Records of Natural Products
Year: 2023 Volume: 17 Issue:4 July-August
1) Research Progress on Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities of Litsea cubeba (Lour) Pers
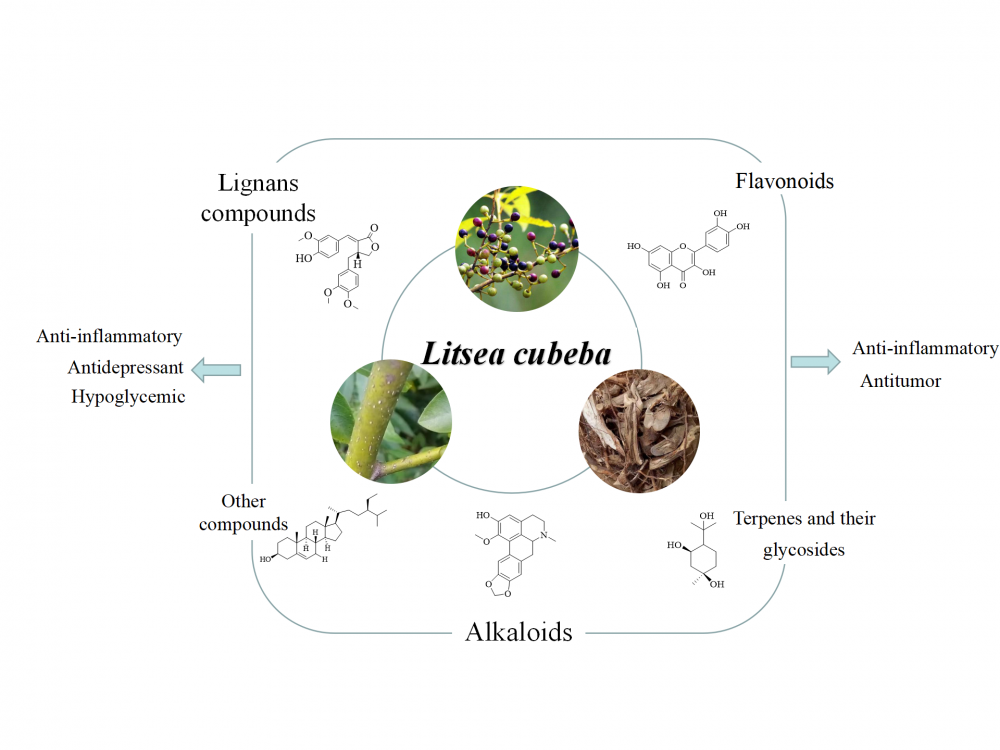
Litsea cubeba, a deciduous shrub belonging to the Lauraceae family, has a variety of medicinal properties, and its fruit, leaves, roots, and bark are used for treating conditions such as spleen-stomach deficiency, dysphagia, and unidentified tumors. The main chemical components of Litsea cubeba are alkaloids, flavonoids, lignans, terpenes, and their glycosides, with aporphine alkaloids being the most characteristic. Recent studies have demonstrated that Litsea cubeba has a wide variety of pharmacological activities, including antitumor, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and hypoglycemic effects. This article summarizes the chemical composition and pharmacological activities of Litsea cubeba and explores their mechanisms of action, providing a reference for the development and utilization of the Litsea cubeba chemical components.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.399.2305.2774 Keywords Lauraceae Litsea cubeba chemical composition biological activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Chemical Compositions of Essential Oils from German, Roman, and Chinese Chamomile Flowers and Their Biological Activities against Three Economically Important Insect Pests
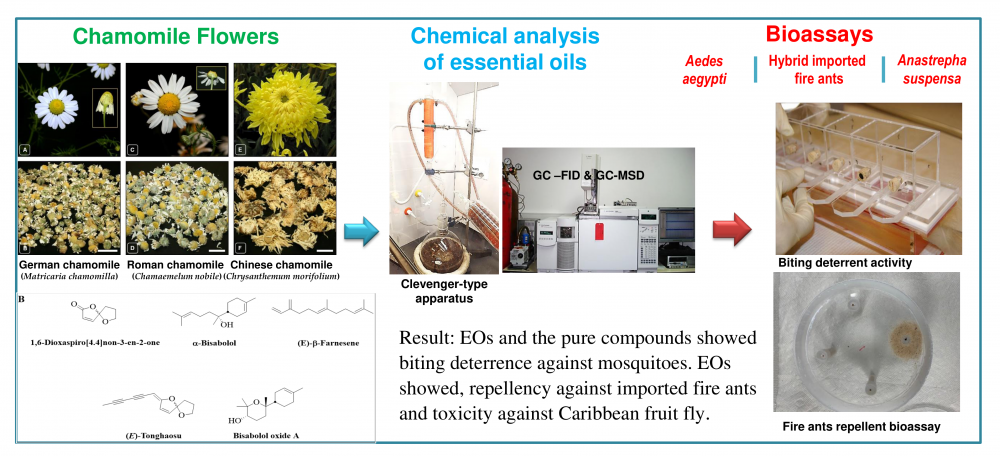
In this study, the essential oils (EOs) of flowers from German chamomile (GCEOs 1-5) Matricaria chamomilla L., Roman chamomile (RCEOs 1-2) Chamaemelum nobile (L.) All, and Chinese chamomile (CCEO-1) or “Juhua” Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat were characterized by GC-FID and GC-MS analysis. EOs were tested for biting deterrence/repellency against Aedes aegypti and hybrid imported fire ants and for toxicity against Anastrepha suspensa. GCEOs 1-5 were characterized by the higher contents of α-bisabolol oxide A (43%-66%) and α-bisabolol oxide B (10%-16%) whereas isobutyl angelate (16%-17%), 2-butenyl angelate (12%-13%), isoamyl tiglate (11%-12%), 3-methyl pentylangelate (8%-11%), and trans-pinocarveol (6%-7%) were major compounds of RCEOs 1 and 2. The CCEO-1 was rich in borneol (31%), ar-curcumene (12%), bornyl acetate (7%) and intermedeol (5%). Biting deterrence of GCEO-2 and -3, and CCEO-1 was similar to N,N-diethyl-3-methylbenzamide (DEET) whereas the activity of the other EOs was lower than DEET against Ae. aegypti. The activity of pure compounds α-bisabolol and 1,6-dioxaspiro[4.4]non-3-en-2-one from German chamomiles was also similar to DEET against Ae. aegypti. Repellency of German chamomile EO, GCEO-F against hybrid imported fire ants was higher whereas the activity of Roman chamomile EO, RCEO-PT was lower than DEET. All EOs, GCEO-4, RCEO-2, and CCEO-1 were toxic against female A. suspensa. Further research using intensive in vivo bioassays will be conducted to explore the potential of these natural products in insect pest management strategies.