Organic Communications
Year: 2022 Volume: 15 Issue:3 July-September
1) Optimization of Kumada cross-coupling reactions of tri- and tetra- bromothiophenes and symmetrical di-bromo-2, 2' bithiophene with cyclohexylmagnesium bromide: Synthesis, DFT studies and nonlinear optical analysis
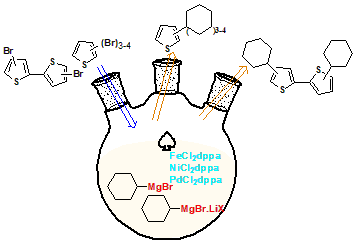
Tri-, tetra-bromothiophene and symmetrical di-bromo-2, 2' bithiophene derivatives were coupled efficiently with cyclohexylmagnesium bromide in the presence of iron, nickel and palladium as catalysts under optimized mild reaction conditions. Additives such as lithium chloride and bromide have been employed to enhance the efficiency of the Grignard reagent. The corresponding coupled products, which widely used as precursors or additives in photonic industries have been studied by DFT method at B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level of theory using Gaussian 09W to explore the global chemical reactivity descriptors and nonlinear optical activities ( NLO). According to results of NLO analysis, polarizability (α), anisotropy hyperpolarizability (Δα) and first order hyperpolarizability (β) exhibit higher value than the standard urea, which reflect a promising molecular non-linear susceptibilities indicating that compounds 4a-4f to be good candidates in the potential photonic applications.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.135.2206.2485 Keywords Iron nickel palladium coupling reaction thiophene nonlinear optical analysis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral activities of pyrimido[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives through computational approaches
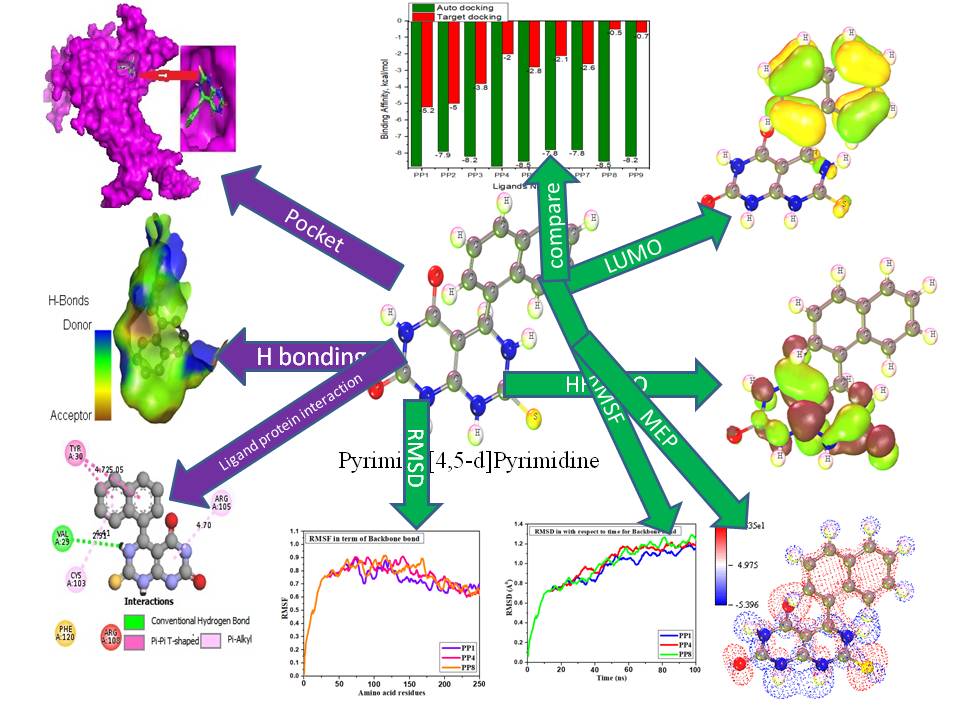
Pyrimido[4,5-d]pyrimidine conveys antimicrobial activity against various micro pathogens having functionalized properties. As a result, this study has designed to illustrate the antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties of pyrimido[4,5-d]pyrimidine. First of all, these structures have been optimized from the characterization of synthesis for calculating chemical descriptors by DFT. Next, the auto docking and target docking against 12 proteins, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa (2Y0H), Bacillus cereus (1AH7), Escherichia coli (6DR3), Shigella dysenteriae (3FHH) Salmonella typhi (3FHU), Aspergillus niger (1ACZ), Aspergillus flavus (1XY3), Rhizomucor miehei (4WTP), Candida auris (6U8J), three proteins of SARS-CoV-2 (7T9J, 7T9L, and 7TB4) were performed for the determination of binding sites and binding affinity. One FDA approved drug (Ampicillin) has docked against 12 proteins while the Bacillus cereus (Bacteria), Aspergillus flavus (Fungus), and SARS-CoV-2, 7T9L (Omicron) are obtained the best binding affinity after docking. The most common residues are the PHE-66, ARG-176 and VAL-124 for Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus flavus and SARS-CoV-2, Omicron (7T9L), respectively, as they blocked the active sites by the ligands as inhibitors. It is revealed that this study contained both auto docking and target docking whereas the binding affinity of auto docking is that the binding affinity for auto docking is higher than target docking. Finally, among the nine compounds, three compounds show outstanding results against bacteria, fungus and virus. At last, molecular dynamics were performed to check the stability and validation of the docked complex and quantum calculations obtained the molecular properties, as well as ADMET, pharmacokinetics, Lipinski Rule and QSAR data.
