Records of Natural Products
Year: 2024 Volume: 18 Issue:4 July-August
1) Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Genus Cercis: A Review
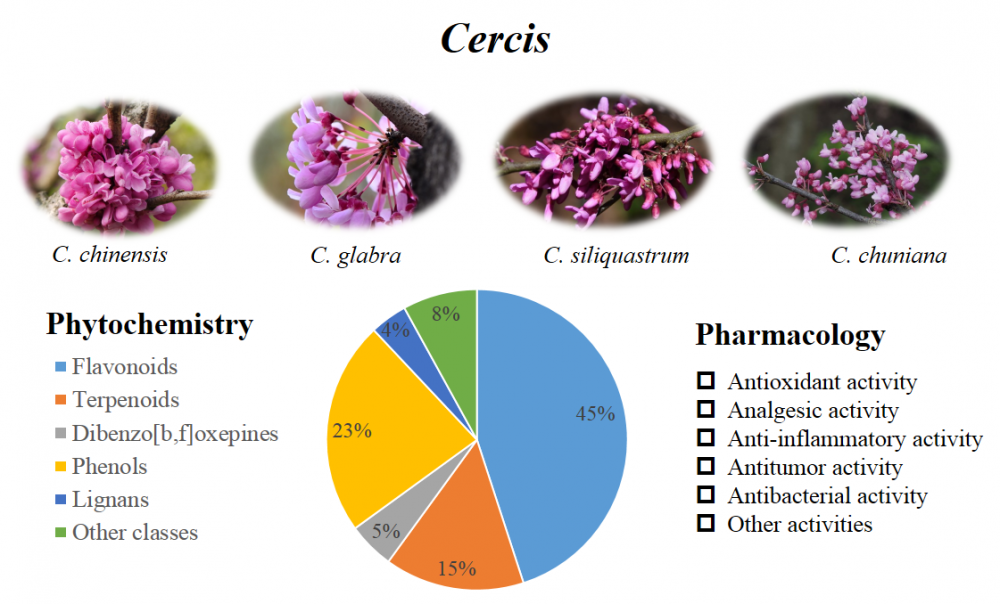
The genus Cercis, belonging to the Fabaceae family, is widely distributed in China and traditionally employed in Chinese medicine to treat various disorders, like irregular menstruation, pain, cough and carbuncle swelling. Despite the availability of numerous scientific studies on this genus, reviews that comprehensively cover its phytochemistry and pharmacology remain limited. This review aims to systematically consolidate the scientific literature on the phytochemistry and pharmacology of eight Cercis species, retrieved from databases like PubMed, Web of Science, SciFinder, Google Scholar, and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure platform. Based on a thorough analysis of the literature, more than 100 compounds have been identified from Cercis species, including flavonoids, phenols, terpenoids, lignins, dibenz[b,f]oxepins and others. Extracts and chemical constituents derived from Cercis species exhibite significant antioxidant, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antibacterial activities. These findings contribute to a deeper understanding of the medicinal potential of Cercis species and their potential applications in healthcare.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.458.2404.3190 Keywords Cercis phytochemistry pharmacology bioactivity flavonoid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Isolation of New Secondary Metabolites from Kedrostis gijef and Evaluation of Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
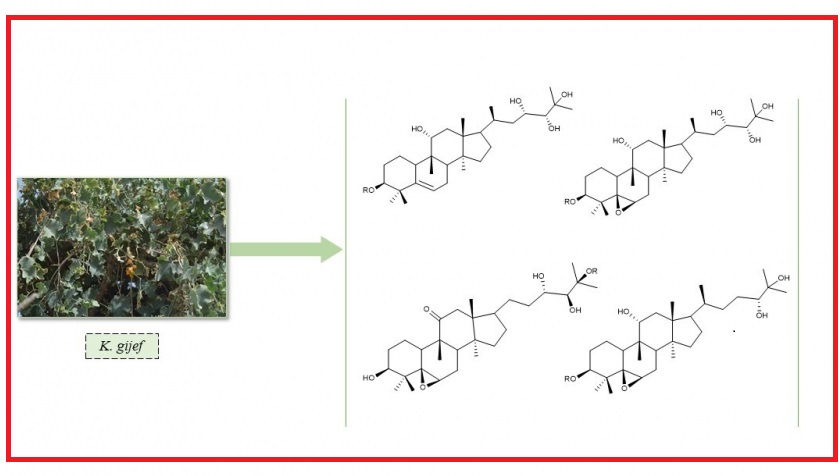