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.378.2211.2627 Keywords Chamomile essential oils α-bisabolol repellency imported fire ant fruit fly mosquitoes DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Chemical Constituents from the Roots of Rehmannia glutinosa

Ten secondary metabolites, including one new monoterpene rhamnoside (1), five terpenoids (2–6), two nucleosides (7–8), and two phenylethanoid glycosides (9–10) were isolated from the roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Their structures were determined by spectroscopic analysis such as NMR and HR-ESI-MS. In the tyrosinase inhibitory assay, compounds 2, 6 and 8 showed inhibition against tyrosinase. Compounds 1, 4, 5, 6, 9 and 10 are being reported in the genus Rehmannia for the first time.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.380.2211.2625 Keywords Rehmannia glutinosa rhamnoside phenylethanoid glycoside tyrosinase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) A Novel Phenanthrene and An Undescribed Alkaloid from the Roots of Stephania tetrandra
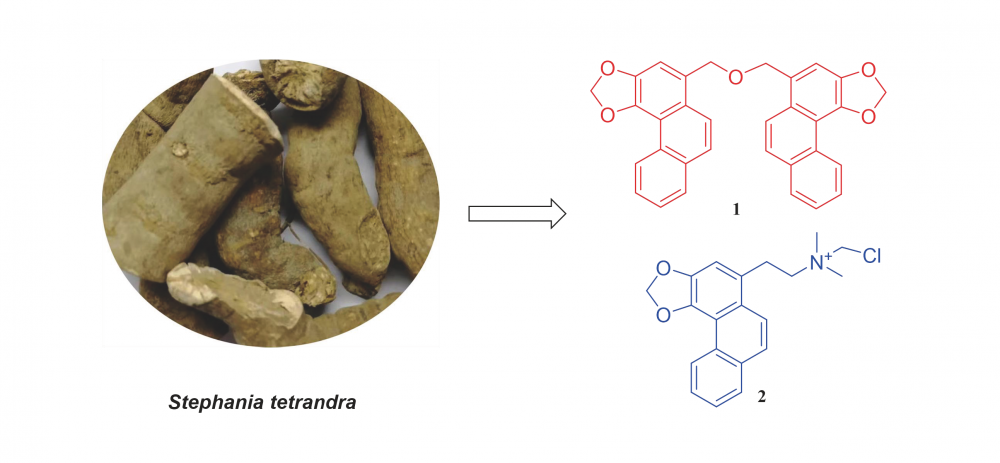
A novel phenanthrene compound, diphenanthrin (1), and an undescribed alkaloid compound, N-chloromethylstephenanthrine (2), together with two known compounds (3-4) were isolated from the EtOH extract of the roots of Stephania tetrandra. Their structures were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR, mass spectroscopy and comparison of NMR data with those of known compounds. In anti-inflammatory assay, compounds 3 and 4 showed the inhibitory effects on NO production, with IC50 values of 41.51 ± 0.20 and 23.87 ± 2.12 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.381.2212.2663 Keywords Stephania tetrandra phenanthrene alkaloid anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Chemical Components of Thymbra spicata subsp. spicata L. Essential Oil and Its In Vitro Physiological Effects on Human Origin Cell Lines

Thymbra spicata subsp. spicata L. is a member of the Lamiaceae family, which is used in Türkiye against various health issues among other uses. The main components of T. spicata essential oil (TE) were identified as carvacrol (52.3%) and p-cymene (21.1%) using GC-FID and GC/MS. The in vitro effects of TE on Miapaca-2 and HUVEC cell lines were reported for the first time. The initial results showed that TE applied to Miapaca-2 