Records of Natural Products
Year: 2019 Volume: 13 Issue:3 May-June
1) Triterpenoids from Acokanthera schimperi in Ethiopia

The studies on the leaves of Acokanthera schimperi, a traditional herb of Ethiopia, afforded eight triterpenoids, including a new triterpenoid ester, lupan-20-ol-3(b)-yl 3-hydroxyoctadecanoate (1), along with seven known triterpenoids, lupeol (2), 28-nor-urs-12-ene-3b,17b-diol (3), ursolic aldehyde (4), 3b-hydroxy-oleana-11,13(18)-dien-28-oic acid (5), alagidiol (6), oleanolic acid (7) and ursolic acid lactone (8). Their structures were determined by spectroscopic methods including 2D NMR techniques and X-ray diffraction analysis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.94.18.07.324 Keywords Acokanthera schimperi triterpenoids Ethiopian medicinal plants spectroscopic analyses X-ray diffraction. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Cytotoxic Activity-Guided Isolation Studies on Fumana procumbens (Dunal) Gren. & Godr.
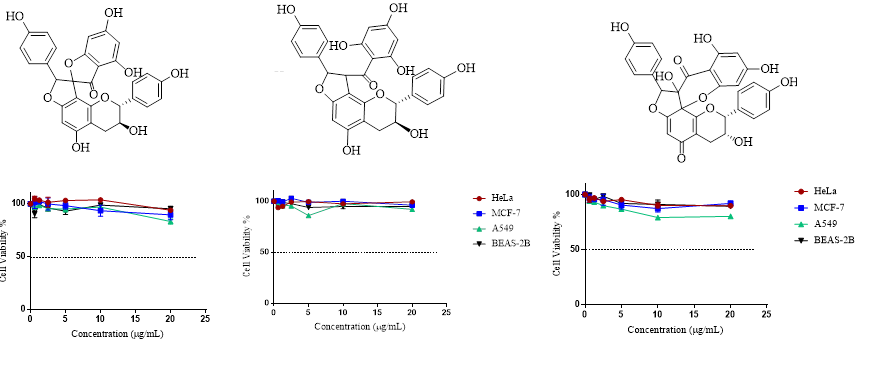
Among the plant secondary metabolites much attention has been given to naturally occurring phenolic compounds as attractive candidates for cancer treatment and prevention. Fumana procumbens (Dunal) Gren. & Godr (Cistaceae) is a perennial herb, distributed in inner and southwest Anatolia, Turkey. F. procumbens was shown to be rich in phenolic constituents especially flavonoids and biflavonoids which are known for their antioxidant and anticarcinogenic effects. Thus, this study aims to investigate the anticancer activity of F. procumbens extracts, fractions and pure compounds by MTT test against HeLa, MCF-7, and A549 as well as BEAS-2B cell lines for determining selectivity. Bioactivity-guided phytochemical investigation on Fumana procumbens (Dunal) Gren. & Godr. led to the isolation and identification of three biflavonoids: genkwanol A, dihydrodaphnodorin B and stelleranol. The structures were elucidated by extensive 1D- and 2D-NMR spectroscopic analysis in combination with MS experiments. This is the first report on the isolation of genkwanol A and stelleranol from the genus Fumana and from the family Cistaceae. As a result, no individual cytotoxic activity was obtained for biflavonoid compounds. However, the former fractions FrC and FrD as well as MeOH and n-BuOH extracts exerted moderate and significant cytotoxic activity which suggested a possible synergistic effect.