Records of Natural Products
Year: 2020 Volume: 14 Issue:6 November-December
1) Overexpression of Global Regulator LaeA Induced Secondary Metabolite Production in Aspergillus versicolor 0312

This experiment investigated the effect of the global regulator laeA on the secondary metabolites of Aspergillus versicolor. The laeA gene was cloned from Aspergillus versicolor 0312 to introduce pSilent I overexpression vector, and the recombinant plasmid was introduced into Aspergillus versicolor 0312 by PEG guided protoplast transformation. Then, the over-expressing strain 0312-laeA was screened and verified by metabolic level and gene level. A new compound versicolor A (1) was obtained by liquid fermentation of the over-expressing strain, together with four known compounds, acetylapoaranotin (2), acetylaranotin (3), diisobutyl phthalate (4) and ergosterol (5). The structure of the new compound was elucidated by using various spectroscopic techniques inclusive of HRESIMS, 1D- and 2D-NMR data. Compound 1 showed cytotoxicity against MOLT-4 cell lines with IC50 values of 29.6 µM, while 2 showed significant cytotoxicities against MOLT-4, MCF-7, and CaCo-2 cell lines with IC50 values of 7.8, 19.9, and 15.9 µM, respectively. The results further supported that laeA is a global regulator that could up-regulate and/or activate cryptic gene clusters to produce new secondary metabolites. This study provides an important basis for exploring the mechanism of laeA gene on the secondary metabolites of Aspergillus versicolor.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.183.20.03.1593 Keywords Natural products Aspergillus versicolor LaeA biosynthetic gene clusters secondary metabolites DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Protective Effects of Origanum onites Essential Oil in the Methotrexate-Induced Rat Model: Role on Apoptosis and Hepatoxicity
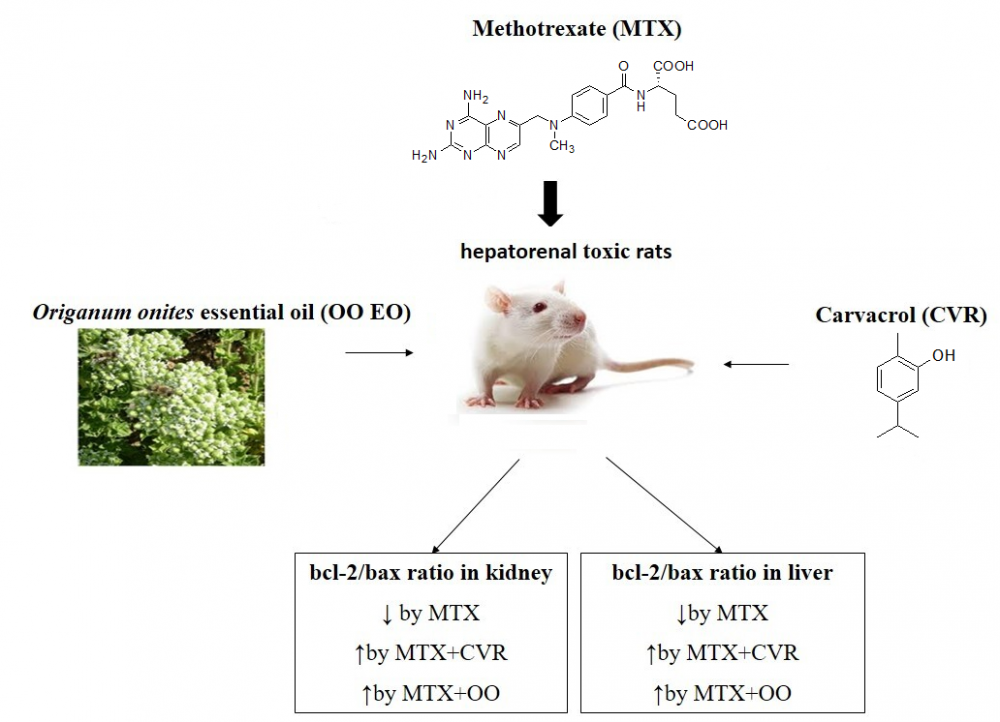
