble drug-like compounds utilizing combinatorial chemical approaches. Various screening techniques are being developed to improve the data mining and drug development campaigns' usage of natural materials. From the tissue extract of the freshwater crab Barytelphusa cunicularis, four chemicals were shown to have biological activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including E. coli and B. subtilis, and S. aureus. Four pathogens were used in this study: A. niger, M. furfur, A. flavus, and P. Chrysosporium. Flavus and P. Chrysosporium, but poorly against A. Niger and M. Furfur. To further the development of potential therapeutics, structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis via a virtual screening protocol was conducted. Bioactivity assessments confirmed the compounds' efficacy against both bacterial and fungal targets. Molecular docking analyses revealed that all four organic compounds exhibit favorable absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADME/T) properties and bind with the protein DNA gyrase at diverse sites. In conclusion, the compounds' notable activity with DNA gyrase suggests their potential for drug design exploration.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.34.2405.3223 Keywords Combinatorial Barytelphus cunicularis molecular docking ADME/T DNA gyrase SAR DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Synthesis, and in-vitro biological evaluation of chalcone derivatives as antimicrobial agents
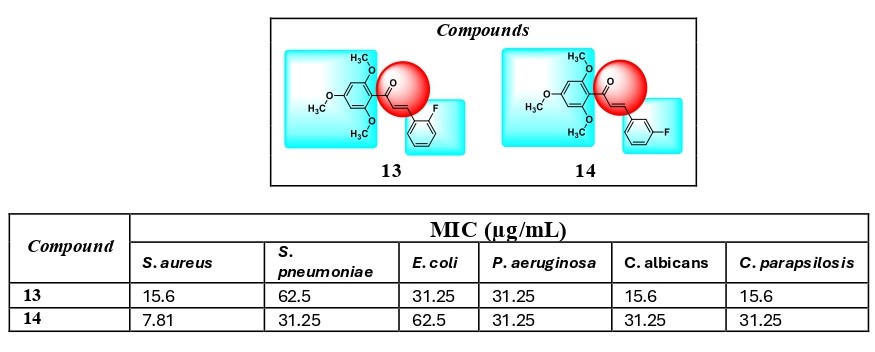
The rising resistance to antimicrobial drugs has highlighted the urgent need for discovering novel compounds with diverse mechanisms of action that can target both sensitive and resistant strains. To address this, we developed some chalcone analogs. In this study, a series of compounds (12-15) featuring fluoro and trifluoromethyl groups on the B ring were synthesized and evaluated for their antimicrobial properties. The positions of the substituents on the B ring were altered to assess their impact on antimicrobial activity. Compounds 13 and 14 demonstrated potent antibacterial activity (MIC = 15.6 and 7.81 μg/mL, respectively) against Staphylococcus aureus. Overall, our findings highlight Compounds 13 and 14 as promising scaffolds warranting further optimization for the development of effective antibacterial agents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/bmcr.35.24.11.3365 Keywords Chalcone synthesis antimicrobial activity MIC SAR DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.