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.98.18.07.331 Keywords Anticancer activity Cistaceae Fumana procumbens cell viability cytotoxicity MTT test. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Two New Lipodepsipeptides from the Endophytic Fungus Colletotrichum aotearoa Y41
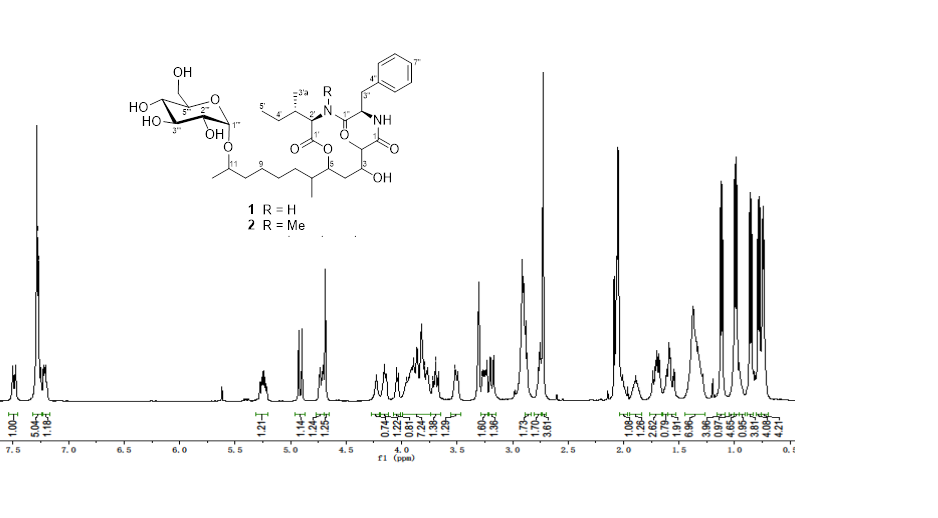
Two closely related lipodepsipeptides, with the same 12-membered oxodepsipeptide ring system, aotearolides A (1) and B (2), together with 1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde (3) and 2-(1H-indol-3-yl)acetic acid (4) were isolated from the endophytic fungal isolate Colletotrichum aotearoa Y41 of Huperzia serrata. The structures were elucidated on the basis of their high-resolution ESI/MS, 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic data.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.90.18.05.298 Keywords Lipodepsipeptide aotearolides A and B Colletotrichum aotearoa Huperzia serrata DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Phytochemical Profiles and Antioxidant Activity of Salvia species from Southern Italy
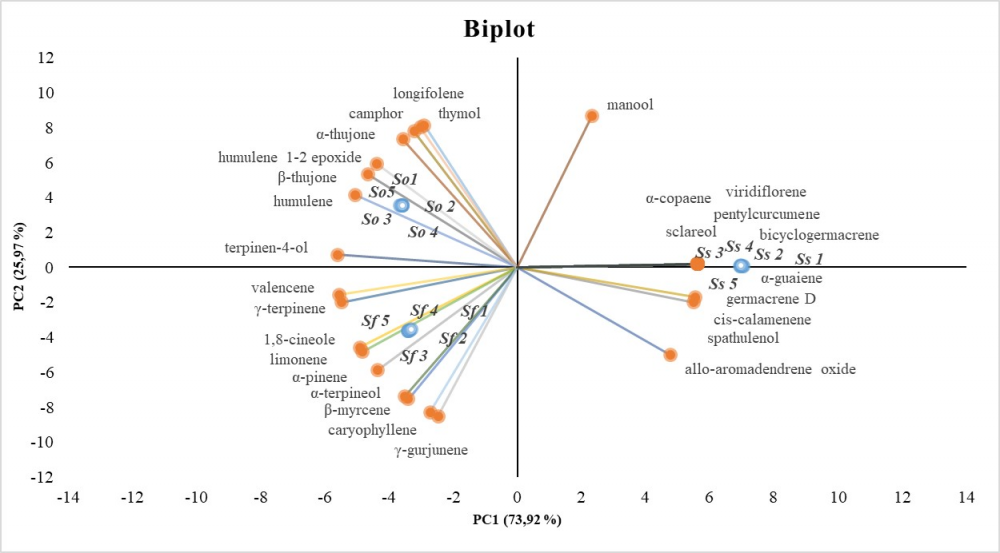
The purpose of this research was to investigate phytochemical profiles and antioxidant activity in four Salvia species growing in Salento (Southern Italy). The hydrodistillation products obtained from the aerial parts of Salvia clandestina, Salvia fruticosa, Salvia officinalis and Salvia sclarea were characterized by GC–MS and 50 compounds were detected. With the exception of S. clandestina, that did not produce essential oils, the other species shared different amounts of monoterpenes oxygenated (camphor 2.13%-9.16%) and sesquiterpenes hydrocarbons (caryophyllene 4.65%-18.33%; humulene 1.87%-12.39%). The phenolic profiling, analyzed by HPLC ESI/MS-TOF, highlights that S. clandestina is a rich source of danshensu (4.76 mg/g DW) while S. sclarea of rosmarinic acid (15.57 mg/g DW). Mutivariate statistical analysis (PCA) of hitherto studied Salvia phenols have shown similarities in profiles between S. fruticosa and S. officinalis, while S. clandestina and S. sclarea showed distinctive profiles. Otherwise, essential oil profiles analysed by PCA