Records of Natural Products
Year: 2020 Volume: 14 Issue:2 March-April
1) Bioassay Guided Isolation of Topoisomerase Ι Poison from Paphiopedilum callosum (Rchb.f.) Stein
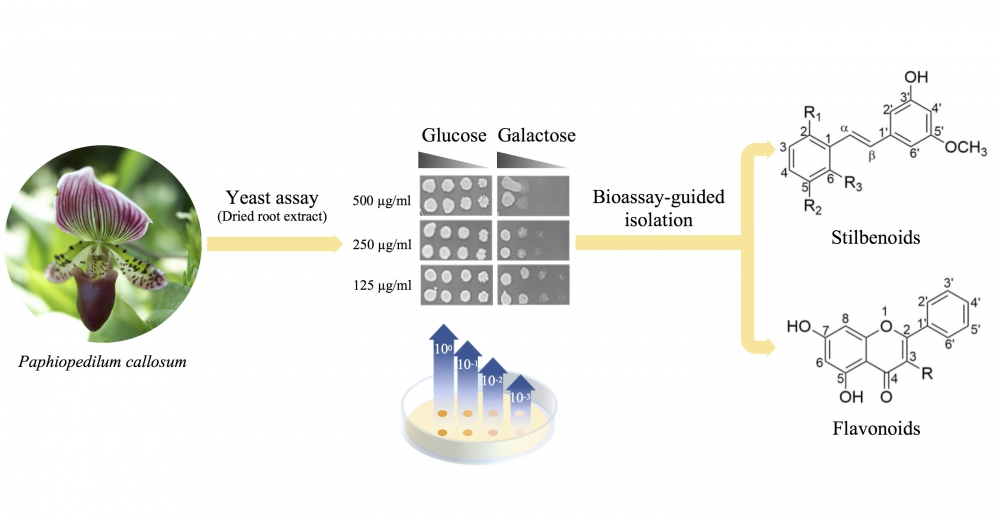
Paphiopedilum callosum (Rchb.f.) Stein belongs to the Orchidaceae family. The phytochemistry and bioactivities of this plant have not been reported. In this study, a bioassay-guided isolation with a yeast cell-based assay was performed to isolate topoisomerase I poison compounds from the roots of P. callosum. One new and five known compounds were isolated. According to their spectroscopic data (ESI-MS, NMR, IR and UV), the new compound (1) is 3′-hydroxy-2,6,5′-trimethoxystilbene. The known compounds (2-6) were identified by comparing their spectroscopic data with those in the literature. According to the yeast cell-based assay, all the compounds were topoisomerase Ι poisons based on their ability to inhibit the growth of yeast cells. As further confirmation, the cytotoxic activities of the isolated compounds were evaluated using human cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and NCI-H187). The compounds exhibited varying degrees of cytotoxicity on the representative cell lines. These isolated compounds could serve as new lead compounds in the development of cancer chemotherapeutics.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.144.19.06.1298 Keywords Paphiopedilum callosum Orchidaceae yeast cell-based assay topoisomerase Ι poison stilbene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) A New 2,2′-dipyridine and Its Analogues from Endophytic Streptomyces sp. KIB H017c with Potent Cytotoxicity

A new 2,2′-dipyridyl compound 1, along with three known analogues (2–4), was isolated from the culture broth of endophytic Streptomyces sp. KIB H017c derived from Fragaria ananassa. Their structures were elucidated by analysis of 1D and 2D NMR as well as HRESIMS data, and comparison with literature data. The biological properties of all isolates were explored for antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic activity. All four compounds exhibited weak antifungal activity against Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and compound 4 exhibited weak antifungal activity against Penicillium decumbens ATCC 10436. Compound 3 displayed moderate cytotoxic activity against HL-60 (human myeloid leukemia), SMMC-7721 (hepatocellular carcinoma), A-549 (lung carcinoma), MCF-7 (breast adenocarcinoma), and SW480 (colon carcinoma) with IC50 values of 12.10, 11.15, 23.64, 31.13 and 14.62 μM, respectively. Compound 4 exhibited potent activity against A-549 (lung carcinoma), MCF-7 (breast adenocarcinoma), and SW480 (colon carcinoma) with IC50 values 0.88, 0.34 and 0.55 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.147.19.05.1268 Keywords Endophytic Streptomyces 2,2′-dipyridine antimicrobial activity cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Phytochemical Investigation of Endemic Sideritis cypria Post