Four new polyoxygenated cucurbitane triterpene glycosides named kedrojiftene A-D (4-7), were isolated via different chromatographic techniques along with three phenolic compounds (1-3) from the crude extract of Kedrostis gijef. The isolated compounds were elucidated based on 1D, 2D-NMR spectroscopic analyses, HRESIMS and comparison with the related metabolites in literature. In bioassay, the α-glucosidase inhibitory assay for the isolated compounds was carried out and compounds (1-3) showed significant inhibitory activities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.468.2405.3236 Keywords Kedrostis gijef triterpene cucurbitane phenolic α-glucosidase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Hydroxytyrosol-1-Glucopyranoside Alleviates Senescence via Nrf2 and AMPK Signaling Pathway
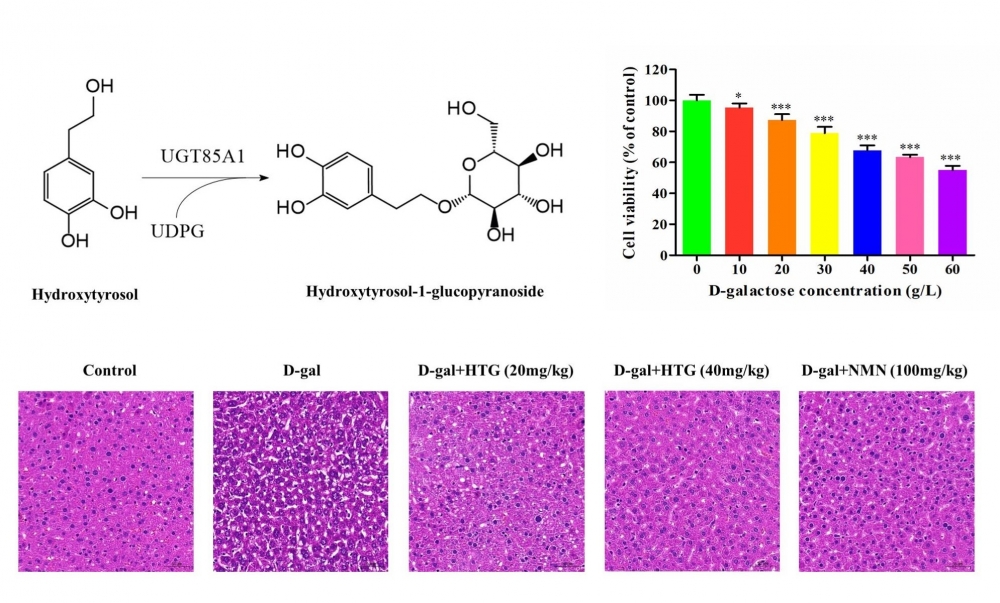
Hydroxytyrosol-1-glucopyranoside (HTG) is a natural phenylethanol glycoside with promising anti-aging properties. In this study, we established a biotransformation and purification process to effectively prepare high-purity HTG. We constructed E. coli strains expressing the glycosyltransferase gene UGT85A1 and UDP-glucose enhancing genes pgm and galU. By optimizing gene expression, the best strain produced 6.8 g/L HTG at 48 hours in fed-batch fermentation. Among the five different macroporous resins tested, SP825L performed the best and was employed to purify HTG from the culture broth. By optimizing the adsorption and desorption conditions, the purity and the recovery percentage reached 81.7% and of 82.4%, respectively. The purity was improved to 95.2% by further purification through preparative chromatography. The anti-aging effects of HTG were evaluated in both cells and mice. The results demonstrated its capacity to enhance cellular antioxidant capacity, reduce apoptosis, and decrease the release of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), effectively mitigating D-galactose-induced cell senescence. The potential mechanism of action suggests that HTG activates the AMPK and Nrf2 signaling pathways to protect mice from liver injury. This study suggests promising application of HTG in cosmetic and nutraceutical fields.