Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2019 Volume: 13 Issue:1 January-June
1) High performance liquid chromatographic analysis of lercanidipine in human breast milk
A simple, rapid, precise and accurate isocratic reversed phase HPLC method was developed and validated for the determination of lercanidipine hydrochloride in pharmaceutical tablets and spiked human breast milk. The chromatographic separation was achieved on C18 (250×4.6 mm×5µm) column using a mobile phase consisting of acetonitrile and phospate buffer (pH=4) (55:45, v/v) at a flow rate of 1.1 mL/min and UV detection at 237 nm. The linearity of the proposed method was investigated in the range of 1.0-40 μg/mL (r2=0.9990). The method was validated in terms of accuracy, precision, reproducibility, specificity, robustness, and detection and quantification limits, in accordance with ICH guidelines. The proposed method is found as suitable for routine quantification of lercanidipine in human breast milk.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.23.19.03.1223 Keywords Antihypertensive Lercanidipine hydrochloride HPLC-UV Human breast milk Method validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Determination of some heavy metals by ICP-OES in edible parts of fish from Sapanca Lake and streams
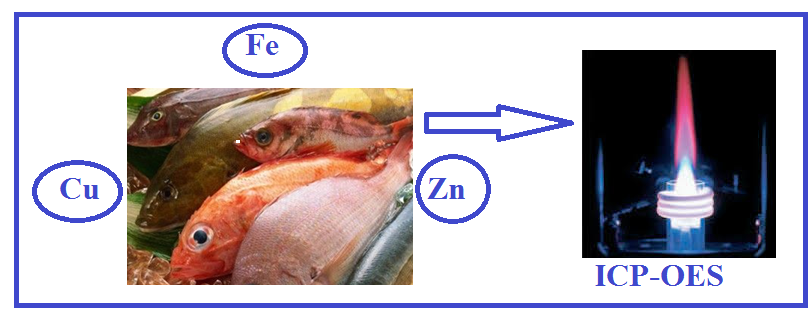
In this study, Heavy metal deposits (Cu, Fe and Zn) accumulated in muscles over 15 different species were detected by ICP-OES device in a total of 20 fish taken from Sapanca Lake, Sakarya River and Western Black Sea (Karasu). When the results were examined, Cu concentration was determined to be 2.60-5.31 μg/g, Fe concentration was determined to be 10.25-54.36 μg/g and Zinc concentration was determined to be 13.66-47.11 μg/g respectively in fish samples. In addition, the same procedures were applied with the standard reference material DORM-3 reference material (Fish Protein Certified Reference Material for Trace Metals) to determine the accuracy of the method. As a result, it has been determined that the amount of heavy metals contained in the analyzed fish samples is below the limit values provided by the Turkish Food Codex, Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization and therefore consumption of these does not constitute a threat to health.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.24.19.03.1219 Keywords Heavy metals fish ICP-OES microwave digestion DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Use of ion chromatography method on the determination of some anions in the water collected from Sakarya, Turkey
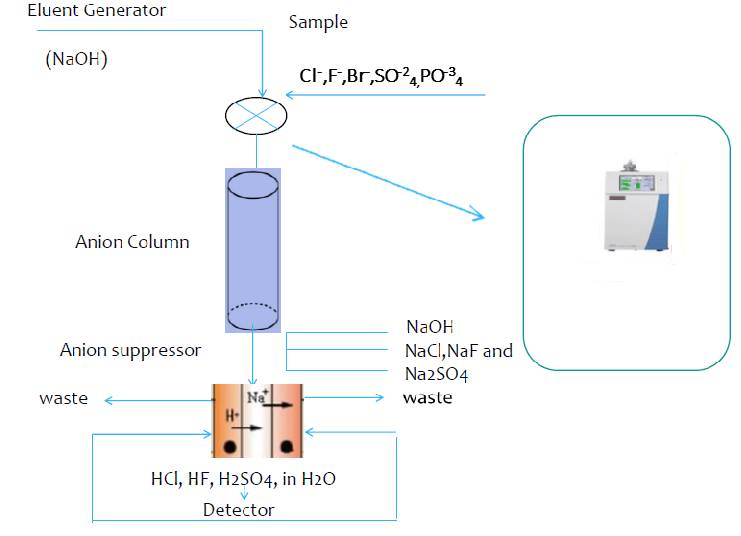
In this study simultaneous analysis of seven different anions (Fluoride, Chloride, Nitrite, Bromide, Nitrate, Phosphate, and Sulfate) in the 13 different water sample collected from Sakarya/Turkey was conducted with ion chromatography method. Analyzes were performed simultaneously using the ion chromatography method. Some validation tests and the optimum conditions for the determination of anions were studied. The analysis of anions was accomplished by the dilution of the sample injection device. Samples were used to adjust the terms of the device and the results were recorded. Ion chromatography (IC) is now considered as an excellent technique for the analysis of ions in many samples.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.26.19.03.1221 Keywords Water ion chromatography anion Sakarya. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Investigation of caffeine concentrations in sport supplements and inconsistencies in product labelling
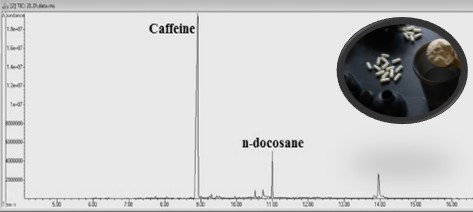
Caffeine is a substance that can be easily consumed in daily nutrition as well as in sport supplements. Exceeding the daily-recommended dose for caffeine may cause serious health problems. Studies illustrated that many concerns have been raising about the incompatibility between labels on sport supplements and their contents. The present study aimed to investigate caffeine contents in sport supplements purchased from Turkey market for the first time and to evaluate label information on products. Caffeine concentrations were determined in 41 sport supplements and possible adverse effects were emphasized considering calculated daily consumption doses. Seventeen samples among 41 products were found to be caffeine containing, ranging from 4.52 to 471 mg/mL. Three of caffeine containing products were undeclared their caffeine ingredients. Although three products were not specified caffeine their amounts, findings were found above the daily-recommended caffeine limit (400 mg/day). Significant differences were observed between the quantities indicated on the labels and the determined caffeine amounts in 7 products (p<0.05). Eight of 17 caffeine labelled products were found between 151-948% higher than stated label information. Overall, 29.4% of caffeine containing products (n=17) were found over the recommended intake. Consuming more than the daily-recommended dose may cause severe adverse reactions and consumers may experience serious health risks such as arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, as well as sleep problems, irritability, anxiety, headache, and restlessness. Considering these health risks, awareness of consumers and accurate product labels on sport supplements gain more importance to prevent people from undesired consequences.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.25.19.04.1252 Keywords Sport supplement caffeine GC-MS label inconsistency daily intake DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.