Records of Natural Products
Year: 2020 Volume: 14 Issue:4 July-August
1) 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics of Clinacanthus nutans Leaves Extracts in Correlation with Their Anti-neuroinflammation Towards LPS-Induced BV2 Cells

The metabolomics approach successfully explained the possible neuroprotective effect of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau (CN) leaf extracts. Forty-four metabolites were putatively identified via proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR and J-resolved NMR) metabolic profiling of CN leaf extracts in three types of solvents, namely water, 50% ethanol, and ethanol. Metabolite fingerprinting has efficaciously differentiated aqueous between the other two extracts. The variable importance of projection (VIP) showed that 30 metabolites were responsible for the discrimination of the extracts by component 1 in the Partial Least Square (PLS) score plot. The lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced murine microglial of the BV2 cell line successfully exhibited aqueous CN as the closest extract related to the nitrite oxide (NO) inhibitory activity via PLS biplot, with an IC50 value of 336.2 ± 4.7 µg/mL through Griess assay. The cytotoxicity assay also indicated that all CN extracts were non-toxic. Schaftoside, acetate, propionate, alanine, and clinacoside C were identified as the most potential biomarkers in the anti-inflammatory assay. Hence, the aqueous CN extract could be further investigated, particularly relating to the anti-neuroinflammation study.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.159.19.08.1384 Keywords 1H NMR Clinacanthus nutans anti-neuroinflammation BV2 cells DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Novel Hopanoic Acid and Depside from the Lichen Dirinaria applanata
.jpg)
From the extract of lichen Dirinaria applanata, two hopane derivatives including 1b-acetoxy-3b-hydroxy-21a-hopan-29-oic acid (1), hopane-3b, 6b, 21a-triol (2) and a depside namely 2-O¢-methylnordivaricatic acid (3) were isolated and identified by extensive analyzing 1D-NMR, 2D-NMR, HRESI-MS, and FT-IR. Notably, compound 1 and 3 were novel compounds while compound 2 was isolated from this lichen species for the first time.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.161.19.10.1441 Keywords Dirinaria applanata lichen hopan-29-oic acid depside DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Ent-kaurene Diterpenoids from Sideritis lycia with Antiviral and Cytotoxic Activities

The genus Sideritis (Lamiaceae) is represented by 45 species (54 taxa) in Anatolia with high endemism ratio (74%), and Turkey is one of the gene centers of the genus along with Spain. Acetone extract of the aerial parts of Sideritis lycia afforded eight known ent-kaurene diterpenoids, structures of which have been identified as linearol, isolinearol, isosidol, sidol, siderol, sideridiol, 7-epi-candicandiol and foliol through 1H NMR, 13C NMR and mass spectroscopic analyses. Cytotoxic and antiviral activities of the acetone extract, linearol, sidol and isosidol were investigated together with insecticidal activity of species. antiviral index of linearol, isosidol and acetone extract of S. lycia were determined as 2.31, 2.01 and 2.58, respectively, except sidol. 7-Epi-candicandiol was found to be the most active diterpene against a series of cancer cell lines with ED50 values; KB (13.3 µg/mL), COL-2 (11.8 mg/mL), LU1 (17.9 mg/mL), LNCaP (14.9 mg/mL) and A2780 (9.0 mg/mL). Activity results of this study indicated that ent-kaurane diterpenes have potential to be considered as antiviral and cytotoxic lead compounds.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.163.19.08.1373 Keywords Sideritis lycia diterpenoid NMR and mass spectroscopy antiviral cytotoxic activity insecticidal activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Bioactive Constituents from the Rhizomes of Sansevieria cylindrica