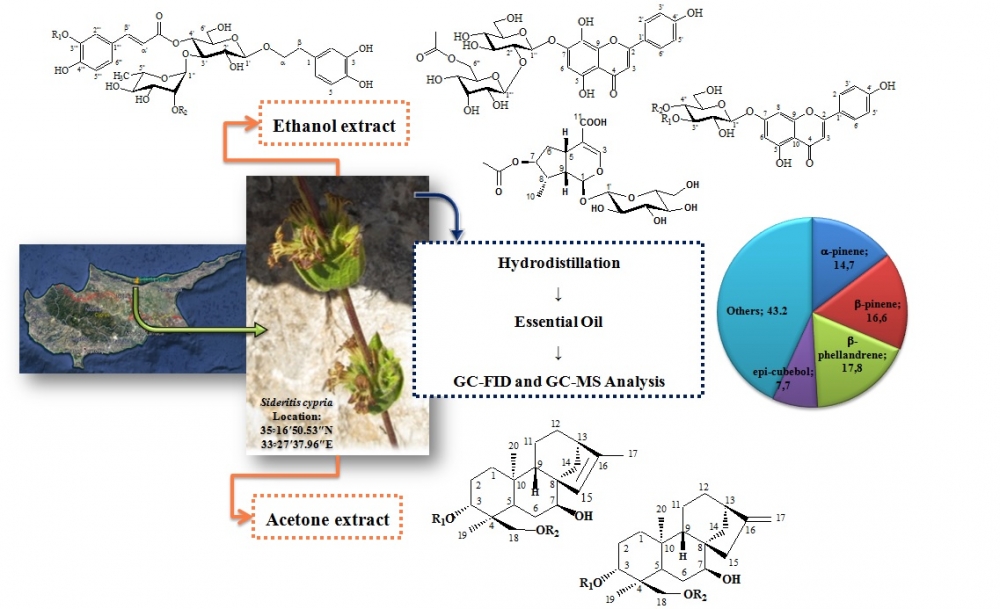
Non-polar and polar compounds were isolated from the leaves and chemical composition of the essential oil from aerial parts of Sideritis cypria endemic in Northern Cyprus was also determined. The structures of all the isolated compounds were elucidated by means of spectroscopic (UV, NMR: 1D and 2D-NMR: 1H, 13C, COSY, HSQC, HMBC) methods and comparison with literature data. The essential oil composition of the plant material was analysed by GC-FID and GC-MS, simultaneously. To the best of our knowledge, secondary metabolites of this endemic species were determined for the first time. As a result, two mixtures of four ent-kaurane diterpenes; sidol (1) and isosidol (2), linearol (3) and isolinearol (4); four phenylethanoid glycosides; verbascoside (5), lavandulifolioside (6), leonoside A (7), leucoseptoside A (8); four flavone glycosides, apigenin-7-O-glucopyranoside (9), isoscutellarein-7-O-[6'''-O-acetyl-allopyranosyl-(1->2)-glucopyranoside] (10) and a mixture of apigenin-7-O-(4''-O-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside (11) and apigenin-7-O-(3''-O-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside (12) were elucidated. 7-O-acetyl-8-epi-loganic acid (13), an iridoid glycoside, was reported herein for the first time for genus Sideritis. In addition, major compounds of the essential oil were determined as a-pinene (14.73±0.15%), b-pinene (16.60±0.20%), b-phellandrene (17.83±0.23%) and epi-cubebol (7.70±0.20%), respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.140.18.11.1079 Keywords Sideritis Phytochemistry ent-kaurane diterpenes iridoids flavonoids essential oil DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) The Efficacy of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Extract in Anti-obesity Therapy
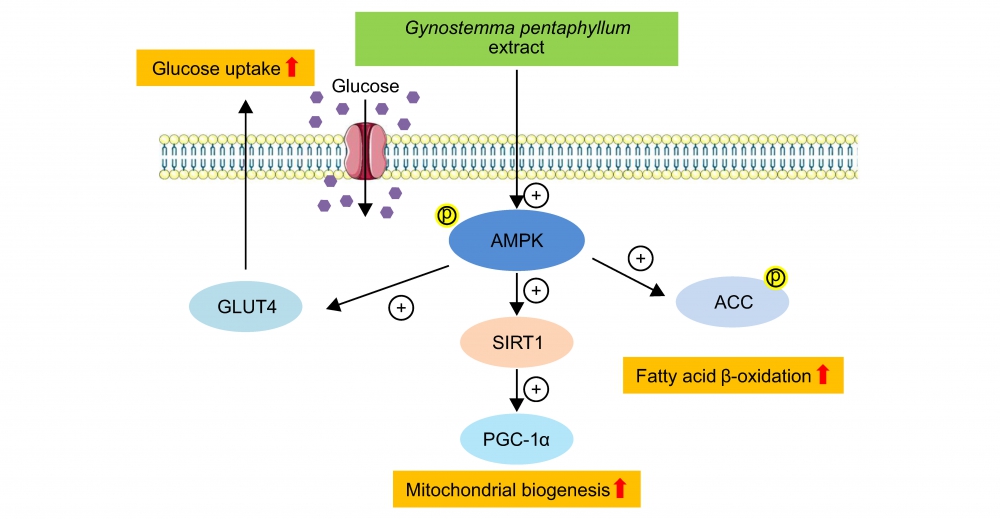
In the present study, we investigated a saponin-enriched fraction from Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract (GPE) and isolated gypenoside L (GL), gypenoside LI (GLI), and ginsenoside Rg3 (Rg3). To explore the anti-obesity activities of these compounds, we investigated the effects of GL, GLI, and Rg3 on glucose uptake and activation of AMPK in L6 skeletal muscle cells. GPE, GL, GLI, and Rg3 markedly increased glucose uptake activity and GLUT4 gene expression in L6 myotubes. The enhanced glucose uptake was mediated by the activation of the AMPK-ACC signaling pathway. In addition, we observed that GPE, GL, GLI, and Rg3 increased the expression of SIRT1 and PPARγ coacvtivator-1α (PGC-1α). Our results suggest the potential use of Gynostemma pentaphyllum in developing a therapeutic agent to reduce body weight and prevent diet-related diseases via glucose uptake and AMPK activation.