Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Volume: 15 Issue:3 May-June
1) Phytochemistry, Pharmacological Potency, and Potential Toxicity of Myoporum spp.
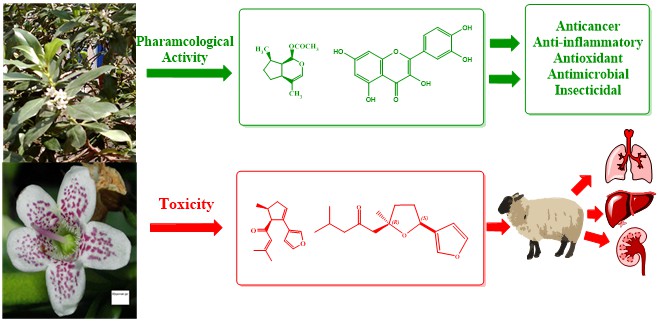
Genus Myoporum family Myoporaceae, includes approximately 32 species of woody small trees or shrubs, most of them are native to Australia and surrounding territories. Only certain species have been thoroughly studied and rich in flavonoids, phenylethanoids, Phenylpropanoids, terpenoids, iridoids, essential oil, and trace alkaloids. The essential oils are characterized by sesquiterpenes type components, either in ketone or alcoholic forms usually combined to a furanoid moiety. Myoporum spp. have been utilized in folk medicine for treatment of various diseases and were used as antidermatitis, antibacterial, antipyretic, anti-pulpitis, antipsychotic, anti-inflammatory, detoxicant, and others. Despite all these benefits, Myoporum spp. must be cautiously employed due to their potential toxicities, which arise from the presence of furanosesquiterpenoid contents, particularly in their essential oil. The toxicity influences liver and can extend to kidney and lung causing injury. The present review aims to explore the phytochemistry, beneficial uses and the toxic potentials of Myoporum spp.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.208.20.10.1833 Keywords Myoporum Myoporaceae secondary metabolites furanosesquiterpenoids biological activities toxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Antiradical Aromatic Constituents from Pleurotus eryngii
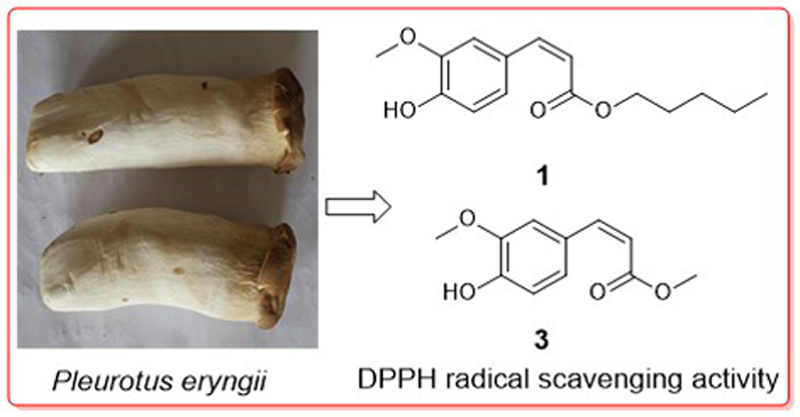
Six aromatic compounds including a new (Z)-ferulic acid ester (1) and a new syringic acid ester (2), as well as four known ferulic acid esters (3–6), were isolated from a well-known edible mushroom, Pleurotus eryngii. Structures of these aromatics were unambiguously characterized via spectroscopic methods especially MS and NMR techniques. All the