Organic Communications
Year: 2020 Volume: 13 Issue:3 July-September
1) A multi-component reaction approach to the synthesis of potent antidiabetic agents five-membered iminosugars analogues

Some novel five-membered iminosugar analogues were efficiently synthesized via the MCRs of three components; amines, aldehydes and oxaloacetate to give 4-hydroxymethylpyrrolidines. Reduction of 3-hydroxy-4-carbomethoxy-3-pyrroliden-2-ones with Pd/C-catalyzed hydrogenation gave the corresponding cis-hydrogenated products at C3/C4 stereoselectively. Then following reductions of ester and amide functionalities with LiAlH4 afforded 4-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidin-3-ols. Among the synthesized compounds 4-hydrazineyl-3-hydroxymethyl-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-N-methylpyrrolidine and 3-hydrazineyl-4-hydroxymethyl-1-methylpyrrolidine were found to be the most promising a-glucosidase inhibitor with IC50 values of 1.12 and 1.17 mM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.85.20.08.1765 Keywords Iminosugar pyrrolidine one-pot reaction stereoselective hydrogenation antidiabetic DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Design and synthesis of novel peptidomimetics for cancer immunotherapy

Tumor cells benefit from some certain signals, which are referred to as “immune checkpoints”, to escape immune-mediated destruction. With that in mind, it is believed that the blockade of these points, such as programmed cell death Ligand-1 (PD-L1) and programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), can restore an adaptative immune response against tumoral cells. In this study, we have designed and synthesized some novel peptidomimetics with a 2-aminobenzathiazole scaffold, which targets the PD-1/PDL-1 pathway. In the viability assay, it was found that these compounds decreased the proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the concentration of 10 uM. Overall, our results indicate that these novel compounds are potential checkpoint inhibitors for cancer immunotherapy.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.86.20.09.1802 Keywords Immunotherapy PD-L1 PD-1 peptidomimetics 2-aminobenzothiazole DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
3) Succinic acid: a novel and efficient organo-catalyst for synthesis of α-amino nitriles under solvent free condition
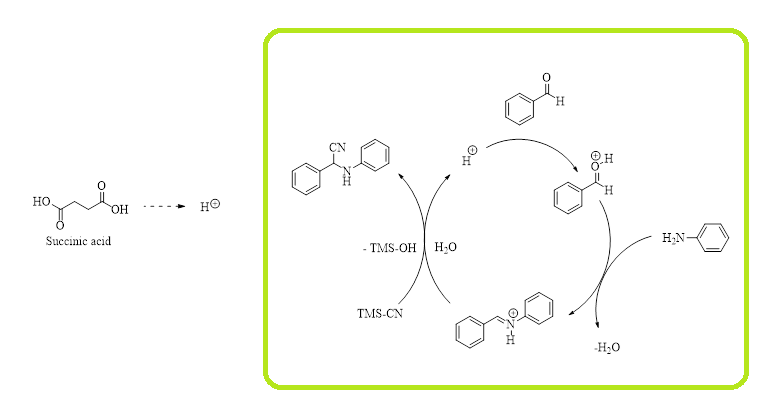
A simple, efficient and eco-friendly general protocol has been developed for the synthesis of three-component reaction methodology of Strecker’s α-amino nitriles by using various aldehyde or ketone, amines and trimethylsilyl cyanide (TMS-CN). In this methodology, succinic acid is used as a novel and efficient organo-catalyst in catalytic amount. This method was carried out under solvent free condition at room temperature for preparation of variety of α-amino nitriles derivatives in excellent yields. The present method provides significant advantages of organo-catalyst such as inexpensive, highly stable, environmentally benign and commercially available as well as solvent free reaction conditions and high conversions of the products with excellent yield.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.81.20.08.1781 Keywords Strecker reaction multicomponent reaction amino nitriles TMS-CN succinic acid, organo-catalyst DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Synthesis of new fatty acid derivatives of oleanane and ursane triterpenoids and investigation of their in vitro cytotoxic effects on 3T3 fibroblast and PC3 prostate cancer cell linesLines
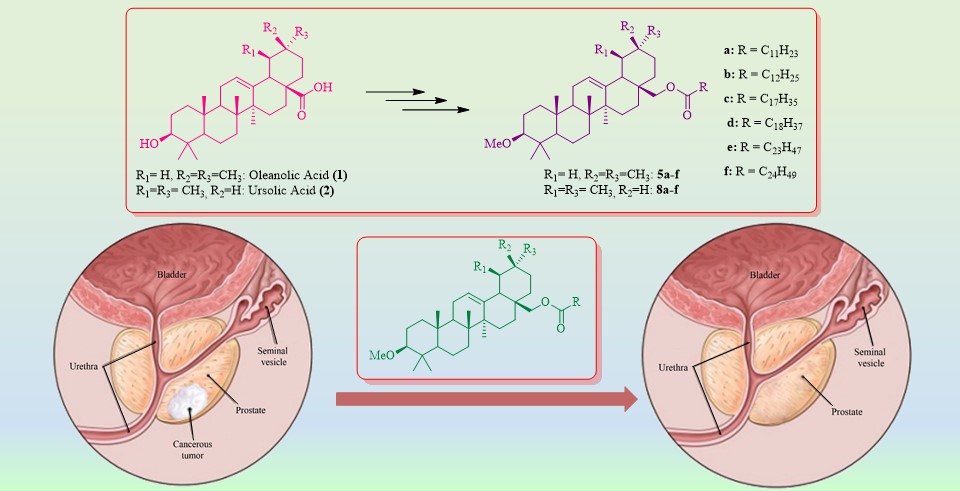