cell lines at concentrations of ≥62.18 g/mL for 48 hours could reduce cell growth and induce apoptosis. The application of relatively high concentrations of TE (≥82.91 g/mL) significantly (P<0.001) suppressed cell growth. Administration of relatively high TE concentrations (≥82.91 g/mL) significantly (P<0.001) suppressed cell growth. Concentrations of TE lower than 20.73 g/mL did not affect the viability of the HUVEC cell line in 48 hours. The IC50 value for Miapaca-2 cells was 62.18 µg/mL, and HUVEC cells’ IC50 value was 263.97 µg/mL for 48h. The number of apoptotic cells in Miapaca-2 (55±5%) and HUVEC (38.33±6%) were significantly higher (P<0.001). Significantly lower migration rates (P<0.001) were seen for Miapaca-2 (52±5%) and HUVEC cell lines (64±1.67%).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.387.23.01.2671 Keywords Thymbra spicata subsp. spicata cancer apoptosis wound-healing cellular-migration proliferation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Evaluation of the Chemotactic and Genotoxic Effects of Selected Cycloartane-type Glycosides on Caenorhabditis elegans
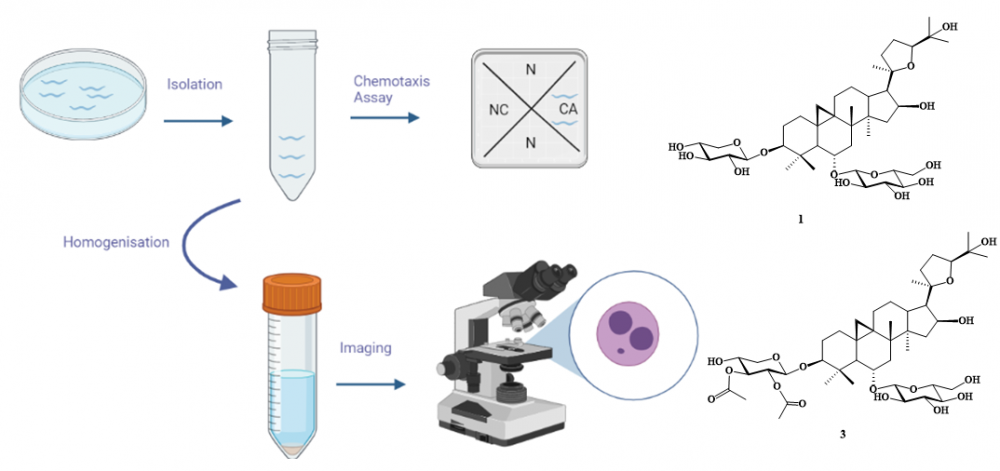
Astragalus L., is the most populated plant genus on the planet. It has found use in folk medicine to treat many different forms of ailment. However, the toxicity studies of the genus and the chemicals isolated from it, are scarce and the toxicological profile is largely unknown. Caenorhabditis elegans has been used in multiple scientific disciplines. Its ease of use, genetic similarity to humans in many pathways, connectome and nervous system and resistance to environmental stress make it among the best organisms for toxicity testing. The present study used C. elegans chemotaxis responses, and micronucleus generation, to evaluate the potential neurotoxicity of some selected cycloartane-type glycosides; astragalosides IV (1) and VI (2), astrasieversianin II (3), baibutoside (4), and macrophyllosaponins B (5) and D (6), in the short- and long-term domain, along with long-term genotoxicity testing. The results indicate long-term chemotaxis inhibition by compounds 1, 2, 3 and 5, whereas only compound 3 inhibited chemotaxis in the short-term. Compound 1 was found to significantly increase micronucleus generation at the highest tested dose. The study demonstrates the usefulness of the Nematode Chemotaxis and in vivo Micronucleus Assays for the determination of the toxicity of natural products, while illuminating the points of consideration that future studies may be designed to address.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.389.2301.2694 Keywords Caenorhabditis elegans chemotaxis toxicity testing experimental toxicology micronucleus cycloartane-type glycosides DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Asperaldehyde, A New Conjugated Compound from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. LPFH-6