isolates were assessed for their antiradical effect and NO production inhibitory activity in RAW264.7 macrophages, and compounds 1 and 3 displayed mild DPPH radical removing activity, with IC50 values of 25.0 and 21.6 mM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.205.20.08.1789 Keywords Pleurotus eryngii aromatics ferulic acid ester syringic acid ester antiradical DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Chemical Composition and Assessment of Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Activities of Essential oil from Clinopodium sericeum, a Peruvian Medicinal Plant
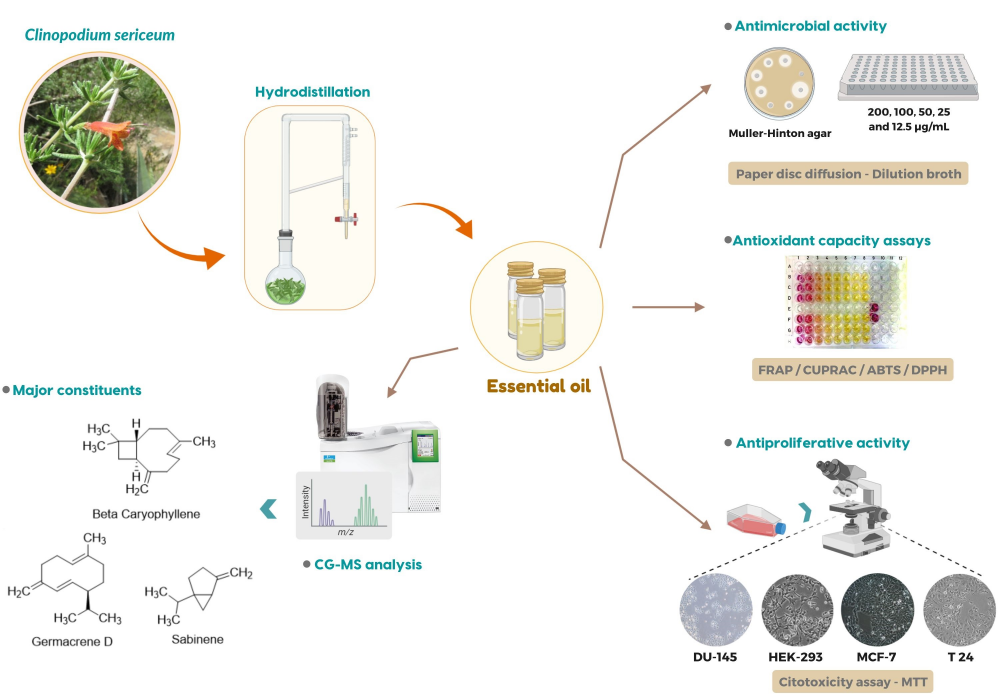
Clinopodium sericeum is widely used in Peruvian folk medicine in the form of infusion to treat stomach distress, indigestion and antiflu. In this study, the essential oil from C. sericeum was obtained by hydrodistillation, analyzed by GC and GC/MS, and 73 compounds were identified. Major components of the oil were b-germacrene-D (15%), b-caryophyllene (13.8%), and sabinene (11.2%). Furthermore, we assessed the in vitro biological activities displayed by the oil obtained from the aerial parts of C. sericeum, namely the antioxidant, antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities. The antioxidant activities of the essential oil were evaluated by FRAP, CUPRAC, ABTS and DPPH radical scavenging activity. The essential oil displays antibacterial activity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial strains (MIC 50-200 µg/mL) in a dose-range close to standard antibiotics. Such activity may be related to the presence of terpene compounds. The antiproliferative activity of the essential oil was measured in vitro using the MTT colorimetric assay in healthy non-tumorigenic cells (HEK-293) and in three human cancer cell lines (T24, DU-145, and MCF-7). The calculated IC50 values were around 0.2 mg/mL. Since the essential oil was almost devoid of antioxidant activity, its anti-proliferative action is unlikely related to oxidative stress and relies on other unknown mechanisms.