Records of Natural Products
Year: 2019 Volume: 13 Issue:5 September-October
1) Biodiversity and Secondary Metabolites of Marine Sponges from Turkey
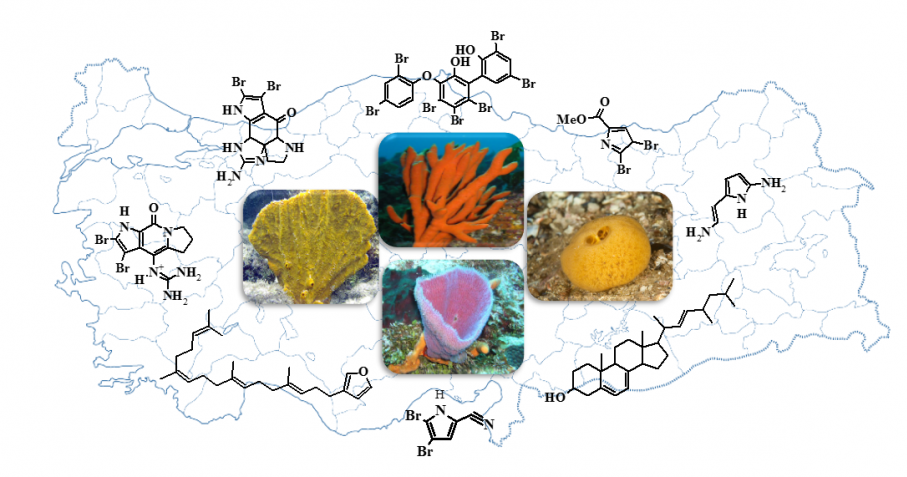
Turkey is surrounded by the Black Sea, the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean sea, comprising a rich source of marine biodiversity. Among all marine species, sponges with a wide range of secondary metabolites are an important potential for drug discovery. There are many studies on sponges and their secondary metabolites, but not enough study about Turkish sponges. The present review gives an overview of the current research trends on secondary metabolites from Turkish marine sponges and some of their biological activities. Until today alkaloids, steroids and phenolic compounds have been isolated and determined from Turkish sponges. To our knowledge, this is the first review about Turkish sponges. Furthermore, we have tried to introduce our Marine Herbarium of Ankara University Pharmacy Faculty (MAP).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.118.18.07.340 Keywords Bioactivity biodiversity secondary metabolite sponge DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Anti-inflammation C19-diterpenoid Alkaloids from Delphinium giraldii Diels
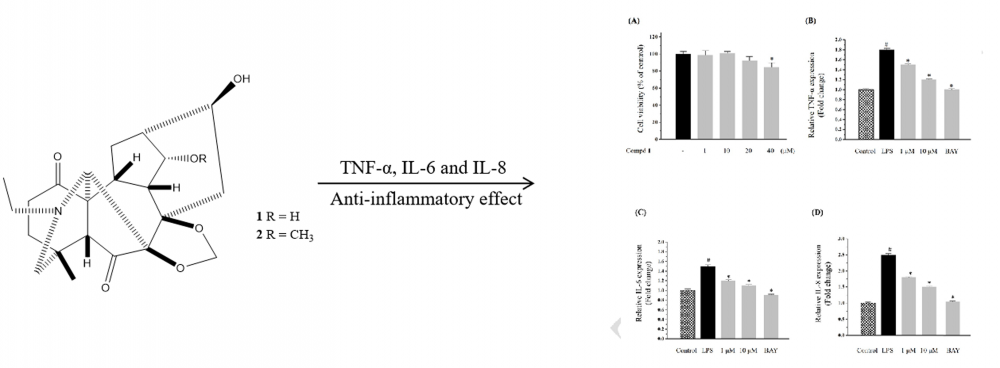
Two new C19-diterpenoid alkaloids named Delphinium alkaloid A (1) and Delphinium alkaloid B (2) were isolated from the Delphinium (Ranunculaceae). Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic and mass-spectrometric analyses, including 1D-, 2D-NMR and HR-Q-TOF-MS. Compound 1 showed anti-inflammatory activity by regulating the inflammatory reaction induced by LPS in Caco2 cell.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.117.18.09.954 Keywords Delphinium giraldii Diels chemical constituents diterpenoid alkaloids anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) New Xanthone from Millettia pachyloba Drake
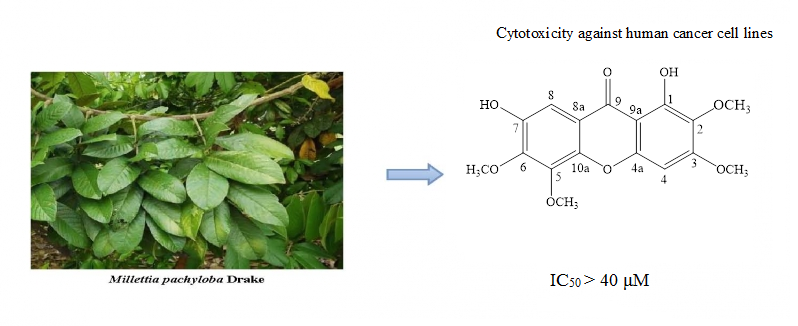
A new xanthone, 1,7-dihydroxy-2,3,5,6-tetramethoxyxanthone (1), together with eight known compounds including one xanthone (2) and seven isoflavones (3-9) has been isolated from the leaves of Millettia pachyloba. This is the first report on the isolation of xanthone from the genus Millettia. The structure of the compound 1 was elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic data interpretation, including 1D and 2D NMR and HREIMS. Compound 1 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against five human cancer cell lines, HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7 and SW480.