Abstract: The fungal strain Aspergillus sp. LPFH-6 was cultured on solid rice medium with the addition of artificial salt. The culture medium was extracted with the solvent EtOAc to afford an extract, which was separated by various chromatographic techniques to give 8 compounds (1-8). The structures were determined by extensive analyses of the spectroscopic data including 1D (1H and 13C NMR), 2D NMR (1H-1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC, NOESY), and the MS data. Compound 1 was identified to be a highly conjugated compound that contained a rare 5-(2-methoxyphenyl)penta-2,4-dienal moiety. The known compounds were identified as yaminterritrem B (2), butyrolactone I (3), butyrolactone V (4), sulochrin (5), monomethylsulochrin (6), questinol (7), and 7-hydroxyemodin (8). Bioasasy showed that compounds 2-4 and 8 displayed better a-glucosidase inhibitory activity than the positive control acarbose with IC50 values of 0.25, 0.09, 0.12, and 0.27 mM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.386.2301.2691 Keywords Aspergillus sp. marine-derived fungus asperaldehyde DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Penicisepene, A New Sesquiterpenoid from the Fungus Penicillium sp. LPFH-Q3
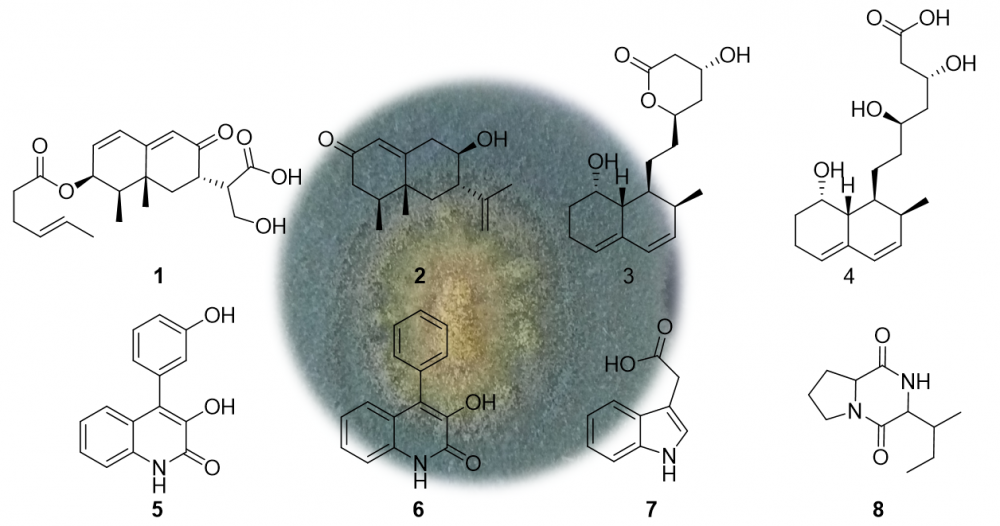
The secondary metabolites of the strain Penicillium sp. LPFH-Q3 isolated from the sea sediment were investigated. A new eremophilane sesquiterpene, named penicisepene (1), along with seven known compounds (2-8) was obtained. The structures of the metabolites were elucidated based on spectroscopic analysis including 1H NMR, 13C NMR, 1H-1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC, NOESY, and the MS data. The absolute configuration of 1 was established via comparison of the experimental and density functional theory predicted ECD data. Compound 1, an eremophilane sesquiterpene containing a hexenic acid, was scarcely found in nature. Besides, the NMR data of 3 and 4 in methanol-d4 were reported for the first time. Biological evaluation showed that compounds 1, 3, and 4 showed inhibitory activity comparable to the positive control quercetin (16.7 uM) on NO production in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages with IC50 values of 13.2, 10.6, 17.9 uM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.390.2303.2747 Keywords Penicillium sp. marine fungus sesquiterpene NO production DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Protective Effect of Syzygium jambos (L.) Leaf Extract and Its Constituents Against LPS-induced Oxidative Stress