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.146.19.05.1270 Keywords Gynostemma pentaphyllum gypenosides L6 skeletal muscle cells glucose uptake AMPK SIRT1 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Secondary Metabolites of Ethanol Extracts of Pinus sylvestris Cones from Eastern Anatolia and Their Antioxidant, Cholinesterase and α-Glucosidase Activities
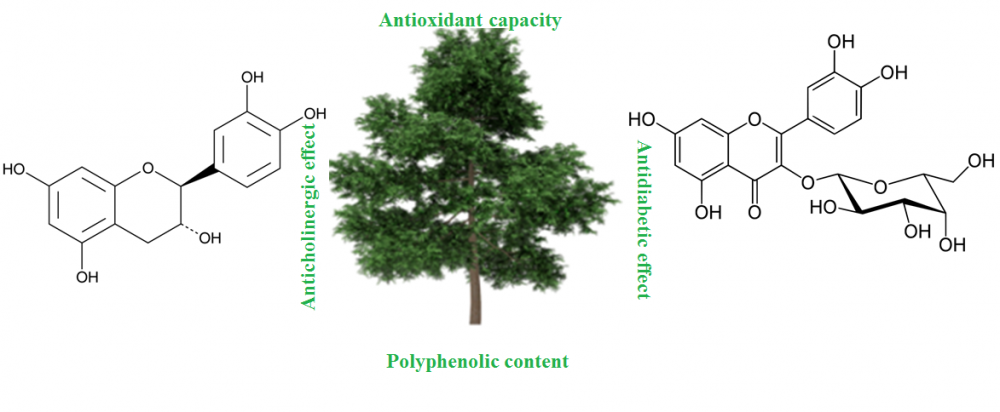
Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) is the most widely distributed tree species among pine species. Antiradical, antioxidant properties and inhibition properties on butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and α-glycosidase activities of ethanol extracts of P. sylvestris were reported from Sarikamis (Kars), Gumushane and Erzurum provinces of Turkey. The cones of P. Sylvestris from Gumushane showed the highest IC50 values in both DPPH. (14.75 µg/mL) and ABTS.+ (12.56 µg/mL) radical scavenging activities. An LC-HRMS method developed and the secondary metabolite composition of extracts were identified. The major compounds are determined as (+)-trans taxifolin, quercitrin, fumaric acid, (-) epicatechin, and nepetin-7-O-glucoside, apigenin-7-O-glucoside in P. sylvestris cones.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.155.19.06.1326 Keywords Pinus sylvestris acetylcholinesterase butyrylcholinesterase antioxidant activity α-glucosidase LC-HRMS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Melanin Synthesis Inhibitors from Olea europeae
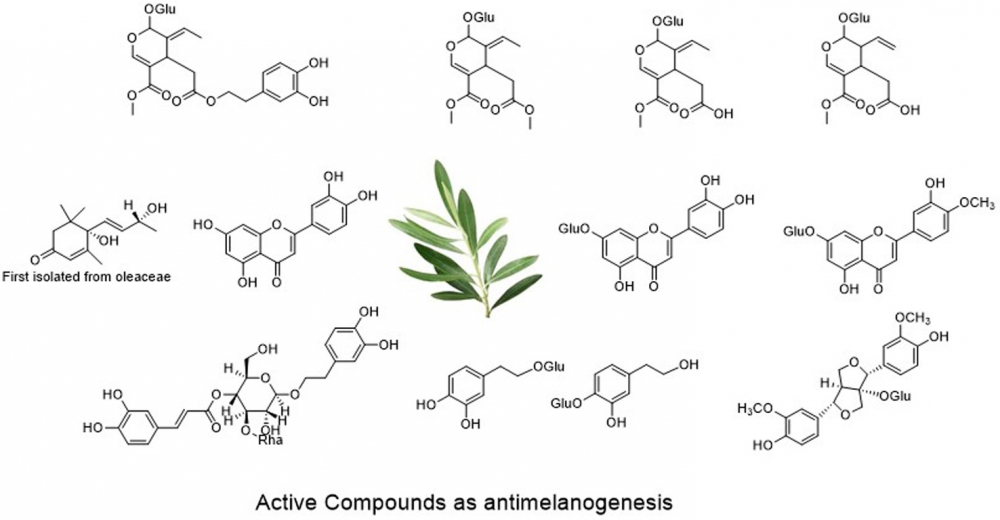
The aim of this study was to discover more candidates for development of novel anti melanogenesis compounds from leaves of O. europeae. Seventeen compounds have been isolated from the leaves of O. europeae. The isolated compounds were identified as α, β-amyrin mixture (1), β-sitosterol (2), uvaol, erythrodiol mixture (3), oleanolic acid (4), maslinic acid (5), vomifoliol (6), β-sitosterol 3-O-β-D-glucoside (7), luteolin (8), oleoside dimethylester (9), oleuropein (10), hydroxypinoresinol 1-O-β-D-glucoside (11), luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucoside (12), diosmetin 7-O-β-D-glucoside (13), verbascoside (14), oleoside 11-methylester (15), secoxyloganin (16) and hydroxytyrosol 8-O-β-D-glucoside, hydroxytyrosol 4`-O-β-D-glucoside mixture (17). This is the first report on the identification of vomifoliol (6) in the oleaceae family. Results showed that several compounds other than oleuropein exhibited inhibition of melanin synthesis and at the same time with low cytotoxicity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.142.19.04.1264 Keywords Olea europeae Melanin Vomifoliol DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Chemical Constituents and Cytotoxic Activities of Essential Oils from the Flowers, Leaves and Stems of Zingiber striolatum Diels