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.213.20.10.1845 Keywords Folk medicine Clinopodium sericeum antioxidant antimicrobial antiproliferative cancer cells DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Three New Polyketides from the Insect-Associated Fungus Letendraea sp. 5XNZ4-2
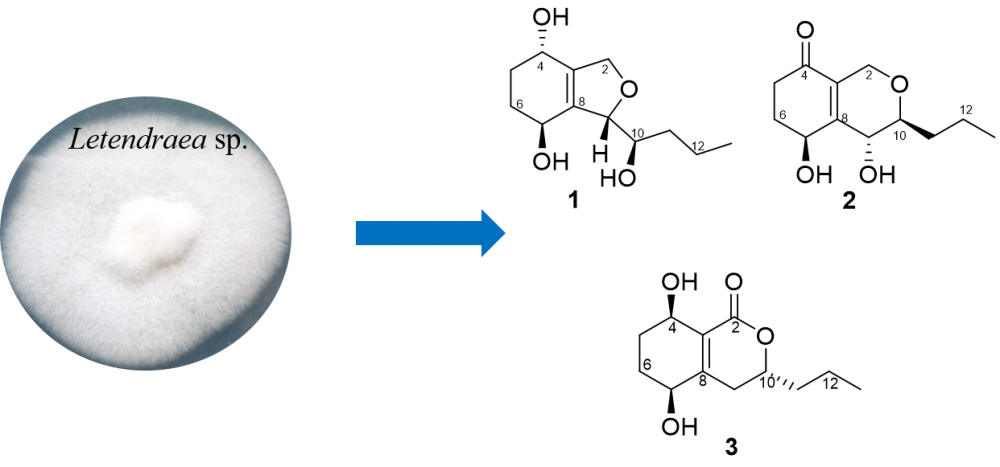
Chemical investigation of the EtOAc extract of an insect-associated fungus Letendraea sp. 5XNZ4-2 cultured in Potato Dextrose Broth (1/2 PDB) medium lead to the isolation of three new polyketides, named letendronol D (1), phomopsiketones H-I (2-3). The structures of new compounds were elucidated by the analysis of HRESIMS and NMR spectroscopic data, and the absolute configurations were determined by modified Mosher’s method, ECD calculation and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities of 1 were assayed and regrettably 1 didn’t display any cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity. 3 was the first phomopsiketone derivative obtaining the lactone.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.206.20.08.1786 Keywords polyketides insect-associated fungus Letendraea sp. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Trimacoside A, a High Molecular Weight Antioxidant Phenylpropanoid Glycoside from Tricyrtis maculata
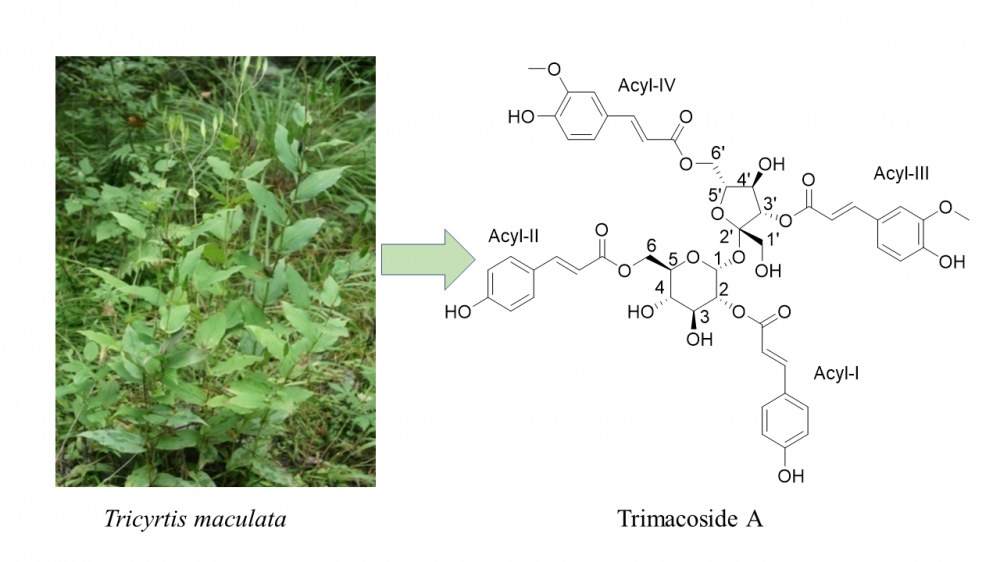
Trimacoside A (1), a new phenylpropanoid glycoside, together with nine known compounds (2−10) was isolated from Tricyrtis maculata. All compounds, except for 8, were firstly isolated from this plant. The structure elucidation of the new compound was carried out by the analysis of spectroscopic data, including 1D, 2D NMR, and HRESIMS. Compounds 1, 4, 5, 7, 8, and 10 showed significant antioxidant activities by DPPH and ABTS assays.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.209.20.09.1810 Keywords Liliaceae Tricyrtis maculata phenylpropanoid glycoside antioxidant DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Aromatic Rosane-type Diterpenoid with Lipase Inhibitory Effect from Euphorbia ebracteolata and Chemotaxonomic Significance of Diterpenoids