Methotrexate (MTX) is an effective cytotoxic agent which is used to treat malignancies and inflammatory diseases. Origanum onites (O. onites) is found throughout the Eastern Mediterranean region and has been used in traditional medicine. The essential oils (EOs) of O. onites rich in highly bioactive phytochemicals such as carvacrol (CVR) and has antiviral, antioxidant, anticancer and proapoptotic properties. The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effects of CVR and O. onites-EO treatment in MTX-induced hepatorenal toxic rats' liver and kidney tissues. The bcl-2/bax ratio, glutathione (GSH) level, malondialdehyde (MDA) level, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity of liver and kidney tissues were evaluated in the MTX-induced rat model. Results showed that the administration of CVR or O. onites-EO significantly increased bcl-2/bax expression and GSH levels as well as reduced MDA level and MPO activity in the kidney and liver tissues of MTX-induced rat model. In conclusion, our results suggest that O. onites-EO and CVR have protective effect in MTX-induced hepatorenal toxic rats' liver and kidney tissues by decreasing oxidative stress and apoptosis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.186.20.04.1631 Keywords Methotrexate Origanum onites essential oil hepatorenal toxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) A New Lignan Glycoside from the Roots of Silene tatarinowii Regel
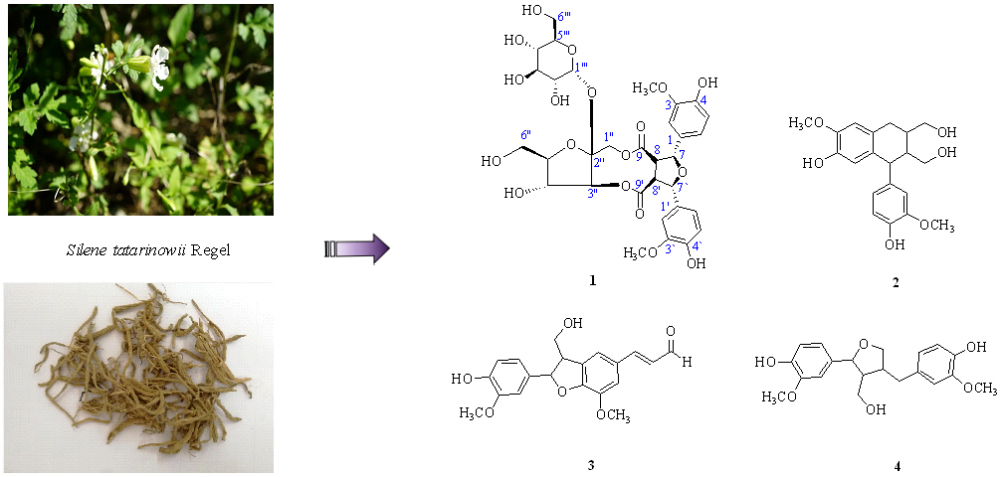
A new lignan glycoside, siletatoside A (1), and three known lignans, (+)-isolariciresinol (2), balanophonin (3), and (+)-lariciresinol (4), were isolated from the roots of Silene tatarinowii Regel. Compounds 2–4 were isolated from the Silene genus for the first time. Their structures were determined based on physicochemical properties and spectroscopic methods. The structure of siletatoside A was elucidated for the first time. The cytotoxicity of 1–4 was evaluated in vitro in human HCT116, HT29, A549, and H1299 tumor cell lines. These compounds displayed weak cytotoxicity in the human cancer cell lines.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.187.20.01.1529 Keywords Silene tatarinowii lignan siletatoside A cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Antioxidants and α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Lactuca serriola L.