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.116.18.10.1020 Keywords Millettia pachyloba Drake Leguminosae xanthone DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) NF-κB Inhibition Activity of Curcumin-Loaded Sterically Stabilized Micelles and Its Up-Regulator Effect on Enhancement of Cytotoxicity of a New Nano-Pirarubicin Formulation in the Treatment of Breast Cancer
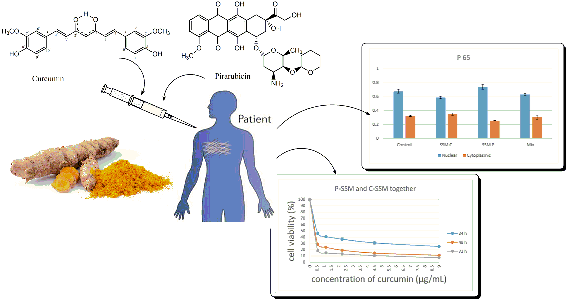
This study aims to investigate the effects of co-administration of nano-Curcumin on anticancer effect of nano-Pirarubicin considering the fact that the clinical use of Pirarubicin and other anthracyclines has been limited by development of multidrug resistance (MDR) and based on previous data which have shown that Curcumin can down-regulate MDR proteins and suppress the activity of Nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) a protein involved in chemoresistance. Nano micellar formulations of both Curcumin and Pirarubicin were separately synthesized using 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-methoxy-[poly(ethylene glycol); PEG MW 2,000] (DSPE-PEG2000). The produced sterically stabilized micelles (SSM) are very well known drug delivery systems in terms of their enhanced efficacy and good toxicity profile. We measured the differences of NF-κB levels in two different situations: when Pirarubicin is used alone and when it is co-administered with Curcumin. This study showed that co-administration of SSM-Curcumin (CSSM) and SSM-Pirarubicin (PSSM) with size of 12.81 nm enhances the efficacy of Pirarubicin by suppressing P65, an NF-κB subunit. Furthermore, we showed that SSM is able to successfully enhance water solubility and therapeutic stability of curcumin for using as a complementary agent.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.108.18.10.984 Keywords Curcumin pirarubicin nanoparticles NF-κB breast cancer DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Volatile Oil Constituents of Crataegus azarolus L. and Crataegus pallasii Grisb.*

In this study the volatile oils constituents of the inflorescence and unripe fruits of Crataegus azarolus L. and Crataegus pallasii Grisb. were investigated. Fifty-four compounds were identified by GC and GC-MS analysis. The major outstanding constituents of the essential oil in all samples (dried and fresh C. azarolus and dried C. pallasii) were; tricosane (33.8%, 29.3%, 34.0 %), pentacosane (24.6%, 21.1%, 30.8%), heptacosane (12.5%, 10.2%, 11.7%), and tetracosane (6.0%, 5.6%, 5.7%), respectively. Besides these alkanes, ten compounds (nonanal, β-elemene, undecanal, β-caryophyllene, (E, E)-α-farnesene, eicosane, hexyl benzoate, (Z)-3-hexenyl benzoate, (E)-2-hexenyl benzoate, docasane) were determined in all samples. Carvacrol, carvacryl acetate, carvone, and thymol were determined for the first time from C. pallasii essential oil. (E)-β-damascenone was determined only in dried C. azarolus oil; sesquiterpene compounds valencene, α-selinene and β-selinene, d-cadinene, germacrene D, selina-3,7(11)-diene, spathulenol, and d-cadinol were determined only in fresh C. azarolus sample. On the other hand (2E,6E)-farnesol was determined in dried C. azarolus and C. pallasii samples.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.123.18.11.1060 Keywords Crataegus azarolus Crataegus pallasii volatile constituents GC-MS analysis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
6) Structural Elucidation of a Coumarin with New Skeleton from Artemisia ordosica
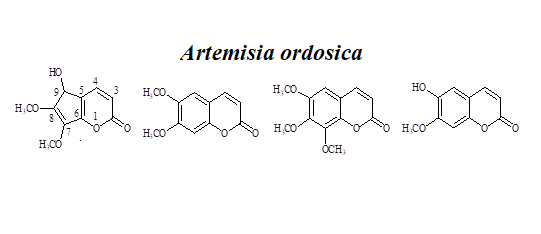
A new coumarin, named as arteordocoumarin A (1), together with three known compounds (2-9) were isolated from the CHCl3 extract of Artemisia ordosica (A. ordosica). The structures of 1 was elucidated by spectroscopic methods, including UV, IR, HR-ESI-MS and extensive 1D and 2D NMR techniques.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.120.18.10.1026 Keywords Arteordocoumarin A Artemisia ordosica NMR DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) A New Isoflavonolignan Glycoside from Abrus cantoniensis
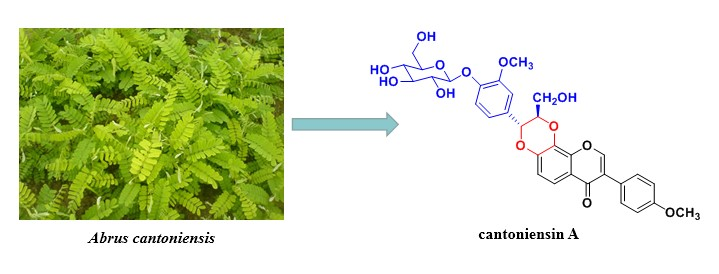
A new isoflavonolignan glycoside, namely cantoniensin A (1), along with three known compounds were isolated from Abrus cantoniensis. The structure of the new compound was elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic analyses, including 1D-, 2D-NMR and HRESIMS. Compound 1 is the second example of isoflavonolignan glycoside from nature and is also the first isoflavonolignan isolated from the genus of Abrus.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.125.19.01.1165 Keywords Leguminosae Abrus cantoniensis cantoniensin A isoflavonolignan isoflavonolignan glycoside DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Polyacetylenes from the Roots of Aralia dumetorum
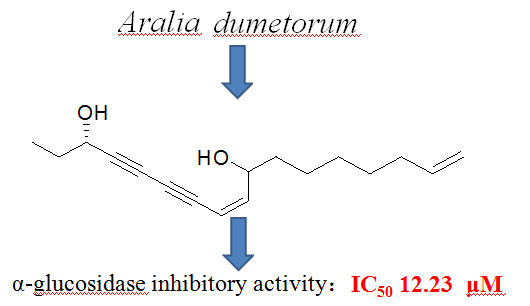
