Organic Communications
Year: 2021 Volume: 14 Issue:1 January-March
1) Carbon-carbon cross-coupling reactions of organomagnesium reagents with a variety of electrophilic substrates mediated by iron catalysts
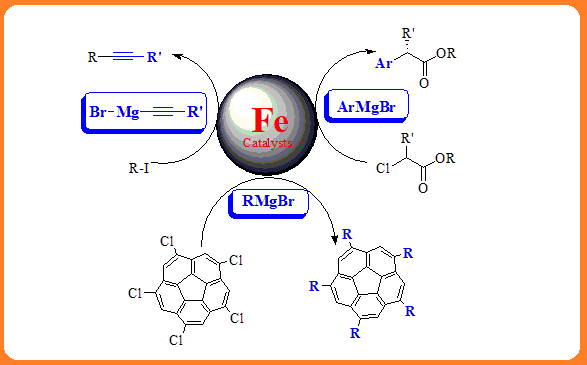
Iron complexes are one of the most promising catalysts for carbon-carbon coupling reactions due to their relatively low cost, widespread availability as well as lower toxicity. Many researches have been successfully done to develop efficient protocols for the cross-coupling reactions of organomagnesium reagents with various substrates mediated by iron catalysts to generate a wide spectrum of important organic compounds. This review covers significant developments in iron catalyzed cross-coupling reactions over the past ten years.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.94.20.12.1916 Keywords Iron catalysts organomagnesium reagents carbon-carbon formation cross-coupling reactions DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Synthesis and characterization of novel mono, bis and tris heteroaryl chalcone derivatives of 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene

In this study, a new series consisting of 12 heteroaryl chalcone derivatives of 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene were synthesised. Chalcones were synthesised in high purity and efficiency, via condensation of mono, bis and tris 2,4,6-trimethoxy acetophenones with hetero-2-carbaldehyde derivatives based on Claisen Schdmit condensation. The reactions feature a good scope for the all products, mild reaction conditions and good yields. The synthesized compounds were characterized by using FT-IR, NMR and elemental analysis spectroscopic techniques.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.95.21.01.1942 Keywords Heteroaryl chalcone synthesis characterization DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) One-pot protocol for the synthesis of quinoxalines from styrenes, o-phenylenediamine and benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-4,5-diamine using triiodoisocyanuric acid
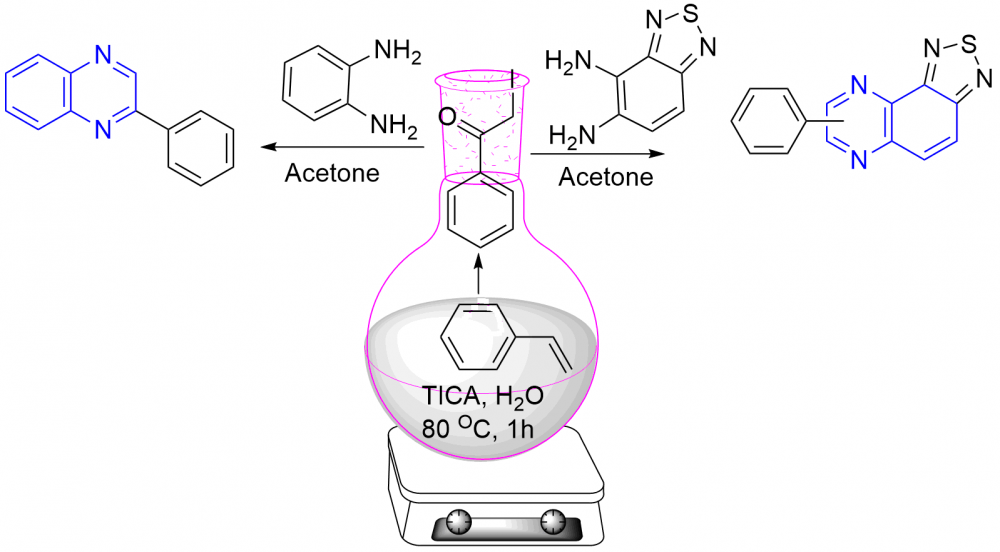
Triiodoisocyanuric acid (TICA) controlled one-pot and easy-operational protocol has been developed for the synthesis of substituted phenylquinoxalines (3a-3i) and phenyl-[1,2,5]thiadiazolo[3,4-f]quinoxaline (5a-5f) from styrenes with o-phenylenediamine and benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-4,5-diamine respectively. The reaction involves co-bromination and oxidation for the formation of an a-bromo ketone as an intermediate in the presence of triiodoisocyanuric acid, followed by