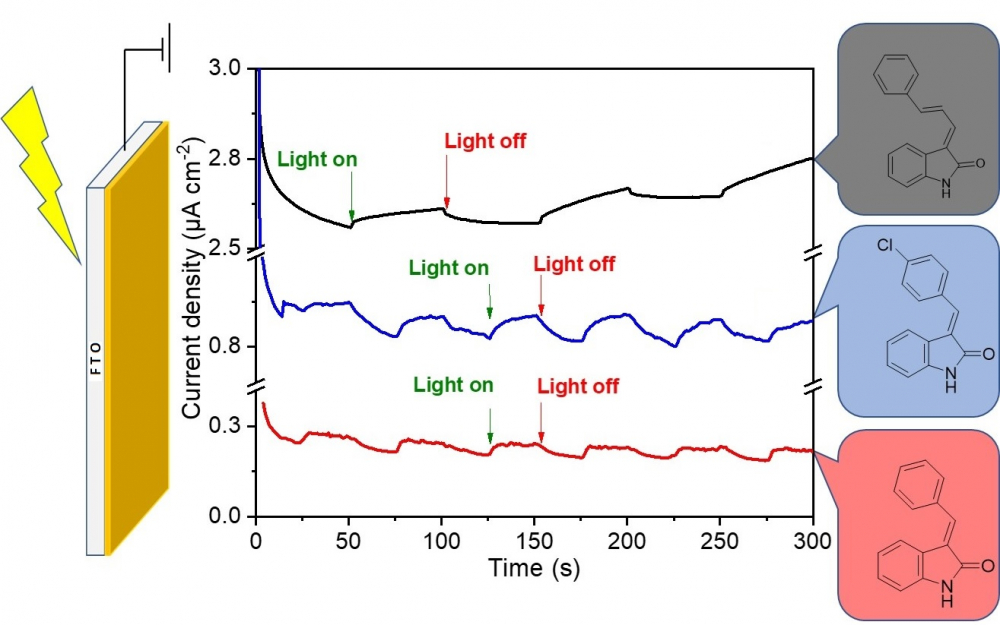
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.133.2204.2439 Keywords DFT molecular dynamics ADMET Omicron Covid19 QSAR DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) A convenient synthesis of 3-arylideneindolin-2-ones and evaluation of their photoelectrochemical properties
 DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.136.2207.2515
Keywords
3-arylideneindolin-2-ones
H-bonding
photoelectrochemical
semiconductor
photoconversion
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.136.2207.2515
Keywords
3-arylideneindolin-2-ones
H-bonding
photoelectrochemical
semiconductor
photoconversion
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
4) Prediction of the antiproliferative effects of some benzimidazole-chalcone derivatives against MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines: QSAR and molecular docking studies
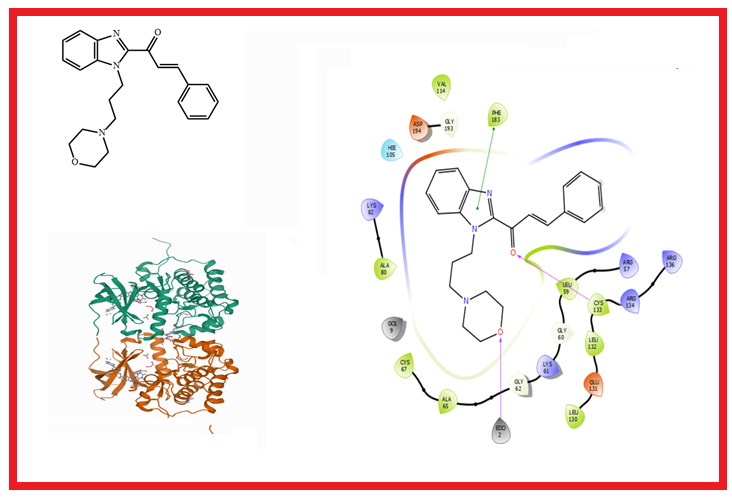
Cancer remains a threat to human existence owing the high number of deaths associated with it. Combating cancer has continued to garner interest from pharmaceutical companies as the resistance and toxicity issues have been observed with the treatment of known drugs. A series of benzimidazole-chalcone derivatives were obtained from literature and investigated for their ability to inhibit MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Lines via QSAR and molecular docking techniques. A QSAR model was generated to establish the relationship between molecular descriptors and bioactivity of benzimidazole-chalcone derivatives. The R2, adjusted R2, Q2 and R2pred values obtained suffice to deem the model fit and reliable. The binding affinities of the lead compounds were obtained via an extra precision docking procedure at the active site of the human serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor, 3FC2. Molecule 21 showed the closest binding affinity (-9.350 kcal/mol) as compared to doxorubicin (-9.305 kcal/mol), and had the best IC50 as compared to other compounds as reported earlier in literature. In-silico ADME and drug-likeness prediction of all the molecules showed good pharmacokinetic properties, bioavailability and non-toxicity. The model generated here could be used in predicting the bioactivity of novel antiproliferative agents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.132.2203.2374 Keywords Breast cancer MCF-7 cell line benzimidazoles quantitative structure activity relationship molecular docking pharmacokinetics DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Computational screening of novel therapeutic and potent molecules from bioactive trehalose and it’s eight derivatives by different insilico studies for the treatment of diabetes mellitus