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.460.2403.3166 Keywords Antioxidant anti-aging macroporous resin hydroxytyrosol-1-glucopyranoside DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Butanedioic Acid Benzyl Ester Glycosides from Pleione bulbocodioides (Franch.) Rolfe: Promising Fungicide Against Phoma herbarum
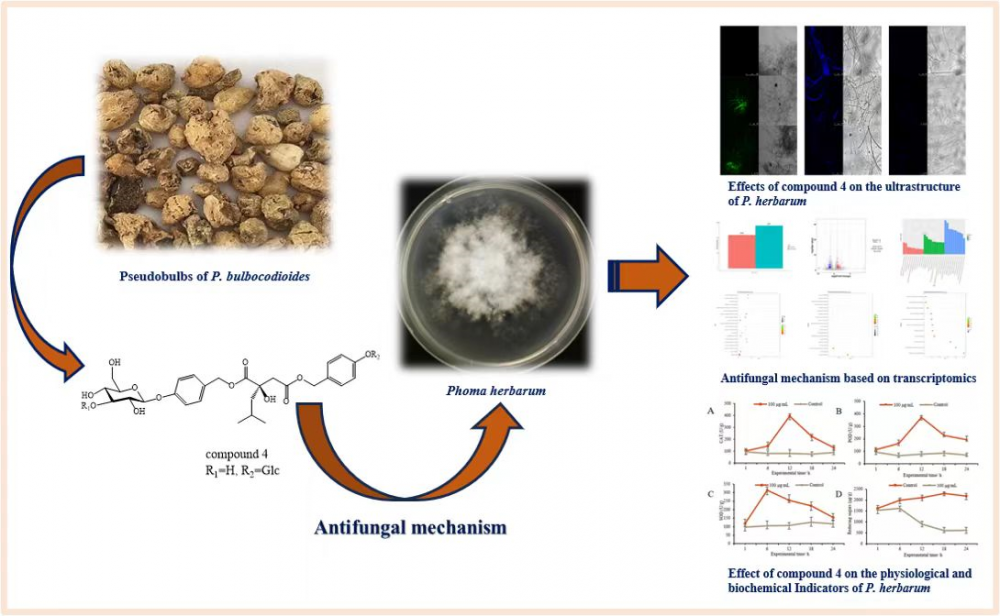
The bioactive compounds of the pseudobulbs of Pleione bulbocodioides were isolated, purified, and identified using modern spectroscopic techniques, which identified seven butanedioic acid compounds. Compounds 1-3, 5, and 6 were isolated for the first time from Pleione bulbocodioides. The antifungal activity of the seven compounds was evaluated through cytotoxic activity assays, revealing that compound 4, militarine, exhibited moderate inhibitory activity against Phoma herbarum, with an effective concentration (EC50) of 68.575 μg/mL. We get further deep insight into the antifungal mechanism of militarine against Phoma herbarum through electron microscopy, transcriptomics, and changes in physiological and biochemical indicators. Transcriptomic sequencing revealed 216 significantly upregulated differentially expressed genes and 277 significantly downregulated differentially expressed genes. Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis showed that differentially expressed genes were involved in pathways related to secondary metabolism, biosynthesis, membrane components, nitrogen metabolism, and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, suggesting that militarine may inhibit the normal growth of hyphae through these pathways.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.466.2404.3217 Keywords Pleione bulbocodioides Phoma herbarum chemical composition antibacterial mechanism DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Assessment of the Allelopathic Effect, Antimicrobial Potential and Chemical Composition of Senecio anteuphorbium L. Essential Oil