condensation with the o-phenylenediamine and benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-4,5-diamine for the formation of phenylquinoxalines (3a-3i) and phenyl-[1,2,5]thiadiazolo[3,4-f]quinoxaline (5a-5f) in 55-79% yield. This protocol environmentally benign and economically viable. Substituted quinoxalines were obtained in good to excellent yields with wide substrate scope and functional-group tolerance.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.93.2009.1800 Keywords Quinoxalines one-pot protocol triiodoisocyanuric acid styrenes DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
4) Exploring the in-silico approach for assessing the potential of natural compounds as a SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors
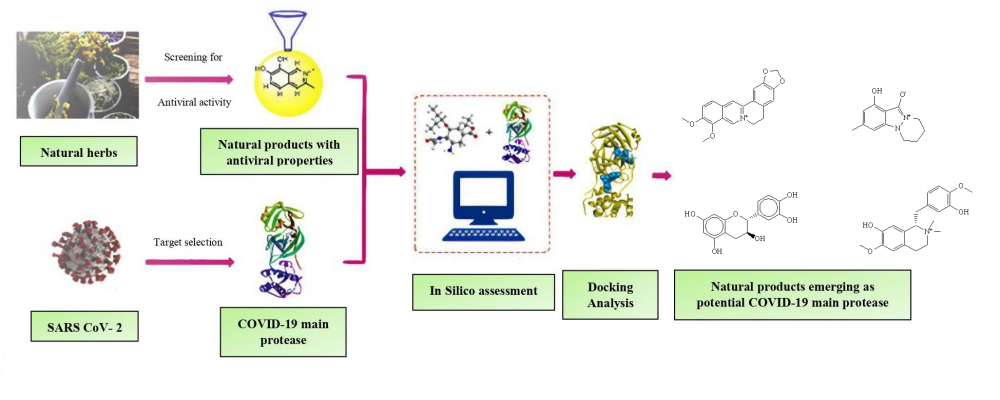
The SARS-CoV-2 virus emerged as a major cause of the COVID-19 pandemic in December 2019. Many attempts have been made to block the viral infection by targeting various processes like its entry, uncoating, replication, activating T cells response, and rising antibody titer. Also, many drugs are repurposed like remdesivir, dexamethasone, tocilizumab, hydroxychloroquine based on their established therapeutic efficacy against other viruses in the past. Natural products (NP) consist of a promising candidate and are needed to evaluate those molecules with molecular docking for preliminary screening and in vitro studies. Therefore, in the present study, a total of 12 active constituents from natural products like Ashwagandha, Tinospora cordifolia, Tea, Neem and lemon balm were docked, using the Autodock tool, onto the crystal structure of SARS CoV-2 main protease (PDB ID-5R80), to study their capability to act as main protease (Mpro) COVID-19 inhibitors. All NPs derivatives displayed good binding energies (ΔG) ranging from -8.8 to -5.2 kcal/mol, but berberine, epicatechin, and rosmarinic acid were found most potent, among others. Therefore, good binding energy, drug-likeness, and efficient pharmacokinetics suggest the potential of NPs derivatives as SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitors. However, further research is necessary to investigate the ability of these compounds as COVID-19 inhibitors.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.97.2012.1895 Keywords SARS-CoV-2 main protease natural products molecular docking viral infection drug-likeness DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Swelling and durability performance of surface-grafted polymer brushes and brush gels
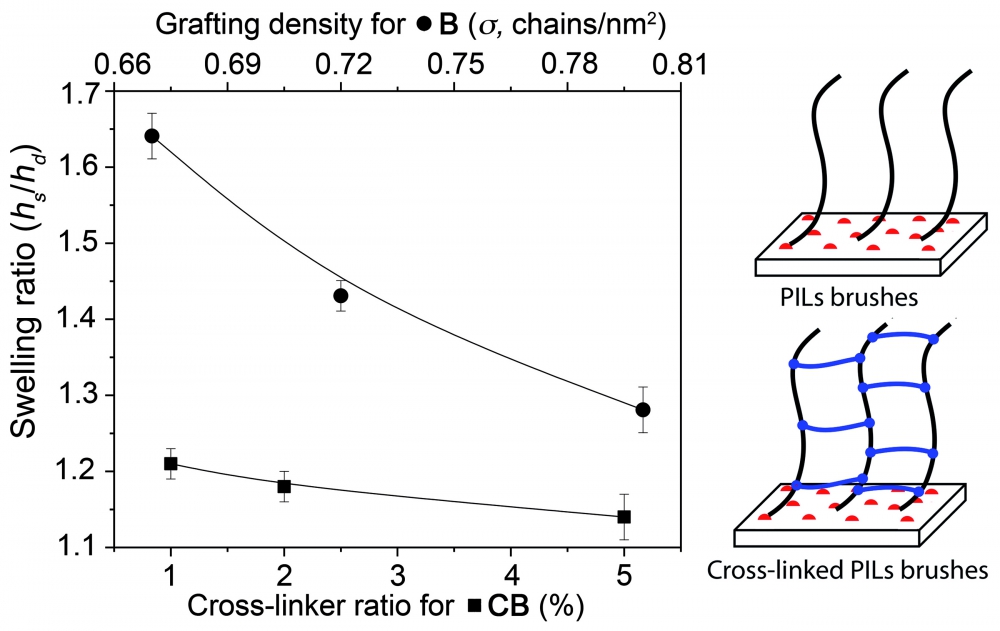