Analysis of the MeOH extract of rhizomes of Sansevieria cylindrica using repeated silica gel and reversed-phase chromatographic separations led to the isolation of ten phenolic compounds (1-10) belonging to five different classes. Their structures, including the absolute configuration, were identified by NMR and CD spectra analysis. The antiradical activity of isolated compounds was tested using the DPPH scavenging method. The cytotoxic effects were assayed against a Hela cell line. Compounds 2-10 have been isolated from a Sansevieria species from the first time and compounds 4-10 have been isolated from species of the Asparagaceae family for the first time. The structure of a homoisoflavanone isolated from S. roxburghiana has been corrected.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.160.19.10.1440 Keywords Sansevieria cylindrica Asparagaceae homoisoflavanone cynnamoyl octopamine tyramine derivatives antiradical activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Chemical Composition and Anticholinesterase Activity of the Essential Oil from the Ecuadorian Plant Salvia pichinchensis Benth
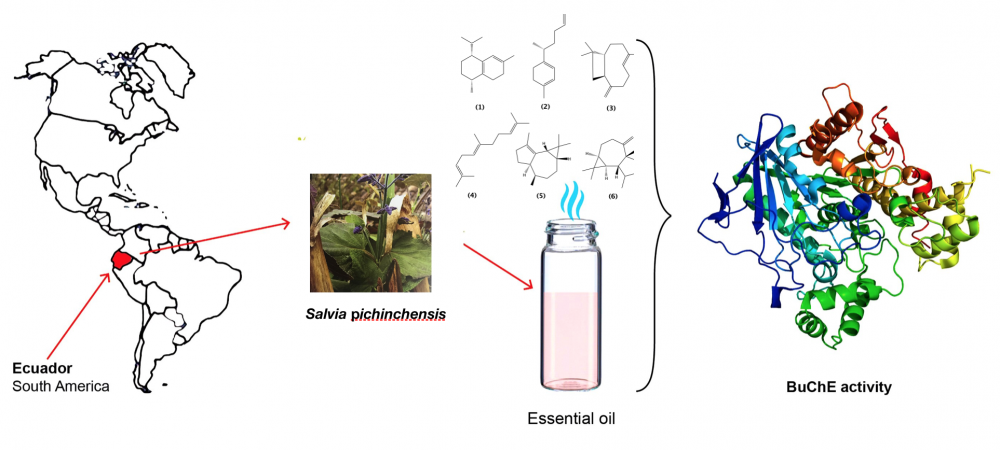
Salvia pichinchensis Benth was collected in the South of Ecuador and the essential oil (EO) was distilled from aerial parts and analyzed by GC-MS and GC-FID. The physical properties, chemical composition, and cholinesterase inhibitory activity were determined. Six major components, all sesquiterpenes, were identified: cis-cadina-1(6),4-diene (17.11%) (1),γ-curcumene (13.75%) (2), (E)-caryophyllene (12.58%) (3), (E,E)-α-farnesene (10.00%) (4), α-gurjunene (9.46%) (5) and allo-aromadendrene (6.96%) (6). The EO showed an interesting selective inhibitory activity against the enzyme butyrylcholinesterase (50.70 μg/mL) and only low inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (117.60 μg/mL). The chemical composition and butyrylcholinesterase activity of the EO of S. pichinchensis Benth was reported for first time.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.164.19.07.1342 Keywords Salvia pichinchensis essential oil GC-MS analysis in vitro ChE inhibitory activity cis-cadina-1(6),4-diene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Cytotoxic Lathyrane Diterpenoids from the Roots of Euphorbia fischeriana
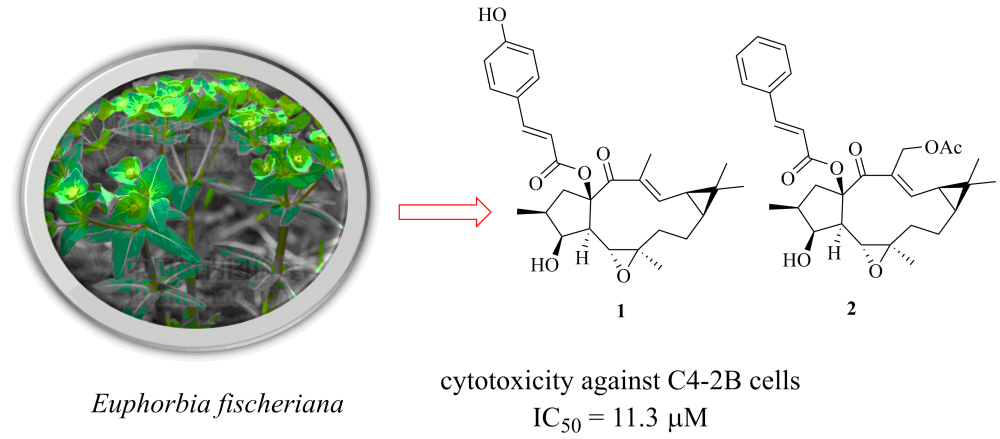
Two new lathyrane diterpenoids, euphofischers A and B (1 and 2), along with three known analogues (3-5), were isolated from the roots of Euphorbia fischeriana. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic analysis. Euphofischer A (1) represents rare example of a lathyrane diterpenoid featuring a 15-p-coumaroyl moiety. All compounds were screened for their cytotoxicity against three cancer cell lines (C4-2B, C42B/ENZR, and MDA-MB-231), and compound 1 exhibited significant cytotoxicity against C4-2B cell line, with an IC50 value of 11.3 mM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.167.19.12.1496 Keywords Euphorbia fischeriana Euphorbiaceae lathyrane diterpenoid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) 3-O-Formyl -27-Hydroxyfusidic Acid: A New Metabolite of Fusidic Acid by Cunninghamella echinulata