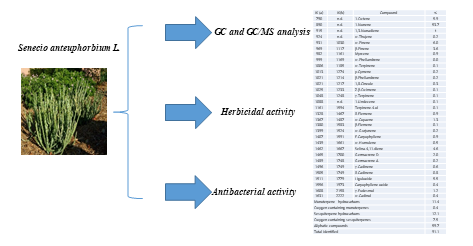
The essential oil of Senecio anteuphorbium L (Kleinia anteuphorbium L.) was isolated by hydrodistillation and analyzed by gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS). A total of 31 compounds were identified, with the dominant compounds being 1-nonene (53.7%), α-pinene (6%), 1-octene (5.9%), luguloxide (5.5%), and selina-4,11-diene (4.6%). The essential oil shows herbicidal activity against Phalaris canariensis, inhibiting seed germination and seedling growth at all concentrations tested (1-4 µL/mL). It also exhibits antimicrobial activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 6.9 and 13.8 µL/mL, respectively. These results suggest that the essential oil of S. anteuphorbium has the potential to be used as a natural herbicidal and antimicrobial agent. This work aims to carry out phytochemical investigations on the herbicide properties of this natural product.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.467.2311-2966 Keywords Senecio anteuphorbium L. essential oil 1-nonene antimicrobial activity herbicidal activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Two Cationic Indole Alkaloids from Ophiorrhiza japonica and Their Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity
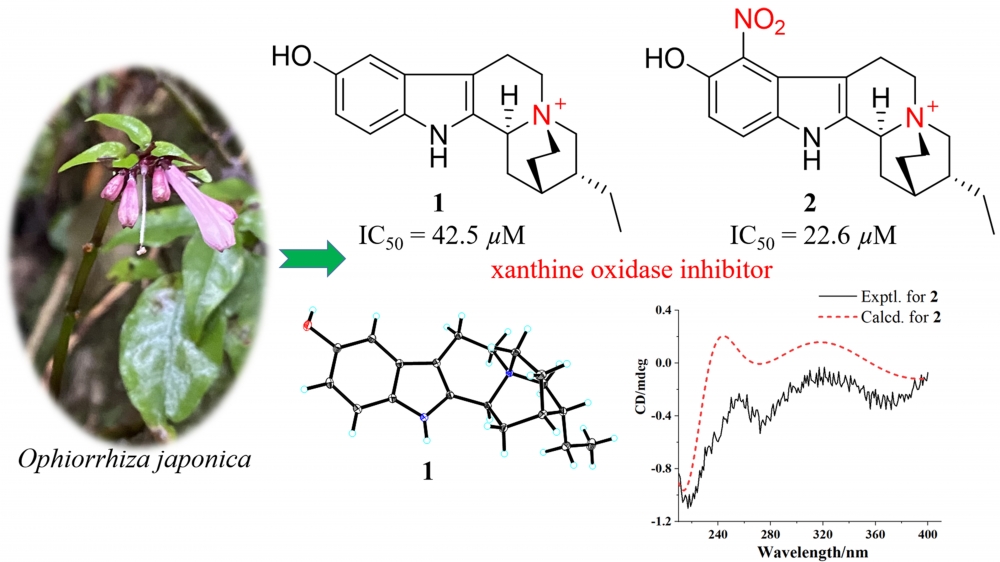
Two previously undescribed cationic indole alkaloids, named ophiorrhines L (1) and M (2), was isolated from the Ophiorrhiza japonica. The structures were elucidated based on spectroscopic data and quantum calculations as well as X-ray crystallographic analysis. Alkaloids 1 and 2 exhibited moderate inhibitory activities on XOD (Xanthine Oxidase) with IC50 values 42.5 and 22.6 µM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.469.2405.3235 