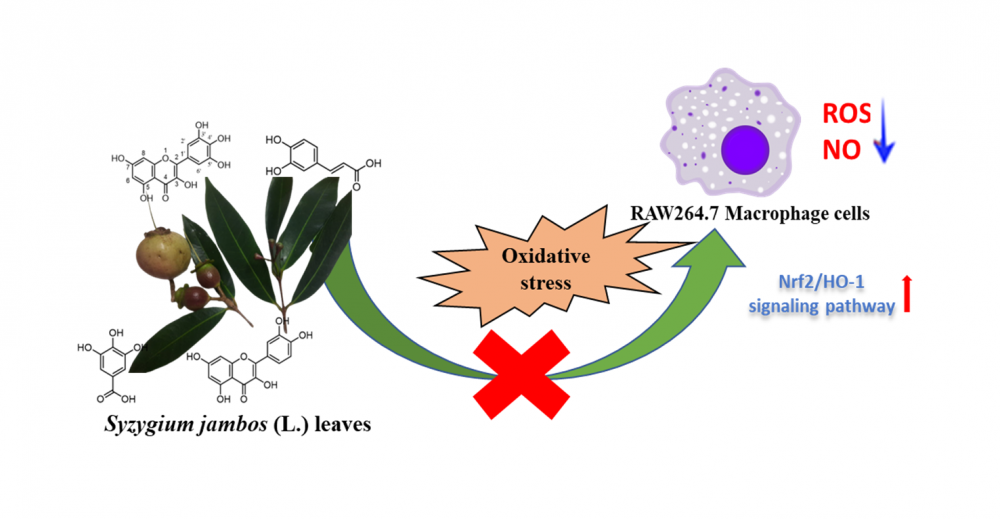
Oxidative stress is one of the leading causes that contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic diseases based on the imbalance between free radicals and the antioxidant defense system. Here, Syzygium jambos (L.) Aston, a traditional herb used to treat various diseases, was evaluated using RAW264.7 macrophages with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulation to demonstrate its effects and find a new therapy for oxidative stress. This study proved that Syzygium jambos leaf extract exerted its ability to protect cells against oxidative stress via activating the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 (Nrf2/HO-1) pathway to suppress reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Moreover, the extract also attenuated the nitric oxide (NO) production and the nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression, suggesting an anti-inflammatory response. In addition, four active compounds, including gallic acid, quercetin, myricetin, and caffeic acid, were isolated from ethyl acetate fraction using column chromatography. The structure of compounds was analyzed based on one-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (1D-NMR) and compared to literature data. Their biological activity was confirmed by promoting the induction of HO-1. Hence, this study provides the initial evidence of Syzygium jambos leaves protective effects and highlights its potential as an antioxidant agent.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.393.2303.2730 Keywords macrophage cell nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 oxidative stress Syzygium jambos (L.) Aston DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Three New Chemical Constituents of Dryopteris crassirhizoma Nakai in Lianhua Qingwen Capsule and Investigation on Their Antiviral Potential Based on 3CL Hydrolase of SARS-CoV-2
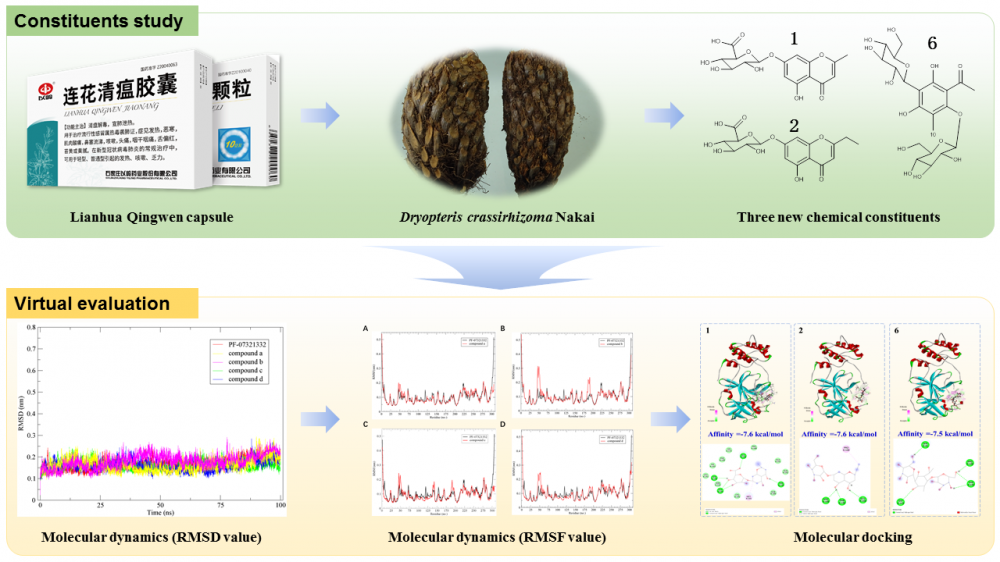
Three new chromone glycosides, named 2-methyl-5-hydroxyl-4-chromone-7-O-β-D-glucuronide (1), 2-ethyl-5-hydroxyl-4-chromone-7-O-β-D-glucuronide (2) and 1-acetyl-3-C-β-D-glucopyranosyl-5-methyl-phloroglucinyl-6-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6), together with eight known compounds were isolated from the water extract of Dryopteris crassirhizoma Nakai,and the water extract preparation process is consistent with Lianhua Qingwen capsule. All the chemical structures of new compounds were characterized by 1D and 2D NMR spectra as well as high resolution mass and IR spectra. The chemical structures of known compounds were characterized by NMR spectra along with comparison of their spectroscopic data with those reported in the literature. The binding ability of these compounds to 3CL hydrolase of SARS-COV-2 was evaluated by molecular docking. The results showed that the chromone glycosides with glucuronic acid fragment had good docking effect with 3CL hydrolase and this indicated the chromone glucuronides could be further studied as potential antiviral compounds.