are clearly different among the three productive species. The extracts from collected plants were found to be effective antioxidant in three different in vitro assays (DPPH, ABTS, FRAP and Superoxide anion scavenging activity). Thus, they can be proposed as natural ingredients in functional foods, herbal medicines or as sources of bioactive molecules.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.96.18.07.119 Keywords Salvia clandestina L. Salvia fruticosa Mill. Salvia officinalis L. Salvia sclarea L. essential oils phenolic compounds. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Inhibitory Effects of Metabolites Isolated from Artemisia dracunculus L. Against the Human Carbonic Anhydrase I (hCA I) and II (hCA II)
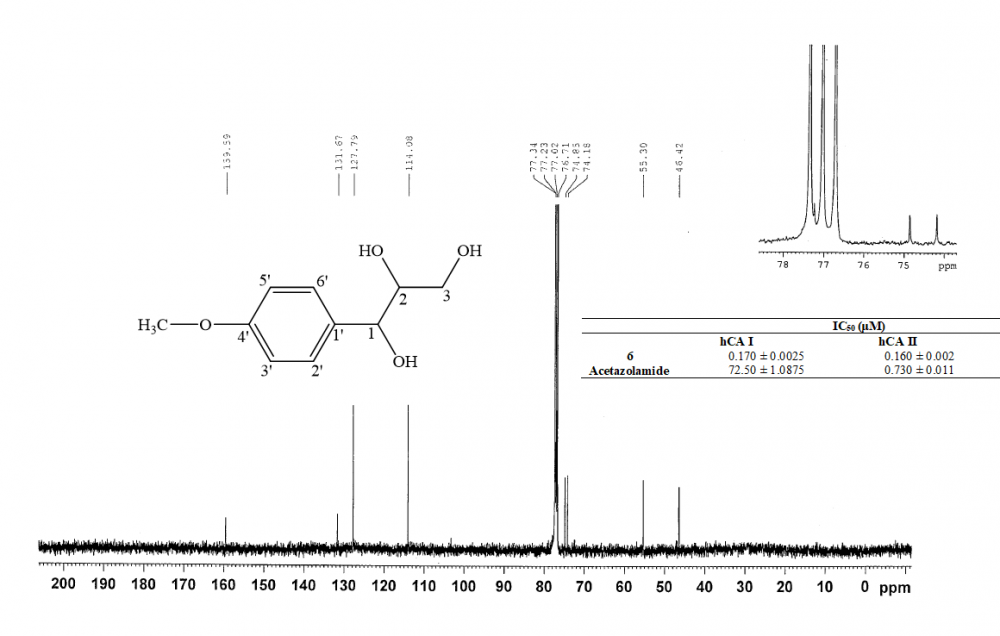
Tarragon or Dragon's-wort (Artemisia dracunculus L.) is widely used as spice and in traditional medicine in various regions of the world. Inhibitory effects of the n-hexane, dichloromethane, ethanol and methanol extracts of the leaves of tarragon on the human carbonic anhydrase (hCA) I and II enzymes were investigated. Dichloromethane extract exhibited the strongest activity with lowest IC50 value (0.020 and 0.031 μg/mL, respectively). The chromatographic studies on the dichloromethane extract of tarragon allowed the isolation of six known strong inhibitors of hCA isozymes as trans-anethole, stigmasterol, herniarin, (2E,4E)-N-isobutylundeca-2,4-dien-8,10-diynamide, (2E,4E)-1-(piperidin-1-yl)undeca-2,4-diene-8,10-diyn-1-one and 1-(4'-methoxyphenyl)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropane. The compound, 1-(4'-methoxyphenyl)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropane was isolated from tarragon for the first time in this study. Among the tested compounds, 1-(4'-methoxyphenyl)-1,2,3-trihydroxypropane showed the highest inhibitiory impact on both hCA isozymes. Also its IC50 values were found lower than positive control, acetazolamide.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.102.18.07.329 Keywords Artemisia dracunculus L. 1-(4'-methoxyphenyl)-1 2 3-trihydroxypropane enzyme inhibition hCA I hCA II. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Bioactivity-Guided Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory Principles from Cistus parviflorus Lam.