The phytochemical investigation has been performed for Euphorbia ebracteolata, the roots of which are usually used natural medicine in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatments of tuberculosis and bacterial infection. A diterpenoid has been obtained using silica gel and ODS column chromatography. Furthermore, on the basis of widely spectroscopic data analyses, including 1D-, 2D-NMR, HR-ESIMS and ECD, the isolated compound was determined to be a rosane type diterpenoid, which possessed a rare aromatic ring. The isolated diterpenoid as a new compound was named ebraphenol E (1). The bioactivity of isolated diterpenoid (1) has been evaluated and moderate inhibitory effect on lipase (IC50 = 12.5 μM) was observed. In combination with our previous phytochemical investigations about E. ebracteolata, the chemotaxonomic significance of diterpenoids was summarized for E. ebracteolata.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.204.20.08.1774 Keywords Euphorbia ebracteolata rosane diterpenoid ebraphenol E lipase Chemotaxonomy DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils from Leaves and Twigs of Magnolia hookeri var. longirostrata D.X.Li & R. Z. Zhou and Magnolia insignis Wall. in Ha Giang Province of Vietnam
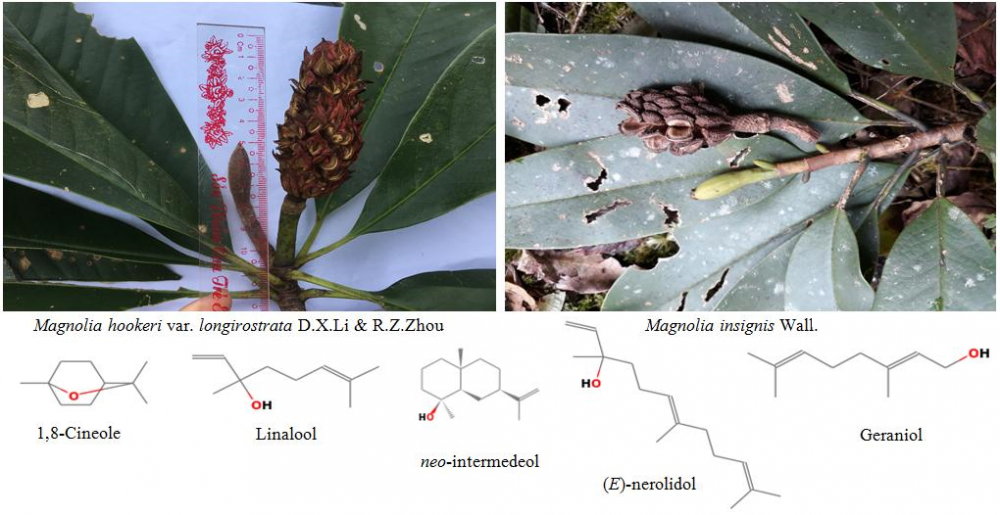
The essential oils from leaves and twigs of Magnolia hookeri var. longirostrata D.X.Li & R.Z.Zhou and Magnolia insignis Wall., growing wild in Ha Giang Province of Vietnam, were obtained by hydrodistillation and analyzed by gas chromatography-flame ionization detector (GC-FID) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The respective yields of the M. hookeri var. longirostrata leaf and twig oils were 0.14% and 0.05% (v/w), and of the