Organic Communications
Year: 2021 Volume: 14 Issue:4 October-December
1) The computational screening of inhibitor for black fungus and white fungus by D-glucofuranose derivatives using in silico and SAR study
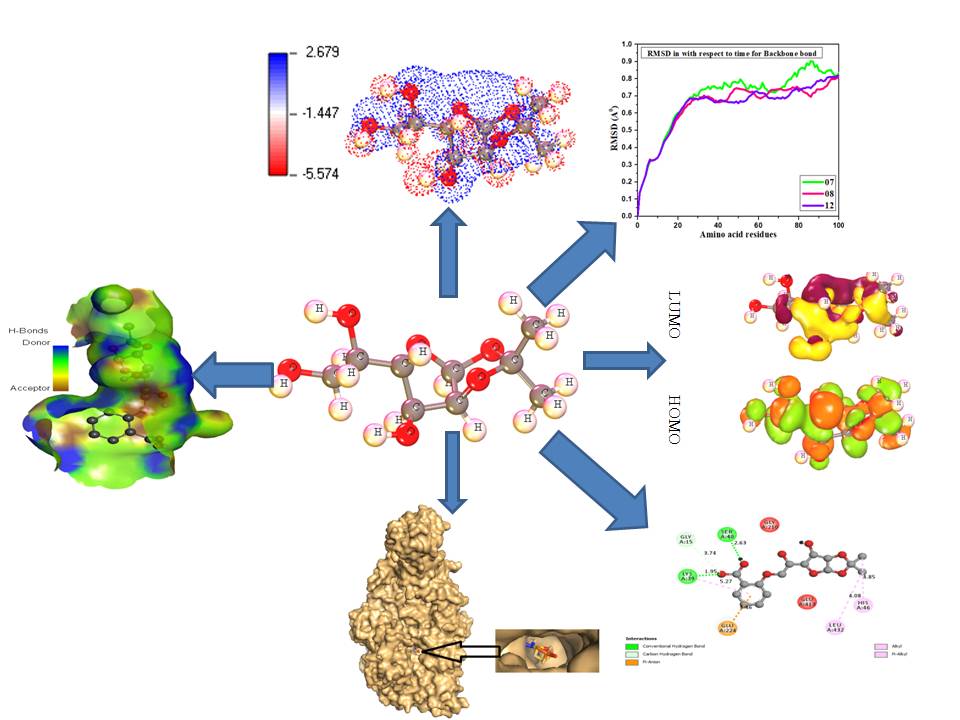
B: Black fungus is the foremost life-threatening disease during the SARS-CoV-2 affected patients and spreading quickly in the region of the subcontinent of India although there was no prescribed proper medication. As the D-glucofuranose and its derivatives are reported to show strong antifungal activity, this study has been designed with them for their computational investigation. Firstly, the overall prediction of activity spectra for substances (PASS) value illustrates a good probability to be active (Pa) and probability to be inactive (Pi) value. Next, pharmacokinetics parameters including drug-likeness and Lipinski's rules, absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) parameters, and overall quantum calculation of computational approaches by Density Functional Theory (DFT) have gradually been performed to analyze quantum calculations. After the analysis of docking score, it is found at -9.4 kcal/mol, -7.5 kcal/mol, -7.8 kcal/mol, -8.5 kcal/mol against the strain of black fungus protein strains Mycolicibacterium smegmatis, Mucor lusitanicus, Rhizomucor mieh, and white fungus protein Candida Auris, Aspergillus luchuensis and Candida albicans. Next, the molecular dynamics of docked complexes have been performed to check their stability in biological systems with water ranging 100 ns calculating the Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) and Root Mean Square Fluctuation (RMSF) where the minimum RMSD and RMSF value indicated the higher stable configuration of docked complexes. These compounds have perfectly matched all the pharmacokinetics criteria to be a good drug candidate against both black and white fungus, and they are non-carcinogenic, low solubility, low toxic for both aquatic and non-aquatic. In addition, the quantum calculation using DFT conveys the strongest support and information about their chemical stability and biological significance. Finally, it could be concluded that the carboxylic group and methyl group in the benzene ring causes higher binding affinity against black and white fungus protein strain through the formation of hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.116.2108.2188 Keywords DFT PASS predication docking molecular dynamics ADMET DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Novel naphthalene-1,5-diamine containing urea/thiourea derivatives – Promising antimicrobial agents
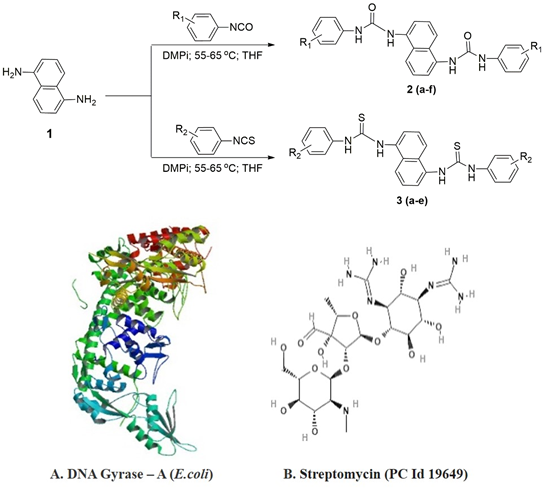
A pioneering class of urea/thiourea derivatives of naphthalene-1,5-diamine was synthesized in excellent yields (89-96%) by one-pot procedure via treatments with phenyl isocyanates or phenyl isothiocyanates. All the constructed derivatives were evaluated for antimicrobial activity using in vitro and in silico methods. The obtained results showed that, all the titled compounds displayed the most significant antibacterial activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria namely B. substilis, B. sphaerius, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, K. aerogenes, C. violaceum and antifungal activity against A. Niger, C. tropicum, R. oryzae, F. moniliforme and C. lunata when compared with the standard drugs such as ciproflaxacin and clotrimazole. Among all, the compounds 2c, 2e and 3d, 3e displayed higher content of antimicrobial activity akin to the rest of the compounds due to the presence of fluoro substitution on aromatic ring. Furthermore, molecular docking studies provided support to the in vitro studies. Four of the synthesized compounds, 4-fluorophenyl, 3-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-chlorophenyl exhibited significant binding modes and were the best target ligands as they fitted more stably into the DNA gyrase binding pocket. Henceforth, it is suggested that, the fabricated urea/thiourea derivatives of naphthalene-1,5-diamine would stand as the prosperous antimicrobial drug candidates for further studies.