Organic Communications
Year: 2025 Volume: 18 Issue:2 April-June
1) Green methods for the synthesis of chalcones: An overview with appraisal to sustainable development and bioactive compounds
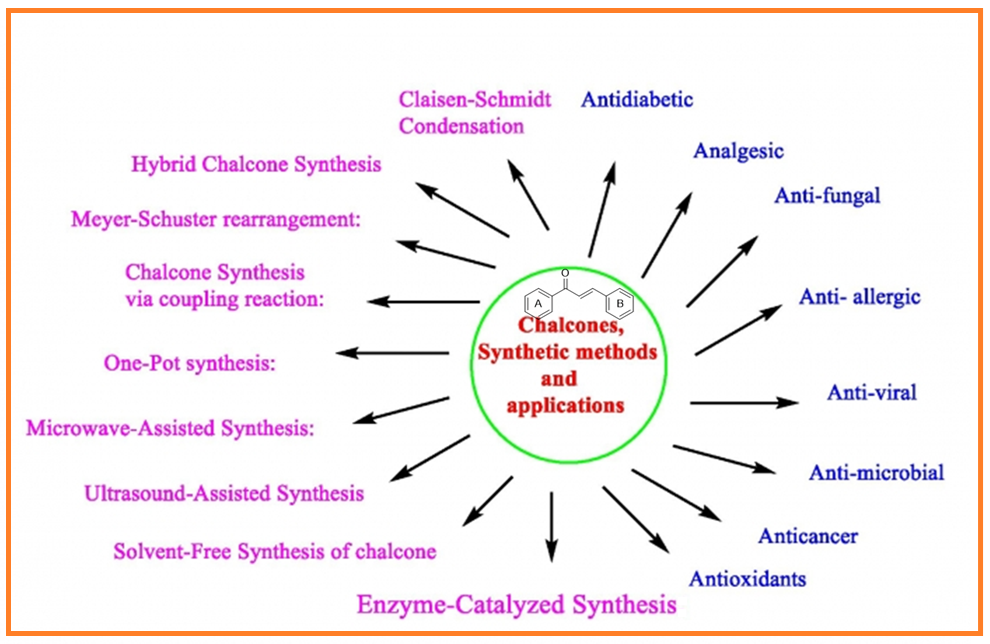
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing green and sustainable synthetic strategies for chalcones, aiming to minimize waste, reduce the use of hazardous chemicals, and enhance the overall efficiency of the reactions. This review provides an overview of various green synthesis approaches for chalcones and their derivatives, emphasizing environmentally friendly techniques such as solvent-free reactions, microwave-assisted synthesis, ultrasound-assisted synthesis, and enzyme-catalytic methods. Additionally, the biological activities of chalcones synthesized via green methods are explored, underscoring their potential in drug development and therapeutic applications
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.189.2504.3495 Keywords Chalcones green synthesis biologically active compounds DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Nano-ZnO catalyzed microwave synthesis of novel α-aminophosphonates: anti-diabetic potential via molecular docking, ADMET analysis, and α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition studies

A more efficient and environmentally friendly approach has been developed for synthesizing α-aminophosphonates through the Kabachnik-Fields (K-F), catalyzed by nano-ZnO in a solvent-free environment, utilizing microwave irradiation. Before synthesis, each compound underwent in silico ADMET analysis and molecular docking to assess drug-like characteristics and their potential to inhibit α-amylase. The structure of the newly synthesized compounds was validated using spectroscopic analysis, and their in vitro inhibitory effects on α-amylase and α-glucosidase were assessed. Among the compounds 8g (IC50, 99.2±0.5 μg/mL), 8i (IC50, 101.2±0.3 μg/mL), 8e (IC50, 102.1±0.4 μg/mL) and 8j (IC50, 103.4±0.4 μg/mL) containing anthracen-9-ylamino, phenanthren-9-ylamino, 2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)amino and 2-benzoylphenyl)amino moieties respectively, exhibited the highest inhibitory activity on α-amylase, superior to the reference compound acarbose (IC50, 104.5±0.1 μg/mL). The remaining compounds demonstrated moderate to good enzyme inhibition. 