.jpg)
Our main objective in the present study was to search for bioactive compounds of potential antidiabetic and antioxidant activities from the methanol extract of Lactuca serriola L. aerial parts for the prevention and treatment of diabetes. Phytochemical investigation allowed the isolation of 17 known compounds identified based on various spectroscopic techniques as lupeol (1), β-sitosterol (2), taraxast-20-ene-3β,20-diol (3), glycerol monopalmitate (4) (2S,3S,4R,2`R,14E)-2-(2`-hydroxytetracosanoylamino)-14-octadecene-1,3,4-triol (5), lactucopicrin (6), daucosterol (7), (E)-p-coumaric acid (8), 11β,13-dihydrolactucin (9), 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (10), protocatechuic acid (11), kaempferol (12), quercetin (13), lactuside A (14), luteolin-7-O-β-D glucoside (15), lactuside B (16) and cichorioside B (17). The antioxidant activity was evaluated using ABTS, DPPH radical scavenging assays and FRAP assay. The ethyl acetate fraction showed remarkable α-glucosidase inhibitory activity (IC50, 9.16±0.17 µg/mL) and antioxidant activity among the tested fractions. The in vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory assay is reported in this study for the first time for L. serriola L. The results strongly suggest that L. serriola L. can be used as a potential good natural remedy targeting oxidative stress-related diabetes mellitus.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.189.2005.1647 Keywords Asteraceae Lactuca serriola antioxidant α-glucosidase inhibitors DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Two New Bibenzyl Compounds from Dendrobium lindleyi
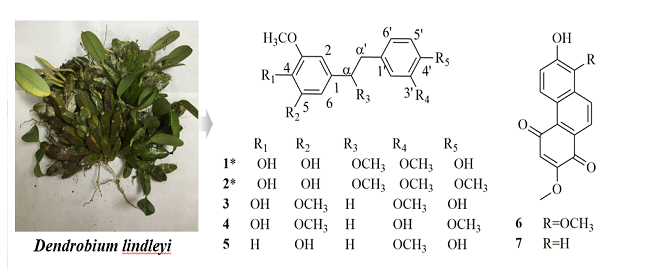
Two new bibenzyl compounds 4,4',5-trihydroxy-3,3',α-trimethoxybibenzyl (1) and 4,5-dihydroxy-3, 3',4',α-tetramethoxybibenzyl (2), along with seven known compounds (3–9), were isolated from the methanol extract of the whole parts of Dendrobium lindleyi. The chemical structures were established on the basis of spectroscopic analysis including one and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy and comparison with previously reported data.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.181.20.02.1557 Keywords Orchidaceae Dendrobium lindleyi Bibenzyl compound DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) A New Diarylbenzophenone from Selaginella tamariscina

A new diarylbenzophenone, namely selagibenzophenone C (1), along with 1,3-di-p-hydroxyphenyl-4-penten-1-one, (2) and unciflavone E (3) were isolated from Selaginella tamariscina. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic and mass spectrometric analyses, including 1D-, 2D-NMR and HRESIMS. Compound 1 represents the first example of naturally occurring diarylbenzophenone. Compound 2 was firstly isolated from the genus of Selaginella.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.182.20.03.1586 Keywords Selaginella Selaginella tamariscina diarylbenzophenone selagibenzophenone C norlignan DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Aromatic Compounds from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus versicolor

Chemical investigation of the EtOAc extract of a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SZW-5 led to the isolation of one new compound, named aspeverether A (1), and seven known compounds. The structures were determined by extensive analyses of spectroscopic data (1D and 2D NMR, and HRESIMS). Compounds 1 and 3 possessed an unusual 1,3-dimethoxy-2-vinylbenzene moiety, which is rarely found in nature. Compound 6 showed strong inhibitory effect toward a-glucosidase with an IC50 value of 71 mM, being more active than the positive acarbose (210 mM).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.188.20.05.1664 Keywords Aspergillus versicolor aspeverether A structure elucidation marine DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.