Organic Communications
Year: 2024 Volume: 17 Issue:3 July-September
1) Evaluation of the mesalazine-loaded nanoparticles-embedded BSA hydrogels for the ulcerative colitis treatment
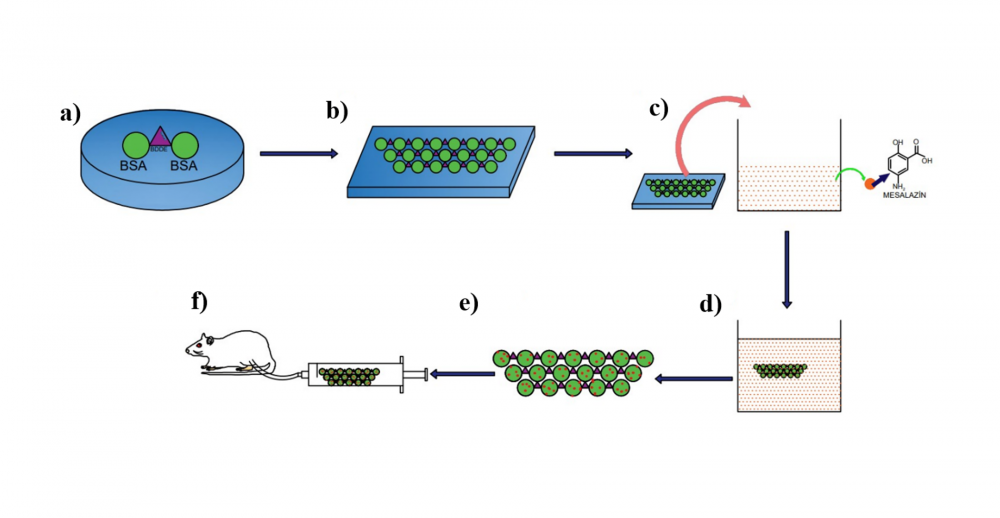
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease mainly affecting the colon and remains a challenging disease to manage clinically with its relapsing-remitting course. Traditional treatments for this disease showed some drawbacks, including systemic toxicity and ineffective targeting of the affected colon areas. This article introduces a unique treatment method that uses mesalazine (MSZ)-loaded TPP/Chitosan nanoparticles (MSZNP)-embedded into bovine serum albumin (BSA) hydrogels (MSZNPH) for targeted intrarectal medication delivery. Additionally, conventional MSZ was integrated into BSA hydrogel (MSZH), and then, MSZH, MSZNP, and MSZNPH were characterized and compared with an emphasis on encapsulation efficiency, drug release profile, and hydrogel swelling behavior. Our findings show that MSZNPH composite technology may improve targeted administration and prolonged release of MSZ, indicating a promising new route for UC therapy with the potential to improve patient adherence and outcomes.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.171.2405.3240 Keywords Ulcerative colitis mesalazine hydrogels nanoparticles DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Eco-friendly synthesis, antimicrobial activity, molecular docking and ADMET studies of novel α-aminophosphonates
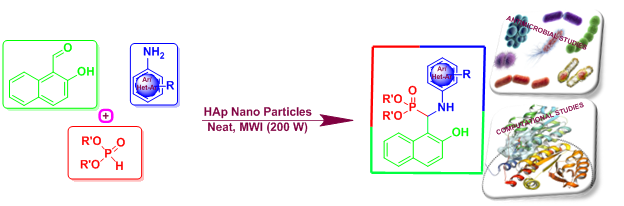
An efficient one-pot Kabachnik-Fields reaction has been carried out for the synthesis of novel α-aminophosphonates under microwave irradiation and solvent-free conditions by 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde, aromatic amines and dialkyl phosphites using Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (HAp NPs) as catalyst. The present new protocol is environmentally benign as it offers some interesting and promising features like solvent-free, low cost, safety, minimal waste, atom efficiency, easy work-up, short reaction time and possessing excellent functional group tolerance to structurally diverse derivatives. The title compounds were subjected to antimicrobial activity against bacterial and fungal strains by disc diffusion and MIC methods. Advanced computational tools were also employed to conduct molecular docking and toxicogenomic investigations on target compounds. Employing ensemble-docking approaches, the primary contenders were identified for their potential to bind to the active sites of GlcN-6-P synthase, with PDB IDs 2VF5 and 2POC acting as target receptors. ADMET studies revealed promising drug-like characteristics of these compounds.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.172.24.07.3269 Keywords α-Aminophosphonates HAp NPs microwave irradiation solvent-free antimicrobial activity docking & ADMET studies DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Synthesis, antimicrobial, and molecular docking studies of furan-based Schiff bases derived from 4 -nitrobenzene - 1, 2 - diamine
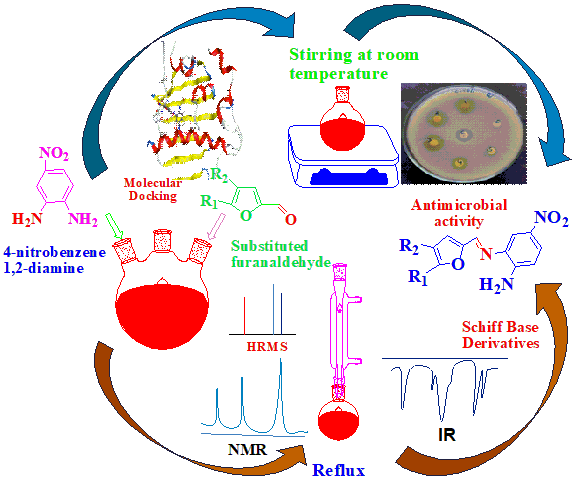
Schiff base compounds contain the azomethine group. They have diverse biological activities such as antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antimicrobial, and anticancer. They are frequently used as catalyst, corrosion inhibition agents and dyes in industrial process. This structure group can also be called as a main structural part of natural products and synthetic drugs. Schiff bases 3a, 3b, 3c, 3d, and 3e were synthesized by reacting 4-nitrobenzene-1,2-diamine with furfural derivatives without acid, base, or Lewis catalytic agents. Reaction progress was monitored by thin-layer chromatography. Each synthesized Schiff base was characterized by UV-visible, FTIR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and HRMS techniques. Nitro-substituted Schiff base 3b shows remarkable antimicrobial activities against bacterial strains E. Coli, S. aureus, and E. faecalis as compared to 3a, 3c, 3d, and 3e which was confirmed by molecular docking studies with protein of E. Coli DNA gyrase (1KZN), S. aureus cell division protein FtsZ (3VOB), and E. faecalis nucleoside diphosphate kinase(3Q8U).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.173.24.07.3274 Keywords Schiff bases synthesis characterization antimicrobial activities molecular docking DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.