Abstract: The purpose of this study was to investigate chemical composition and cytotoxic activities of essential oils from Zingiber striolatum Diels flowers, leaves and stems. 73, 68 and 66 compounds representing 97.0%, 94.8% and 93.7% of flowers, leaves and stems essential oils were identified using GC-FID and GC-MS, respectively. The main constituents of the flowers oil were β-phellandrene (28.5%), α-humulene (14.7%), β-pinene (8.2%), β-elemene (5.5%), humulene oxide II (3.5%), cryptone (3.3%) and tricosane (3.2%). The predominant components in the leaves oil were hexahydrofarnesyl acetone (24.7%), α-humulene (12.2%), phytol (11.9%), humulene oxide II (6.3%), β-pinene (4.3%), sandaracopimaradiene (3.1%) and β-elemene (3.0%). The stems oil contained mainly α-humulene (15.6%), humulene oxide II (7.9%), hexahydrofarnesyl acetone (7.4%), phytol (7.2%), humulene oxide I (4.1%), β-elemene (3.8%) and 4-terpineol (3.2%). The cytotoxic activity against human leukemic (K562), prostatic carcinoma (PC-3) and lung cancer (A549) cell lines of essential oils was assessed using MTT assay. The essential oils of flowers, leaves and stems exhibited significant cytotoxicity against K562 (IC50: 12.94–37.89 μg/mL), PC-3 (IC50: 69.06–82.56 μg/mL) and A549 (IC50: 45.73–66.12 μg/mL) cell lines. This is the first report on the chemical constituents and cytotoxic activities of Z. striolatum flowers, leaves and stems essential oils.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.143.19.05.1291 Keywords Zingiber striolatum Diels essential oils GC-FID/MS cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A New Record of the Marine Red Alga Laurencia snackeyi from Japan and its Chemotaxonomic Significance

The constitution of Laurencia snackeyi (Weber-van Bosse) Masuda (Ryukyu-sozo in Japanese) from three locations, Minna Island, Sesoko Island and Kayo Coast in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, is reported. This species produced snyderane-type sesquiterpenes, palisadin A (1), palisadin B (2) and aplysistatin (3) as characteristic metabolites. The species name of "Laurencia luzonensis Masuda", which has previously been reported in several papers, should be revised to L. snackeyi.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.145.19.06.1310 Keywords Laurencia snackeyi Laurencia luzonensis Rhodomelaceae chemotaxonomy snyderane-type sesquiterpene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Alkaloid Profiling of Hippeastrum Cultivars by GC-MS, Isolation of Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids and Evaluation of Their Cytotoxicity

