Organic Communications
Year: 2019 Volume: 12 Issue:4 October-December
1) Synthesis, characterization and theoretical studies of novel sulfonamide-aldehydes derivatives having tautomeric forms
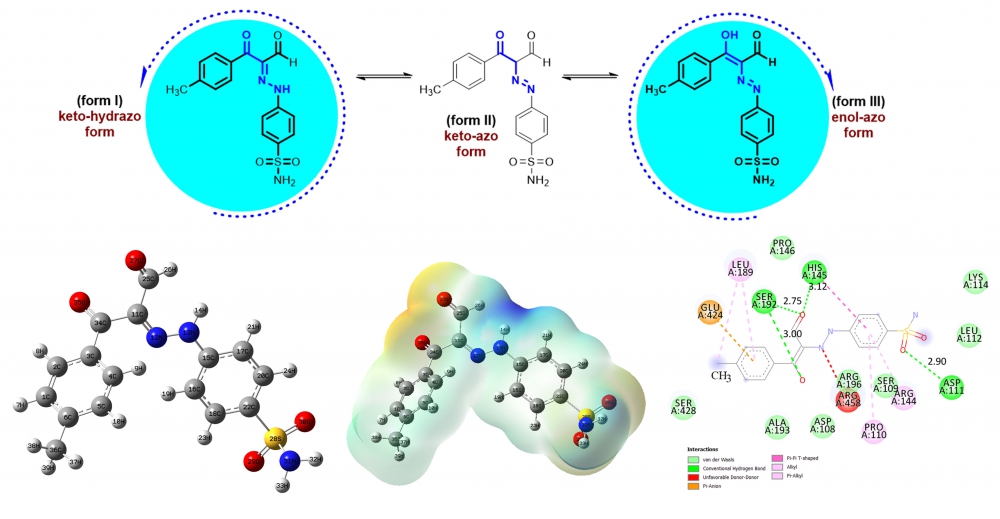
The newly synthesized six tautomeric aldehydes were characterized by 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra. As a result of experimental characterization studies of target products, two tautomer structures named enol-azo and keto-hydrazo were observed. To support other experimental quantum chemical computations were utilized by Density Functional Theory using B3LYP functional and 6-311++G (d,p) basis set. All theoretical calculations were performed only for molecules M1 and M4 after each tautomer was optimized. The form III tautomers with lower energy of compounds M1 and M4 were determined as preferential structures in the ground state. From the MEP analysis, it is evident that the negative charge covers the C=O group and positive region is over the hydrogen groups. Finally, molecular docking calculations between 4F5S receptor and six ligand interactions were carried out by using AutoDock Vina program, and results were evaluated in detail.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.67.19.09.1407 Keywords Keto-hydrazo tautomer enol-azo tautomer sulfonamide DFT molecular docking GIAO DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Gluconic acid aqueous solution: A bio-compatible media for one-pot multicomponent synthesis of dihydropyrano [2,3-c] Pyrazoles
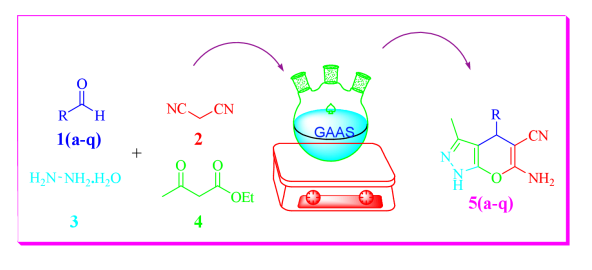
A new facile, green and efficient protocol was developed for synthesis of Dihydropyrano [2,3-c] pyrazoles using gluconic acid aqueous solution (GAAS), as catalyst and solvent under environmentally friendly conditions. The advantageous features of this methodology are the environmentally benign character, operational simplicity, high yield processing (91-96%), easy handling; reaction medium can be recycled and reused several times without significant loss of its efficiency. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for antimicrobial and antioxidant activity and also analyzed for ADME properties. The structure of compounds has been confirmed by IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, Mass spectrometry and elemental analysis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.71.19.08.1386 Keywords Dihydropyrano [2,3-c] pyrazoles gluconic acid aqueous solution (GAAS) green media antimicrobial antifungal antioxidant DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Synthesis and cholinesterase inhibitory activity studies of some piperidinone derivatives

AA series of a,β-unsaturated carbonyl based piperidinone derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their abilities to inhibit AChE and BuChE. All compounds exhibited AChE and BuChE inhibitory activity in different ratios. Among the series, compound 1d, (1-benzyl-3,5-bis(4-nitrobenzylidene)piperidine-4-one), was found to be the most potent derivative against AChE (IC50= 12.55 µM) and compound 1g, (1-benzyl-3,5-bis(4-chlorobenzylidene)piperidine-4-one) showed the best anti-BuChE activity (IC50= 17.28 µM). The derivatives exhibited selectivity on AChE enzyme with respect to BuChE. Only compound 1g, bearing chlorine substituents, demonstrated as a dual inhibitor of cholinesterases. Taken together, these results indicated that a,β-unsaturated carbonyl based piperidinone scaffold might be a promising drug candidate for further anti-AD drug development.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.69.19.09.1399 Keywords Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors Butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors Piperidinone Alzheimer’s disease DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Microvawe assisted synthesis of N-(methyl and methoxy) benzylidene-4-fluoroaniline derivatives and their carbonic anhydrase I and II inhibition properties