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.391.2301.2683 Keywords Dryopteris crassirhizoma Nakai chromone glycosides molecular docking molecular dynamics simulation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) A New Megastigmane Glycoside and Anti-Inflammatory Bibenzyls from the Stems of Dendrobium henanens
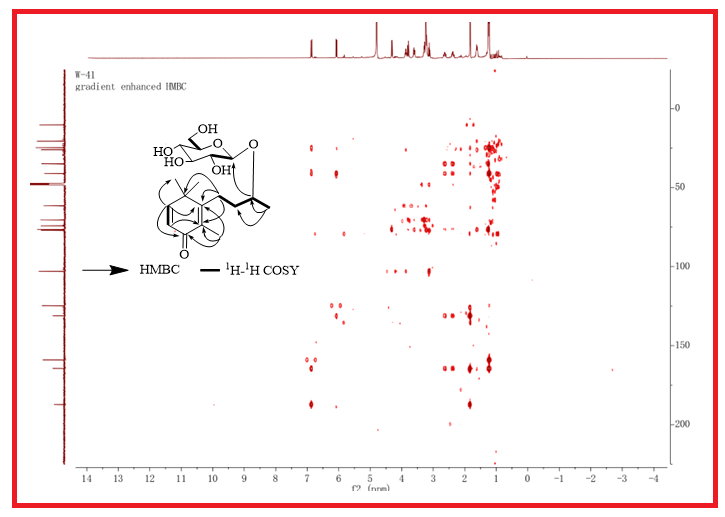
A new megastigmane glycoside, namely (9S)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-2,5-megastigmen-4-one (1), along with seven known bibenzyls (2-8) were isolated from the aerial stems of Dendrobium henanense. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic and mass-spectrometric analyses, including 1D-, 2D-NMR and HR-MS. The anti-inflammatory activities of compounds 1-8 evaluated its anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines such as NO, TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Compounds 3, 4, 6-8 exhibited moderated anti-inflammatory activity with IC50 values of below 100 µΜ.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.382.2211.2626 Keywords Dendrobium henanense megastigmane glycoside anti-inflammatory RAW264.7 macrophages DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) A New Ingenane Diterpenoid from Euphorbia jolkinii
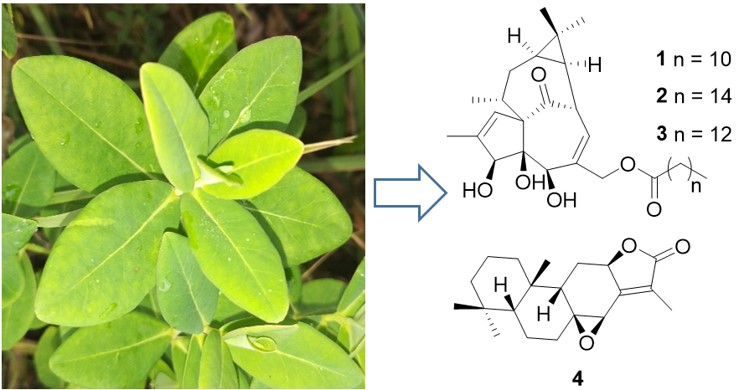
A new ingenane diterpenoid, named ingenol-20-laurate (1), and two known analogues (ingenol-20-palmitate (2), ingenol-20-pentadecanoate (3)) and an ent-abietane diterpenoid (euphopilolide, 4) were isolated from the whole plants of Euphorbia jolkinii. The structure of compound 1 was elucidated by HRESIMS and 2D NMR methods. The cytotoxicities of compound 1 against SMMC-7721, MDA-MB-231, and SW480 cell lines were 27.22±0.58, 17.69±0.29 and 16.19±0.77 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.384.2301.2685 Keywords Euphorbia jolkinii diterpenoids cytotoxicities DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.13) Evaluation of Therapeutic role of Thymus capitatus (L.) Hoffm. & Link, Origanum dubium Boiss. Essential Oils and Their Major Constituents as Enhancers in Cancer Therapy