Polymer brushes and brush gels were prepared by RAFT polymerization. Prepared surfaces were characterized by XPS, AFM, ellipsometry, and water contact angle measurements. The swelling properties and stability of surfaces were compared. It was determined that the swelling ratio decreased with increasing grafting density and cross-linker ratio for polymer brushes and brush gels, respectively. As a result, it was observed that cross-linked polymer brushes were more stable than polymer brushes, and the stability and swelling properties of polymer brushes could be controlled by cross-linking.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.96.2012.1902 Keywords Polymer brush brush gels polymeric ionic liquid RAFT polymerization DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
6) Knoevenagel condensation reaction catalysed by agro-waste extract as a greener solvent catalyst

This paper present a novel Knoevenagel reaction protocol for the condensation of aromatic/heteroaromatic aldehydes with malononitrile to give α, β–unsaturated benzylidene derivatives. The main focus of this work is to reveal the usability of agro-waste extracts as a catalyst in the Knoevenagel condensation. The present protocol proceeds efficiently for various substituted aromatic and heterocyclic aldehydes in the Knoevenagel reactions. In addition, the present method describes direct isolation of the formed products without using organic solvent extraction gave good yields product.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.99.21.01.1948 Keywords green chemistry Agro-waste Knoevenagel condensation solvent-free DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Ultrasound-assisted efficient synthesis of 3-[4-(2-methoxyethyl) phenoxy] propane -1,2 -diol (Metoprolol EP impurity D)
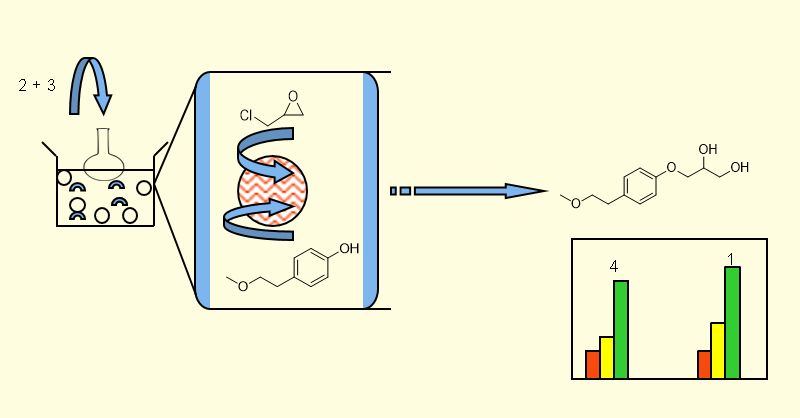
Safety of the drug molecule is dependent on the various impurities formed during chemical transformation which may cause drug product instability, decreased product performance, loss in potency, and/or formation of potentially genotoxic impurities. Therefore, it is essential to identify and quantify the impurities generated during the drug development stage. Herein, we describe the synthesis and characterization of Impurity D of Metoprolol, 3-[4-(2-methoxyethyl)phenoxy]propane-1,2-diol (1), reported in European Pharmacopeia. The synthesis of impurity D has been accomplished in two steps; starting from Epichlorhydrin under three different set of conditions.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.98.20.10.1844 Keywords Keywords: Impurity D Metoprolol synthesis characterization ultrasonic waves DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.