IIn this study, some Schiff base derivatives (6a-f) were synthesized using a microwave method. The synthesized compounds were characterized by 1D, 2D NMR and mass spectral data. Their inhibitory effects were studied on carbonic anhydrase isozymes (hCA I and II), purified from human erythrocyte cells by Sepharose-4B-L-tyrosine-sulfanilamide affinity chromatography and the compounds N-3-Methylbenzylidene-4-fluoroaniline (6b), N-4-Methylbenzylidene-4-fluoroaniline (6c), N-2-Methoxybenzylidene-4-fluoroaniline (6d) showed moderate activity on hCAII in the range of IC50 values.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.66.19.07.1327 Keywords Schiff base carbonic anhydrase N-benzylideneaniline NMR HRMS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Oxidation of some benzyl substituted fused quinazoline derivatives
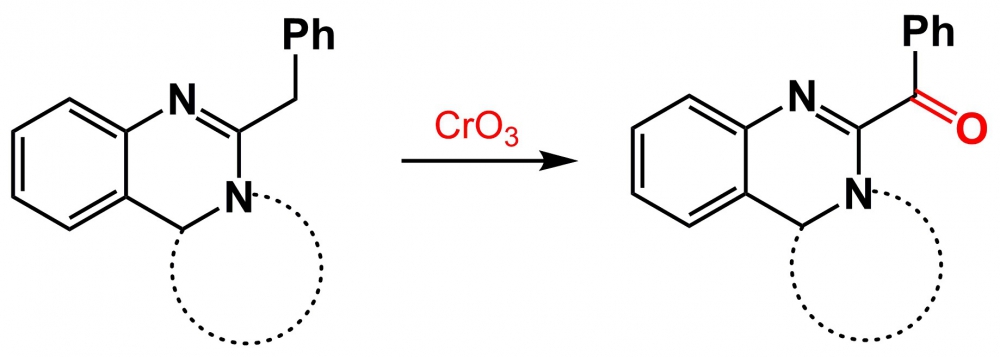
In this study, some benzoyl substituted fused quinazolines derivatives 4a-d were synthesized using Fieser’s reagent. Also this work reports about two non-specific products 5a and 6 of the reaction which were isolated from the reaction mixture. Based on the experimental data the potential oxidation mechanism of ketone 4a by chromium trioxide was described. The synthesized compounds were characterized by 1H, 13C, 19F NMR and LC-MS data.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.70.19.11.1468 Keywords oxidation fused quinazolines derivatives Fieser’s reagent benzyl to benzoyl mechanism DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) One-step transformation of a fluoro-based polymer into a superhydrophobic polymer composites
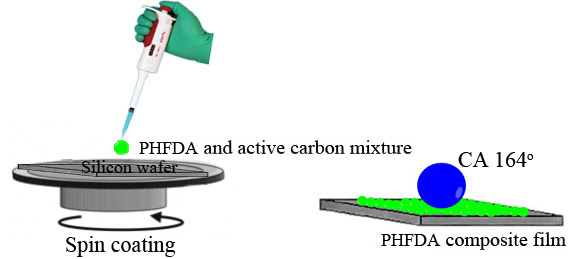
We describe the formation of superhydrophobic surfaces by controlling the surface roughness using some simple processing methods, such as annealing at 120 °C, freeze-drying at -40 °C and composite film preparation. The root-mean-square (rms) roughness and the water contact angle values of untreated poly(3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,9,9,10,10,11,11,12,12-heneicosaffluorododecyl acrylate) (PHFDA) film prepared on silicon substrate using spin-coating technique were about 1.35 nm and θA/θR = 125o/103o , respectively. On the other hand, the annealed film at 120 °C and the freeze-dried film at -40 °C with only a small increase in the rms roughness and the water contact angle values were 2.05 nm and θA/θR = 126o/111o , and 2.28 nm and θA/θR = 130o/123o, respectively. However, these values for the composite film composed of PHFDA and active carbon were 2.54 nm and θA/θR = 165o/164o, respectively. This method can be applied to various surfaces as long as the composites composed of nanoparticles and polymeric materials do not cause any aggregation in spin-coating.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.68.19.09.1403 Keywords Superhydrophobic surfaces surface roughness composite film active carbon spin-coating DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.