Minor metabolites of Fusidic acid (1) using the fungus Cunninghamella echinulata NRRL 1382 were investigated for discovering previously unstudied reactions. An unprecedented fusidic acid derivative, C-27-hydroxy-3-O-formyl fusidic acid (2) was isolated, and its chemical structure was fully elucidated using various spectroscopic techniques including 1D, 2D NMR and HRESIMS. This is the first report for formylation reaction by C. echinulata.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.168.19.12.1505 Keywords Fusidic acid Cunninghamella echinulata 3-O-Formylation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A New 4,5-Secofurancadinene from the Rhizome of Curcuma kwangsiensis
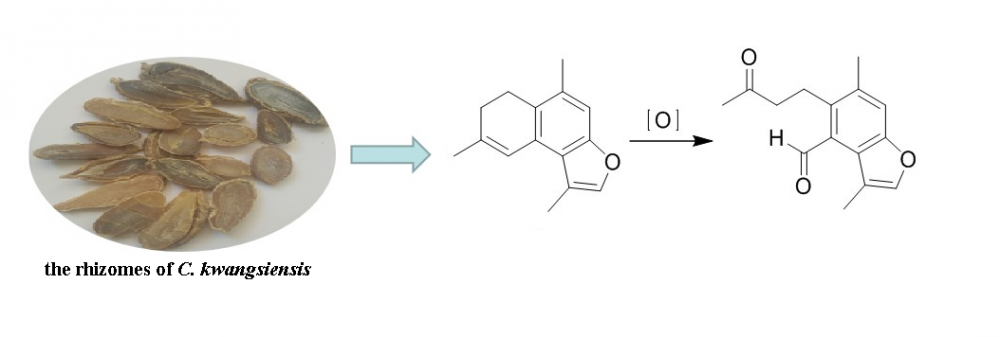
The rhizome of Curcuma kwangsiensis S. G. Lee et C. F. Liang is a Traditional Chinese Medicine indexed in Chinese Pharmacopoeia. A new compound, 4,5-seco-pyrocurzerenone (1), was isolated from the species along with sixteen sesquiterpenoids (2-17). Their structures were elucidated based on the spectroscopic evidence, mainly including NMR and HRESIMS. All the compounds were reported for the first time from this species.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.169.20.01.1520 Keywords Sesquiterpenoid 4,5-secofurancadinene Curcuma kwangsiensis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) A New Oleanane Type Saponin from the Aerial Parts of Elaeocarpus hainanensis

Elaeocarpus hainanensis has been used in the Oriental medicine but there are very few studies on its phytochemical profile. Our ongoing research on chemical constituents from Elaeocarpus plants in Vietnam led to the isolation of a new oleanane-type saponin from the aerial part of E. hainanensis. Its structure was identified as 1α-hydroxy-olean-11-oxo-12-en-3-O-β-L-arabinopyranoside (1) on the basis of extensive chemical and spectroscopic analyses including NMR and MS spectra. The occurence of the unique oleanane-type saponins in E. hainanensis contributed to impact phytochemical profile associated with chemotaxanomy meaning of the title plant.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.160.19.09.1414 Keywords Elaeocarpus hainanensis Elaeocarpaceae oleanane-type saponin 1α-hydroxy-olean-11-oxo-12-en-3-O-β-L-arabinopyranoside DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Two New Compounds from the Deep-Sea-Serived Fungus Aspergillus sp. YPGA8

Chemical examination of a fraction of the EtOAc extract of a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. YPGA8 resulted in the isolation of two new compounds, namely aspertriols A-B (1-2). Compounds 1-2 possess an identical 2,3,4-trihydroxybutoxy moiety, which is rarely found in natural products. Their structures were determined by extensive analyses of spectroscopic data (1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS). The bioassay study revealed that compounds 1 and 2 were inactive toward a-glucosidase.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.162.19.11.1487 Keywords marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. YPGA8 aspertriols A-B isolation structure identification DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.