M. insignis leaf and twig oils were 0.16% and 0.05% (v/w), calculated on a dry weight basis. Major components of the oils of M. hookeri var. longirostrata were: Linalool (21.3%), (E)-nerolidol (12.2%) and neo-intermedeol (13.5%) (leaf oil); 1,8-cineole (13.3%) and linalool (17.1%) (twig oil). Major components of the oils of M. insignis were: Linalool (24.1%), geraniol (14.9%) and (E)-nerolidol (22.5%) (leaf oil); 1,8-cineole (9.5%) and linalool (26.9%) (twig oil). The essential oils from M. insignis showed stronger inhibitory effects on the seven test microorganisms than those from M. hookeri var. longirostrata. Candida albicans and Lactobacillus fermentum were more sensitive to the essential oils than the other tested microorganisms. This is the first time information on essential oils of M. hookeri var. longirostrata leaves and twigs and of M. insignis twigs are reported.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.212.20.10.1842 Keywords Magnolia hookeri var. longirostrata Magnolia insignis antimicrobial activity essential oil DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A New Angular Naphthopyrone from Crinoid Colobometra perspinosa
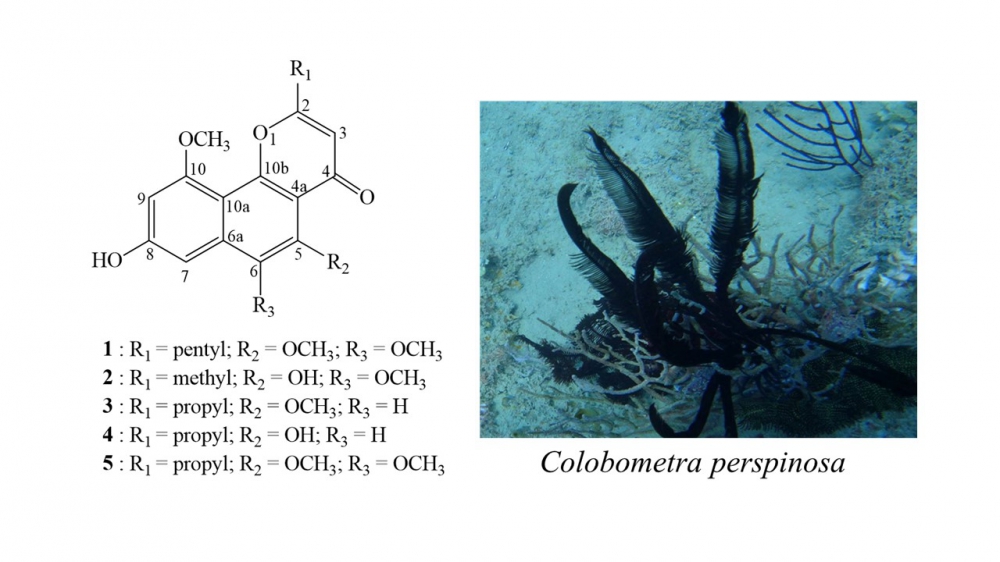
A chemical investigation was carried out on a crinoid Colobometra perspinosa collected from Hengchun Peninsula in the South China Sea, which led to the isolation of five angular naphthopyrones (1–5), including one new metabolite, 8-hydroxy-5,6,10-trimethoxy-2-pentyl-4H-naphtho[1,2-b]pyran-4-one (1). Their structures were assigned based on spectroscopic methods, including UV, HRESIMS, 1D- and 2D-NMR spectra. The anti-inflammatory activity of the isolated compounds was evaluated and compound 5 was found to inhibit the accumulation of the pro-inflammatory iNOS protein in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.207.20.07.1757 Keywords angular naphthopyrone crinoid Colobometra perspinosa iNOS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.