Aim of the study is to evaluate the potential use of Thymus capitatus (L.) Hoffm. & Link and Origanum dubium Boiss. essential oils and their major constituents; thymol and carvacrol in cancer therapies. For this aim hMSC-telo1 cells and their tumorigenic counterpart were exposed to varying concentrations of Thymus capitatus (L.) Hoffm. & Link and Origanum dubium Boiss. essential oils, thymol and carvacrol and cellular viability and proliferation have been evaluated by MTT assay. TUNEL assay has used for evaluation of apoptosis. Study suggested that, Thymus capitatus (L.) Hoffm. & Link essential oil and thymol have an enhancer effect once combined with conventional chemotherapeutic agents. 0.005 v/v % of Thymus capitatus (L.) Hoffm. & Link, 0.005 v/v % and 0.05 v/v % of thymol showed enchancer effect by sparing the normal hMSC-telo1 cells from the cytotoxicity of Deferasirox while these combinations were cytotoxic towards tumorigenic hMSC-telo1 cells.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.379.2210.2613 Keywords Anticancer human mesenchymal stem cells tumorigenic essential oil thymol carvacrol DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.14) Trichonafurin A: a New γ-Lactone Compound from the Marine-Derived Fungus Trichoderma atroviride ZW-7

A new γ-lactone compound, trichonafurin A (1), was obtained from the culture of Trichoderma atroviride ZW-7, an endophyte of the marine brown alga Sargassum thunbergii. Its structure was unambiguously assigned by detailed interpretation of 1D/2D NMR and HRESIMS data. Trichonafurin A (1) exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against HeLa and HepG2 cell lines with IC50 values of 20.2 and 32.1 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.388.2302.2714 Keywords Trichoderma atroviride secondary metabolites cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.15) Bromophenols from the Marine Red Alga Symphyocladia latiuscula and Their Radical Scavenging Activity
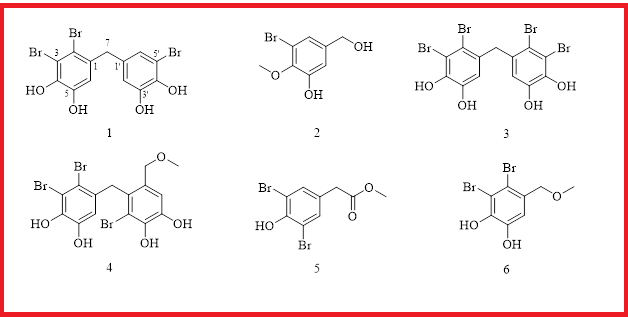
A new (1) and five known (2-6) bromophenols were isolated from the organic extract of the marine red alga Symphyocladia latiuscula. Their structures were assigned by interpretation of NMR and MS data, and these compounds were determined as 2,3,5′-tribromo-3′,4,4′,5-tetrahydroxy-diphenylmethane (1), 2-methoxy-3-bromo-5-hydroxymethylphenol (2), 5-(2,3-dihydroxybenzyl)-3,4-dibromobenzene-1,2-diol (3), 5-(2-bromo-3,4-dihydroxy-6-(methoxymethyl)benzyl)-3,4-dibromobenzene-1,2-diol(4), methyl 2-(3,5-dibromo-4-hydroxybenyl) acetate (5), and 3,4-dibromo-5-(methoxymethyl)benzene-1,2-diol (6). All these compounds were evaluated for DPPH radical scavenging activity, and they displayed potent antioxidant activity with IC50 values ranging from 9.6 to 31.5 μM. These compounds also showed moderate ABTS radical scavenging activity with TEAC value ranging from 2.1 to 3.0 mM. The results suggested that these bromophenols or the marine red alga S. latiuscula may have potential application in food as natural antioxidants.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.394.2304.2764 Keywords Symphyocladia latiuscula bromophenols secondary metabolites antioxidant activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