A new polyacetylene, heptadeca-8,16-dien-4,6-diyn-3,l0-diol (1) along with four known polyacetylenes, 1,2-dihydrodendroarboreol B (2), heptadeca-1,8-dien-4,6-diyn-3,l0-diol (3), 3R, 8S-falcarindiol (4) and 3R,8R-dehydrofalcarindiol (5) were isolated from the ethanol extract of Aralia dumetorum. The structures of the isolates were elucidated on the basis of 1D and 2D NMR spectrums and by comparison of the spectroscopic data with those reported for structurally related compounds. The α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of compounds 1-5 was evaluated using α-glucosidase inhibitory assay, in which all compounds displayed good inhibitory activity with IC50 values ranging from 4.2 ~ 36.2 μM..
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.119.18.09.940 Keywords Araliaceae Aralia dumetorum polyacetylenic compound α-glucosidase inhibitor DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) A New Ursane-Type Triterpene from the Roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge
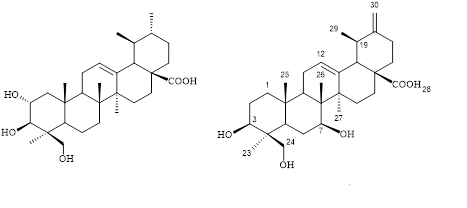
Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) is a one of the most well-known medicinal herbs in the Oriental medicine for treatment of certain cardiovascular disoders. Our current research on triterpenoid component in danshen roots led to the isolation of a new highly hydroxylated ursane-type triterpene, urs-12,20(30)-dien-3β,7β,24-triol-28-oic acid (2) and one known triterpene, epiasiatic acid (1). Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analyses including NMR and MS spectra and comparison with literature data. The new compound 2 showed medium activity against HL-60 cells with the IC50 value of 16.3 μM. The obtained results of unique bioactive triterpenes from danshen contributed not only to its phytochemical profile associated with chemotaxanomy but also to biological evidence of the title plant.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.97.18.07.330 Keywords Danshen Salvia miltiorrhiza Lamiaceae triterpene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Thymol Derivatives from Eupatorium fortunei
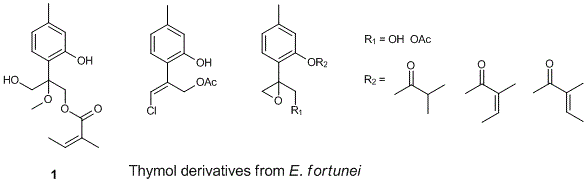
The presence of thymol derivatives in the leaves and twigs of E. fortunei collected in Northern Vietnam was investigated. Five thymol derivatives, including new 9-O-angeloxy-10-hydroxy-8-methoxythymol, 10-acetoxy-9-chloro-8,9-dehydrothymol, 9-acetoxy-8,10-epoxythymol-3-O-isobutyrate, 8,10-epoxy-9-hydroxy-thymol-3-O-tiglate, and 9-acetoxy-8,10-epoxythymol-3-O-angelate together with six other compounds, including taraxasteryl acetate, o-coumaric acid, trans-melilotoside, (–)-loliolide, coumarin, and b-sitosterol were isolated. The structures of the isolated compounds were determined on the basis of MS and NMR spectroscopic data.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.122.18.11.1032 Keywords Eupatorium fortunei Asteraceae thymol DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.