8c bearing with 4-fluorophenyl substituent (IC50, 88.4±0.7 μg/mL), 8e (IC50, 90.0±0.4 μg/mL) bearing with 2-oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl substituent and 8d (IC50, 91.1±0.9 μg/mL) bearing with 2-methylbenzo[d]oxazol-5-yl moiety have shown the highest inhibitory activity on α-glucosidase than the reference drug, Acarbose ((IC50, 93.1±0.8 μg/mL). The remaining compounds exhibited moderate to good inhibition on the enzyme with IC50 ranging 94.5±0.9 to 141.4±0.7 μg/mL.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.187.2501.3413 Keywords Kabachnik-Fields (K-F) reaction nano-ZnO, microwave irradiation molecular docking α-amylase α-glucosidase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
3) Stereoselective reduction of enantiopure α-l-amino-β-keto esters using oxazaborolidine catalysts for the synthesis of statine analogues
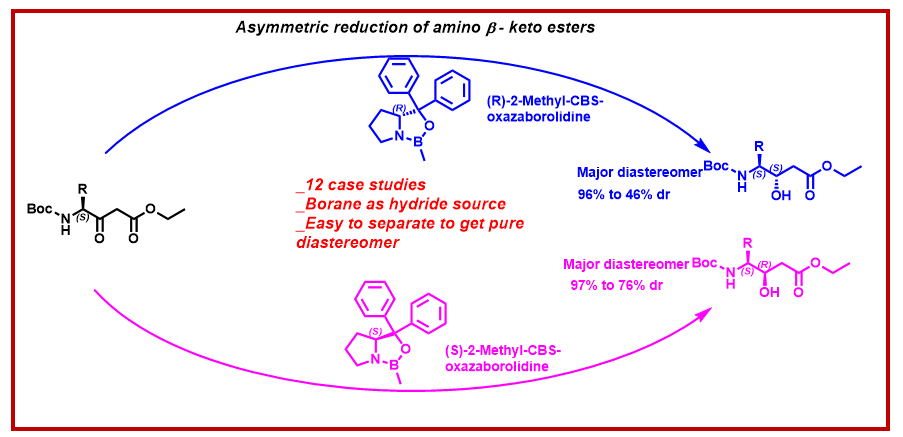
An efficient diastereoselective synthesis of Boc-protected 4-amino 3-hydroxy esters starting from natural amino acids is described. The key synthetic strategy involves diastereoselective reduction of α-L-amino-β-keto esters in the presence of enantiopure R and S-2-Methyl-CBS-oxazaborolidine catalysts using borane as hydride source. The product diastereoselectivity depends upon the use of (R) or (S) enantiomer of 2-Methyl-CBS-oxazaborolidine. A reasonable mechanism is included which explains the diastereoselectivity of the reactions with the use of different enantiomers of 2-Methyl-CBS-oxazaborolidine. Furthermore, the resulting diastereomeric mixture of the reduced products can be separated by column chromatography to gain access to the single pure diastereomers.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.191.2504.3501 Keywords L-amino-β-keto esters statine; (R)-2-Methyl-CBS-oxazaborolidine (S)-2-Methyl-CBS-oxazaborolidine borane reduction DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Two-steps synthesis of hexasubstituted porphyrins at the β-pyrrolic positions
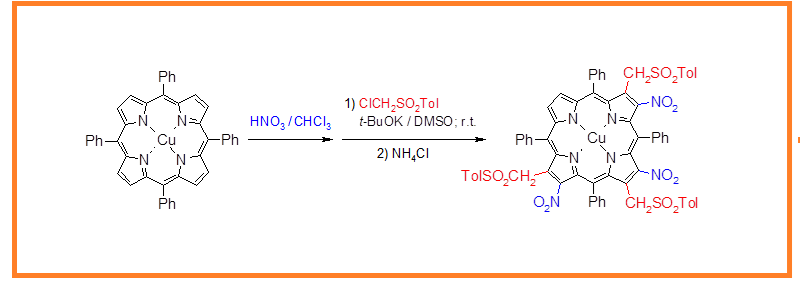
meso-Tetraarylporphyrin chelates are easily available from parent porphyrins. Their reactions with nitric acid (yellow fuming HNO3, d = 1.52), under optimized conditions in CHCl3 at room temperature, can be carried out selectively, thus giving mainly β,β,β-trinitro-substituted moieties (usually two or three isomers of the above complexes). These intermediates (