Different species, hybrids and varieties of the genus Hippeastrum (Amaryllidaceae) are planted for ornamental purposes and at the same time they represent a rich source of interesting secondary metabolites called Amaryllidaceae alkaloids. These compounds display a wide spectrum of biological activities. In the current study, six Hippeastrum taxa were evaluated for their alkaloid profile by GC-MS. Using preparative TLC, five alkaloids were isolated in pure form, and three of them evaluated for cytotoxic and antiproliferative potencies on a panel of human cancer cells of different histotype (Jurkat, MOLT-4, A549, HT-29, PANC-1, A2780, HeLa, MCF-7 and SAOS-2). In parallel, normal MRC-5 human fibroblasts were employed to determine the compounds´ overall toxicity against non-cancer cells. The most intriguing cytotoxic profile was demonstrated by montanine (1) with IC50 values between 1.04 – 1.99 µM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.147.19.06.1302 Keywords Amaryllidaceae Hippeastrum alkaloids montanine cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Chemical Composition, Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities of the Essential Oil of Dianella ensifolia
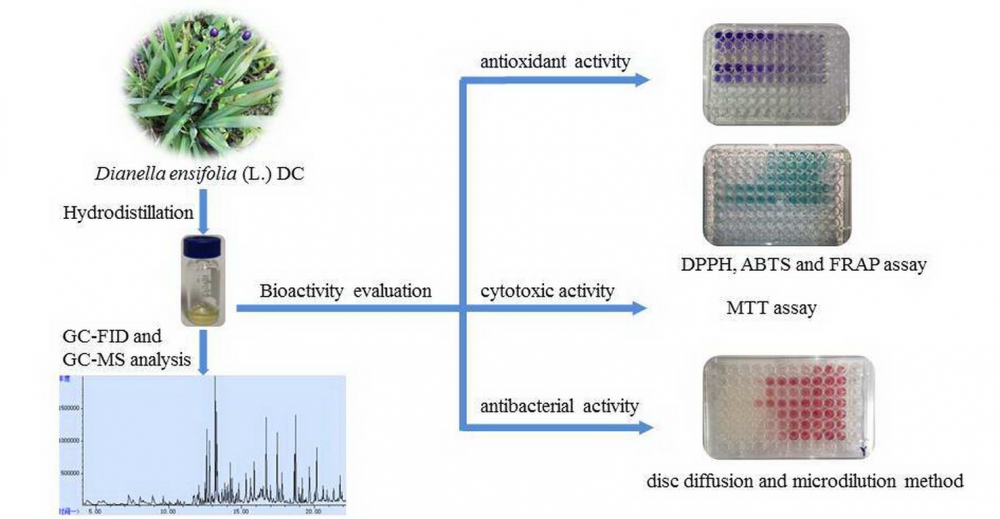
TThe essential oil (EO) was isolated from aerial parts of Dianella ensifolia (L.) DC by hydro-distillation and its chemical constituents was determined by GC-FID and GC-MS. In total, sixty-three compounds comprising 97.2% of the EO were identified. The major compounds in D. ensifolia EO were found to be allo-aromadendrene (7.3%), geranylacetone (6.2%), hexahydrofarnesyl acetone (4.4%), longifolene (4.2%) and β-caryophyllene (4.0%). Besides, the essential oil was evaluated for its antibacterial activity by disc diffusion and broth microdilution method. The D. ensifolia EO exhibited a potential broad-spectrum in vitro antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Also, antioxidant activities of the EO were examined by employing DPPH, ABTS as well as FRAP assays. A weak to moderate antioxidant activity of the EO was observed. Furthermore, in vitro cytotoxic activity evaluation against the cell lines HepG2 and MCF-7 by MTT method showed a potent cytotoxicity with IC50 values of 61.35 μg /mL and 56.53 μg /mL, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.150.19.07.1321 Keywords Dianella ensifolia (L.) DC essential oil antibacterial activity antioxidant activity cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.