In this study, 12 new oleanane and ursane derivative triterpene compounds, having fatty acids in the form of esters with carbon numbers of 12, 13, 18, 19, 24 and 25, were synthesized starting from natural products oleanolic and ursolic acids. Initially, 3-methylerythrodiol (3β-methoxyolean-12-en-28-ol) and 3-methyluvaol (3β-methoxyurs-12-en-28-ol) were synthesized from oleanolic acid and ursolic acid, respectively. For this purpose, secondary OH group at C-3 of oleanolic and ursolic acids were protected as methyl ether and, then, their carboxylic acid moieties were reduced by aluminum hydride. New fatty acid derivatives 5a-f and 8a-f were synthesized through the reaction of 3-methylerythrodiol/3-methyluvaol and corresponding fatty acid halides. In vitro cytotoxic activities of the all synthesized compounds were investigated on 3T3 fibroblast cells and PC3 prostate cancer cell lines. While all the compounds showed at least 70% inhibition on PC3 prostate cancer cells at a concentration of 25 µM, they had average of 50% inhibition on 3T3 fibroblast human healthy cells at the same concentration. Compounds 5c and 8c demonstrated the least toxic effect on 3T3 fibroblast human healthy cells and the highest toxic effect on PC3 prostate cancer cells at a concentration of 12.5 µM. Moreover, compounds 8c and 8e had the least toxic effect on 3T3 fibroblast human healthy cells and the highest toxic effect on PC3 prostate cancer cells at the same concentration.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.84.20.09.1792 Keywords Oleanolic acid ursolic acid prostate cancer 3T3 cells cytotoxicity fatty acid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Investigation of sensor characteristics of Au and Cu modified PEDOT electrodes for dopamine
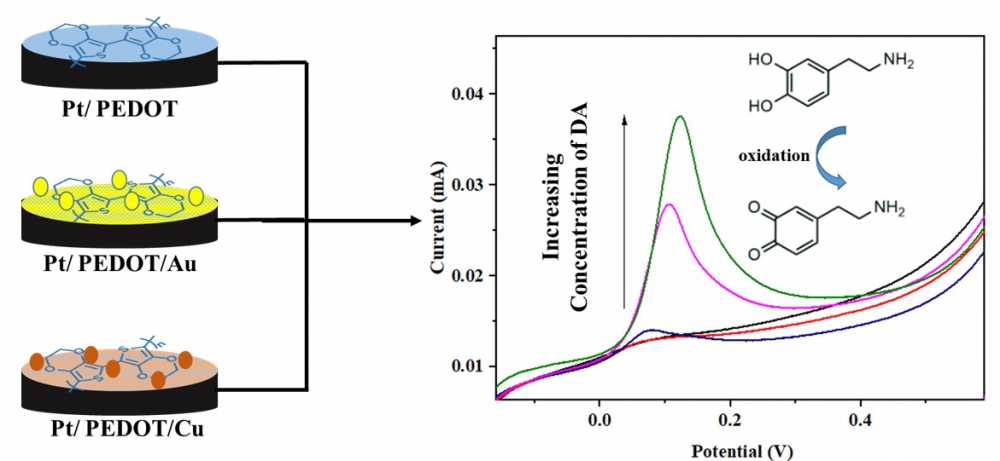
Hormones are important and necessary for the continuity of many vital functions in human body. Dopamine (DA) is a neurotransmitter affecting pain and pleasure perceptions, emotions, and movements. In the case of DA deficiency, severe discomforts such as Schizophrenia and Parkinsonism may happen. Thus, DA detection is an important subject. Electrochemical methods have been used in this work by developing a sensor for rapid and easy detection of DA. 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) monomer was polymerized on a platinum electrode using cyclic voltammetry method, and the film properties of the resultant polymer were investigated. Additionally, gold and copper coated PEDOT films, Pt/PEDOT/Au and Pt/PEDOT/Cu, respectively, were prepared to improve the sensitivity and stability of the films, compared to Pt/PEDOT electrode. The calibration curves were found to be linear in the concentration range of 50-1000 μM for DA in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA). The detection limits were determined as 18.46 μM, 13.33 μM and 6.80 μM for Pt/PEDOT, Pt/PEDOT/Cu and Pt/PEDOT/Au electrodes, respectively. Moreover, the electrodes demonstrated an electrochemical catalytic effect toward DA.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.82.20.09.1796 Keywords 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) PEDOT Au and Cu nanoparticles, electrochemical polymerization, biosensor dopamine DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
6) Acceleration of transfer-hydrogenation of cyclohexene with palladium catalysts in the presence of polysaccharides
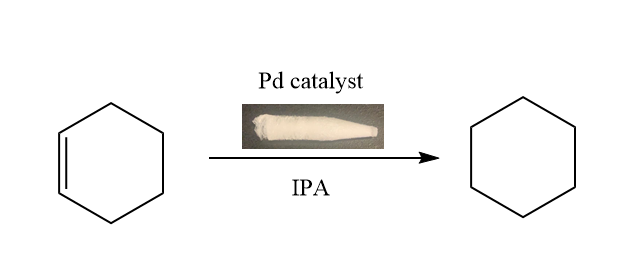
Transfer hydrogenation of alkenes is a very attractive reduction pathway, as it does not involve hazardous metal hydrides or high pressure hydrogen. It can be easily performed with isopropanol as the solvent and hydrogen donor, using a homogenous or heterogeneous palladium catalyst. We present here, for the first time, that the addition of a xerogel composed of natural polysaccharides to the transfer hydrogenation of cyclohexene with palladium salts or Pd/C in isopropanol tremendously increased the reaction activity rate. The Carrageenans forms, and especially iota, were found to be the most useful additives in the two scales that were tested.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.83.20.08.1771 Keywords cyclohexene; palladium catalyst transfer hydrogenation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.