16) A New Isobenzofuranone Derivative from Arctic Fungus Gyoerffyella sp. CPCC 401434

A new isobenzofuranone derivative, (R)-3-acetyl-[5,7]-dimethoxy-3H-isobenzofuran-l-one (1), together with six known compounds, (R)-3-acetyl-7-hydroxy-5-methoxy-3H-isobenzofuran-l-one (2), banksialactone D (3), (3R,4S)-3,8-dihydroxy-3-hydroxymethyl-6-methoxy-4,5-dimethyl-isochroman-1-one (4), 1-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl]-2,5-dimethyl-3-phenol (5), p-hydroxybenzaldehyde (6), 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) ethanol (7), were isolated from Arctic fungus Gyoerffyella sp. CPCC 401434. Their structures and absolute configurations were elucidated by the analysis of spectroscopic data, electronic circular dichroism, and comparison with reported literature data. Herein, all compounds were reported for the first time from the genus Gyoerffyella and their cytotoxic and antibacterial activities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.392.2211.2629 Keywords Arctic fungus Gyoerffyella isobenzofuranone cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.17) Penioctadecatrienoic A: A New Polyketide from Endophytic Fungus Penicillium pinophilum J70
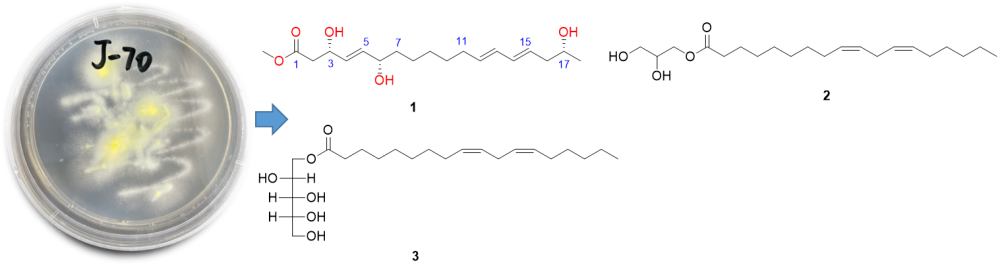
Chemical examination of the rice solid fermented cultures of the fungus Penicillium pinophilum J70 isolated from the fresh leaves of Hypericum japonicum Thumb led to the isolation of one new polyketide, namely penioctadecatrienoic A (1), together with two known compounds (2 and 3). The structure of the new metabolite 1 was resolved on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analysis (NMR and HRESIMS data), in association with the modified Mosher's method for the absolute configurational assignment. All isolated metabolites were evaluated for their cytotoxic activity against ECA-109, the anti-inflammatory activity against NO production in lipopolysaccharides (LPS) stimulated RAW264.7 cells, and the antibacterial activity on Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213. As a result, compounds 1‒3 showed moderately anti-inflammatory effects with the inhibitory rates ranging from 44.5% to 60.7% at the concentration of 20 μM. In addition, compound 1 exhibited weakly antibacterial effect with an MIC value of 32 µg/mL.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.397.2304.2752 Keywords Endophytic fungus Penicillium pinophilum polyketides cytotoxic activities anti-inflammatory activities DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.