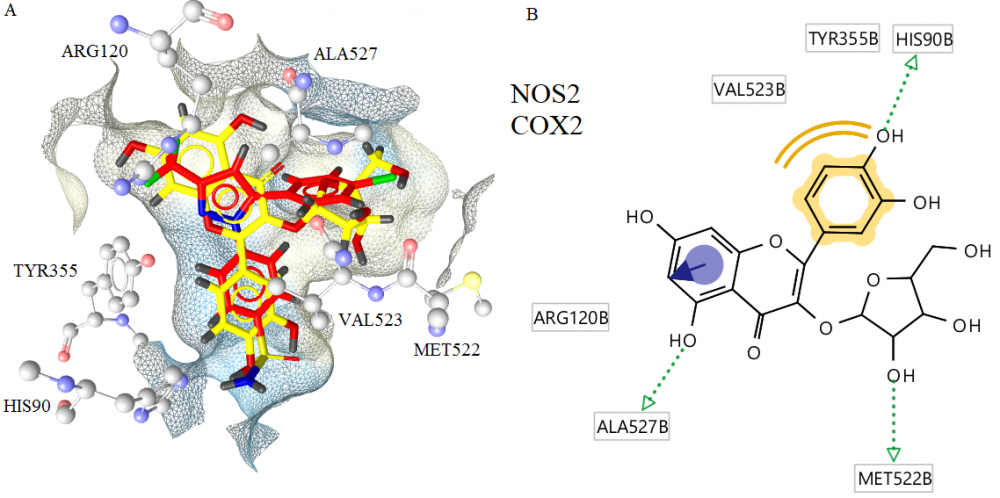
Bioactivity-guided fractionation and purification of Cistus parviflorus led to the isolation of two flavan-3-ol derivatives; gallocatechin (1) and epigallocatechin (2) and two flavonoid glycosides; avicularin (3) trans-tiliroside (4). The structures of the compounds were elucidated on the basis of NMR and ESIMS data. All compounds were isolated from C. parviflorus for the first time. Compounds 2 and 3 exhibited anti-inflammatory activity through decreasing the NOS2 and COX2 levels on LPS+IFN-γ treated RAW 264.7 cells. Molecular docking studies of avicularin, the most potent compound, were carried out in the active sites of NOS2 and COX2 to predict the most plausible binding modes and support the experimental data.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.106.18.09.883 Keywords Cistaceae; inflammation; flavonoids; structure elucidation; avicularin; molecular modelling DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Composition of the Essential Oils of Two Endemic Helichrysum Species in Turkey
The aerial parts of Helichrysum noeanum Boiss. and H. chionophilum Boiss. et Balansa were hydrodistilled for 3 h using a Clevenger-type apparatus. The essential oils were analyzed by GC-FID and GC-MS, simultaneously. The main constituents were identified as hexadecanoic acid (25.3%), dodecanoic acid (17.8%), tetradecanoic acid (13.7%), and decanoic acid (4.2%) for H. noeanum. Decanoic acid (18.7%), tetradecanoic acid (16.9%), dodecanoic acid (13.8%), hexadecanoic acid (12.2%) and hexahydrofarnesyl acetone (3.2%) were found to be the major compounds for H. chionophilum. Several reports have been encountered in the literature dealing with the oil composition of several Helichrysum species. To the best of our knowledge, the essential oil of H. chionophilum has not previously been investigated.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.93.18.06.113 Keywords Helichrysum noeanum H. chionophilum essential oil GC GC-MS. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) New Diterpenes Isolated from the Colombian Caribbean Soft Coral Pseudoplexaura flagellosa and Their Cytotoxic Properties
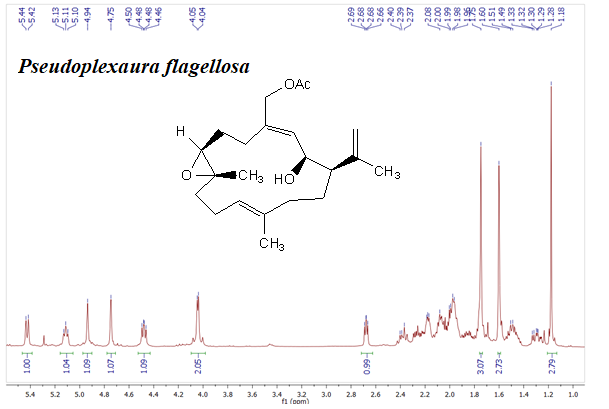
Studies about secondary metabolites isolated from soft corals around the world have proven the potential of these organism as producers of compounds with a potent cytotoxic activity. In this work, we obtained the extract of Pseudoplexaura flagellosa collected in Santa Marta, Colombia, the cytotoxic activity of this extract, fractions and compounds was established against SiHa (ATCC® HTB-35™), MDA-MB-231 (ATCC® HTB26™), A549 (ATCC® CRM-CCL-185™), PC3 (ATCC® CRL1435), and L929 (ATCC® CCL1™) cell lines. The results showed that the extract of soft coral P. flagellosa has cytotoxic activity with an IC50 of 35.4, 72.3, 49.8 and 40.5 μg/mL against SiHa, A549, PC3 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines, respectively. Thus, this extract was repeatedly subjected to different chromatographic columns and final purification of these fractions afforded pure compounds 1 – 4, which were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR experiments including 1H, 13C, COSY, HSQC, HMBC and NOESY, and HRESIMS. In addition, Mosher method was used to establish the stereochemistry of compound 2 and chemical interconversion allow establishing the stereochemistry of compound 1. These results let to conclude that compound 2 is a new stereoisomers of acetylated asperdiol previously reported on literature. Additionally, three analogues 5, 6, and 7 were synthesized from compound 1 and the cytotoxic activity of all compounds was evaluated using doxorubicin as positive control. The results showed that 6 (IC50 of 19.3, 23.7, 13.4 and 18.7 μg/mL against SiHa, A549, PC3 and MDA-MB-231, respectively) was the most active compound against all the cancer cell lines.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.100.18.07.325.1 Keywords Pseudoplexaura flagellosa cytotoxic activity absolute stereochemistry stereoisomers soft corals DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Curcuma kwangsiensis Extracts Produced Antioxidant Effects Against Injury Induced by H2O2 on PC12 Cells
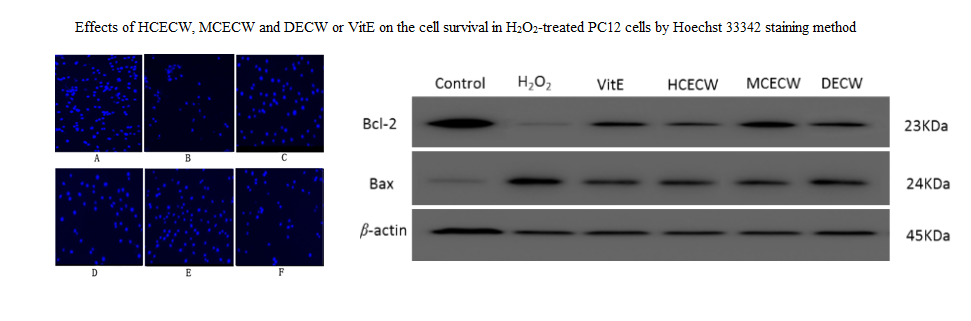
The radix of Curcuma kwangsiensis S. G. Lee & C. F. Liang (Zingiberaceae) is a traditional medicine in China, and used for treating qi stagnation and blood stasis. Previous chemical study showed it is rich in sesquiterpenoids and diarylheptanoids, similar to those in Curcuma longa L., which showed obviously protective effects against oxidative damage. However, the antioxidant and underlying mechanism of C. kwangsiensis has not been studied yet. In current study, the antioxidant activities of C. kwangsiensis extracts (ECWs), including 95 % EtOH extract (HCECW), 75 % EtOH extract (MCECW), methanol extract (MECW), dichloromethane extract (DECW) and petroleum ether extract (PECW), and their possible mechanisms, were studied on the model of H2O2-induced PC12 cell damage in vitro. The results showed different concentrations (1, 10, 50 µg/mL) of HCECW, MCECW and DECW could increase damaged PC12 cell viability significantly. In the extract-treated groups, the release rate of LDH significantly decreased, while SOD, CAT, and GSH markedly increased. In the meantime, the intracellular Ca2+ and cell apoptosis decreased significantly, while MMP increased and apoptosis morphology was clearly improved. Compared with the model group, they produced effects on up-regulating of Bcl-2, down-regulating of Bax and Caspase-3. Further, the chemical analysis of those five extracts by UPLC-DAD-Q-TOF-MS showed their major constituents were sesquiterpenoids and diarylheptanoids, indicating both of them presented in ECWs are antioxidant substances in this plant. This study provided an experimental basis for the future development of antioxidants from the genus Curcuma.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.104.18.08.342 Keywords Curcuma kwangsiensis antioxidant effect PC12 cell oxidative injury chemical analysi DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Chemical Composition and Anti-Candida and Anti- Trypanosoma cruzi Activities of Essential Oils from the Rhizomes and Leaves of Brazilian Species of Renealmia L. fil.