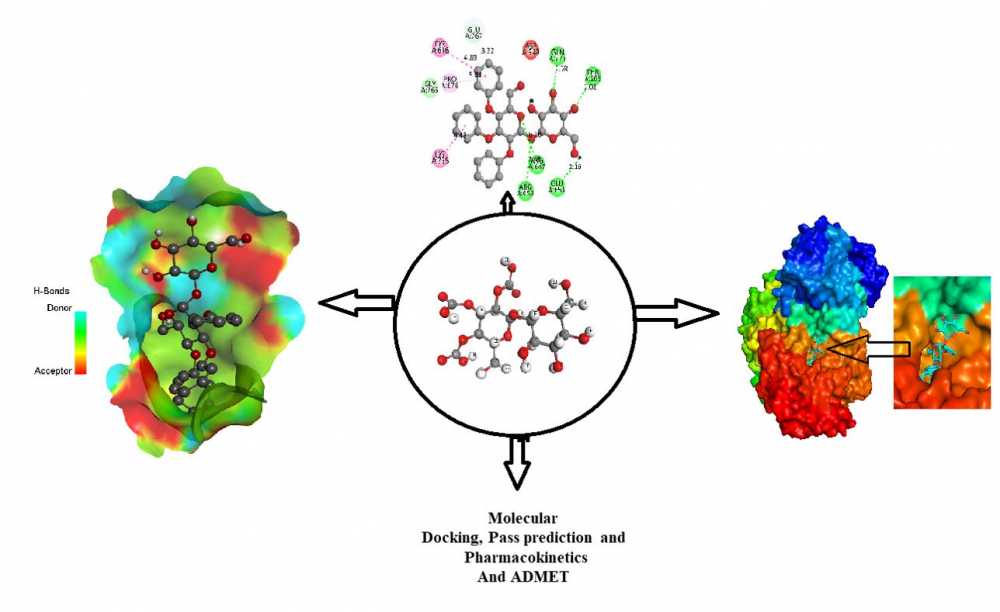
Diabetes mellitus represents a set of disorders that impact how your body utilizes sugar levels (glucose), and it is a chronic disease. Every year, a huge portion of people have diagnosed with this disease globally. So, it is an urgent and required effective treatment to manage this disease. Trehalose is a potent biomolecule, So in this research, bioactive Trehalose and its derivatives have been studied to find potent molecules and inhibitors. Numerous studies have been included to make them as potent medications, such as Pass perdition, molecular docking, ADMET, and Pharmacokinetics experiment. When the pass prediction value has been satisfied, the docking studies were then conducted to determine how actively binds with the targeted protein. The docking score was seen as -7.0 kcal/mol to -9.1 kcal/mol against Human Maltase-Glucoamylase (PDB ID 2QMJ), and -7.0 kcal/mole to -9.8 kcal/mol was found against Human CYP3A4 bound to metformin PDB ID 5G5J. At the same time, standard FDA-approved Metformin Hydrochloride was also studied, and it provided -5.3 kcal/mole and -5.0kcal/mol. So, it is visualized that newly generated molecules are better scores than the standard.In the overall investigation, all drugs have satisfied and obtained Pass prediction score, excellent binding affinities, ADMET, and Pharmacokinetics profiles, and it could be concluded that all the medicines could be used as potent drugs.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.134.2204.2446 Keywords Diabetes mellitus pass prediction molecular docking ADMET drug-likeness DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Efficient one-pot cascade synthesis of pyrazolopyridazine in PEG-400
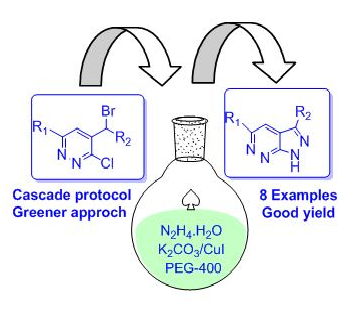
A one-pot cascade synthesis of pyrazolopyridazine from 4-(bromo(aryl)methyl)-3-chloropyridazines in PEG-400, in an ecofriendly solvent system has been developed. A series of pyrazolopyridazines (2a-i) were synthesized by using bidentate electron-donor ligand in good yield (60-85%). The present cascade protocol included nucleophilic substitution, ring closer and oxidative aromatization in single precedential step.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.135.2204.2408 Keywords Pyrazolopyridazine heterocyclic compound cascade PEG-400 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.