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.115.2111.2257 Keywords Naphthalene-1,5-diamine antibacterial Activity DNA Gyrases urea/thiourea derivatives DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Design, synthesis and antimicrobial screening of some new thienopyrimidines
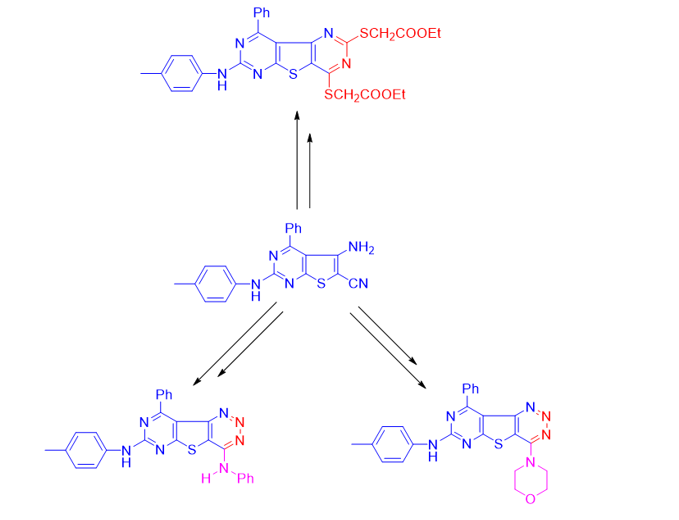
Heterocyclic compounds play an important role in our life due to their biological importance in the struggle of microorganisms. Herein, a series of novel hybrid compounds of thienopyrimidine with triazine and pyrimidine scaffolds were synthesized starting from difunctionalized compound 5-amino-4-phenyl-2-(p-tolylamino)thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carbonitrile (1). Moreover, the diazotization of compound 1 with sodium nitrite in an acidic medium gave the chloro-triazine compound 2 which was subjected to the nucleophilic substitution of chlorine atom with different nucleophiles delivered compounds 3a-5c. Furthermore, the reaction of compound 1 with carbon disulfide led to the formation of dithione derivative 6 which was alkylated with ethyl chloroacetate to give compound 7, on the other hand, the reaction of compound 1 with phenyl isothiocyanate produced 4-imino-3,9-diphenyl-7-(p-tolylamino)-3,4-dihydropyrimido[4',5':4,5]thieno [2,3-d]pyrimidine-2(1H)-thione (8), while acylation of the amino group in compound 1 with acetic anhydride gave compound 9. All synthesized compounds were characterized by elemental and spectral analysis techniques (IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, Mass spectroscopy). Furthermore, the synthesized compounds were tested for their antimicrobial activity against different strains of bacteria and fungi, and the results obtained showed good to moderate activity with almost all the strains.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.114.2109.2214 Keywords Thienopyrimidne synthesis antibacterial antifungal triazine. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Effect of reactor configurations on the Suzuki cross-coupling reaction using a carrageenan-based RhCl3 catalyst
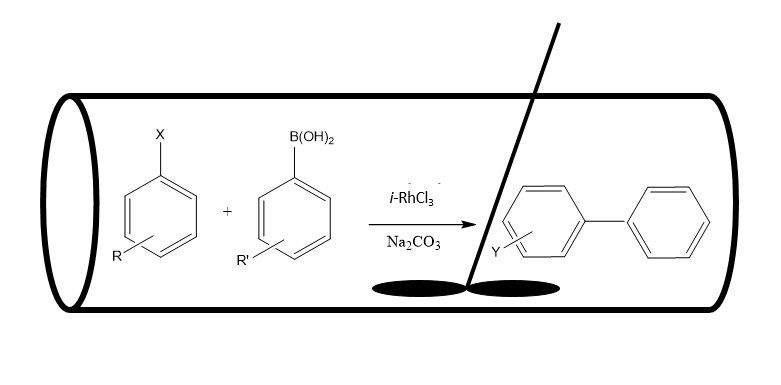
RhCl3 was heterogenized into an iota-carrageenan polysaccharide support, and the effect of various reactor configurations on catalyst performance in a Suzuki cross-coupling reaction was studied. It was found that performing the reaction in a high-volume, well-agitated, mechanically mixed high volume reactor, or circulating the reaction mixture through the catalyst, which was placed in a tabular reactor, yielded higher product yields in comparison to magnetically stirring or shaking. In addition, the catalyst was also successfully recycled in all the systems. Moreover, the reaction solution in each reactor configuration did not contain any traces of rhodium, while elemental composition of the iota-based rhodium catalyst, ἰ-RhCl3, following the first and the second cycle in the glass tubular reactor was similar to the fresh ἰ-RhCl3 catalyst, demonstrating the high xerogel stability.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.113.2108.2189 Keywords Heterogeneous catalysis polysaccharides rhodium Suzuki cross-coupling DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.