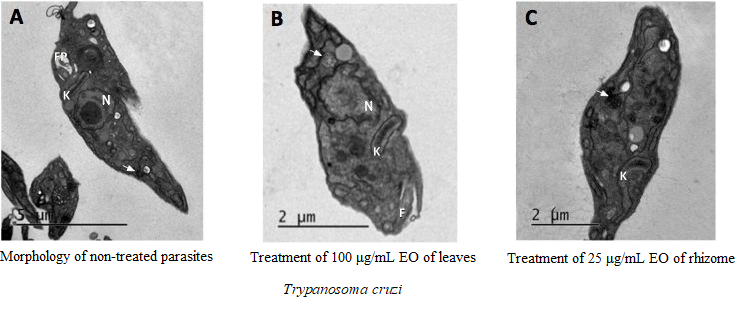
This work aimed to determine the chemical composition of essential oils from rhizomes and leaves of Renealmia chrysotricha Petersen, R. breviscapa Poepp. & Endl. and R. nicolaioides Loes., and to evaluate the biological activities of these oils on three Candida species and the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. The rhizomes and leaves were collected in the Atlantic and Amazon rainforests. Essential oils were isolated and characterized by gas chromatography. Βeta-Caryophyllene was found to be the most predominant compound in the essential oils of rhizomes and leaves of R. breviscapa, and the rhizomes of R. nicolaioides, whereas (E)-nerolidol was the most abundant compound in the oils of leaves of R. nicolaioides. In R. chrysotricha, α-terpineol, coronarin-E and 1,8-cineole were found to be the most predominant compounds in the essential oils of rhizomes, whereas cis-3-hexenol was predominant in the leaves. The tested oils did not inhibit C. albicans growth at 1000 µg/mL, whereas leaf oils from R. chrysotricha and R. nicolaioides inhibited the growth of C. buinensis and C. tropicalis by about 50%. Essential oils from the rhizomes and leaves of R. chrysotricha exhibited efficient antiparasitic activity against Trypanosoma cruzi. Damage to T. cruzi epimastigotes was confirmed by LM and TEM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.105.18.08.125 Keywords Zingiberaceae rhizomes leaves terpenoids anticandidal activity antiparasitic activity. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Essential Oil Constituents from the Leaves of Anoectochilus setaceus, Codonopsis javanica and Aristolochia kwangsiensis from Vietnam
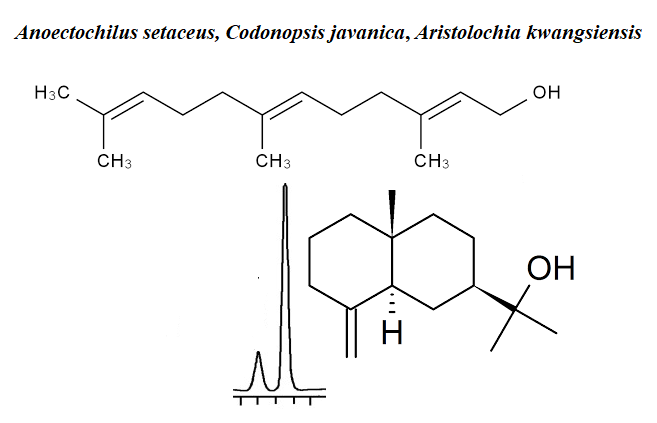
There are very few reports on the phytochemistry of Anoectochilus setaceus Blume, Codonopsis javanica (Blume) Hook. f. and Aristolochia kwangsiensis Chun & F.C.How ex S.Yun Liang species in the literature. Here we present essential oil compositions of the three endemic plants from Vietnam. The analysis of the chemical constituents of the hydrodistilled essential oils was achieved by using gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The essential oils of A. setaceus, C. javanica and A. kwangsiensis afforded very low oil yields: 0.12%, 0.31% and 0.10% (v/w), respectively, calculated on a dry weight basis. The result indicated that the major components of the leaf oil of A. setaceus consist mainly of α-cadinol (17.1%), (E,E)-farnesol (14.0%) and terpinen-4-ol (11.0%) while β-pinene (20.8%) and α-pinene (15.4%) were the main compounds identified in C. javanica. However, the significant compounds of A. kwangsiensis were sabinene (34.8%), β-caryophyllene (8.8%) and terpinen-4-ol (8.6%). To the best of our knowledge this is the first report on the essential oil compositions of these species.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.103.18.08.124 Keywords Anoectochilus setaceus Codonopsis javanica Aristolochia kwangsiensis essential oil terpenoids. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.