Keywords Ophiorrhiza japonica indole alkaloids XO inhibitory effect DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) A New Benzofuran from the Heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera T. Chen and Its Protective Effect on Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in H9c2
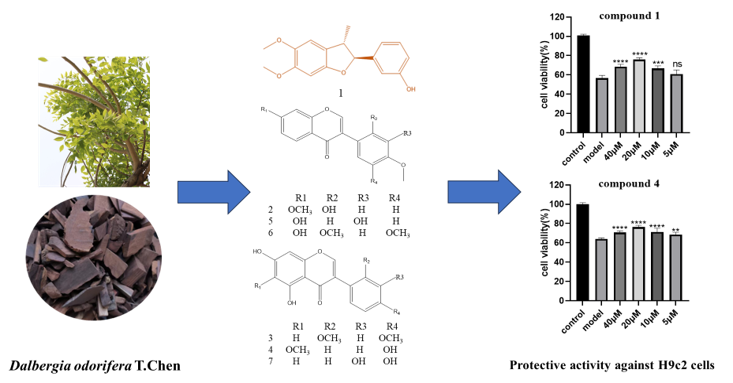
Abstract: A new benzofuran, named as (2S,3S)-5,6-dimethoxy-3-methyl-2-(3’-hydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran (1), along with the six known isoflavonoids, 2'-hydroxy-4',7-dimethoxyisoflavone (2), 2′-methoxybiochanin A (3), tectorigenin (4), calycosin (5), 7-hydroxy-2',4',5'-trimethoxyisoflavone (6) , orobol (7) were isolated from the heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera T.Chen. The structure of compounds was characterised by NMR spectroscopic data and comparisons with relevant literature data. The absolute structural configuration of compound 1 was determined through X-ray single crystal diffraction. Moreover, compounds 1-7 have no significant cytotoxic effects on H9c2 cells (IC50 > 200 µM). Compound 1-7 exhibit a significant protective effect against H/R (hypoxia/reoxygenation) induced H9c2 cell damage at 10~40, 5~40, 5~40, 5~40, 5~40, 5~40 and 5~10 µM (P<0.05).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.464.2404.3202 Keywords Dalbergia odorifera T.Chen benzofuran H9c2 hypoxia/reoxygenation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Streptolactone A, A New Antibiofilm Lactone Derivative from Streptomyces sp. A31
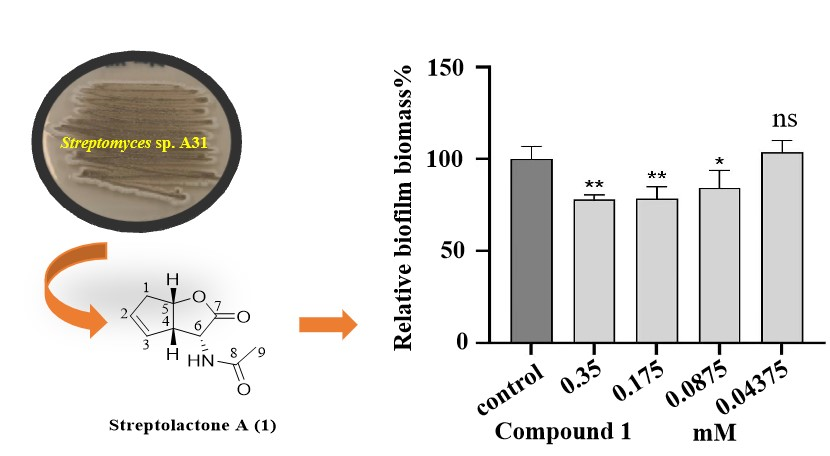
A novel lactone derivative, named Streptolactone A (1), was unearthed from Streptomyces sp. A31 isolated from marine sediments. Its structure was elucidated through a comprehensive analysis of 1D, 2D NMR, and HRESIMS data. Assessment of its antibiofilm and antibacterial effects against P. aeruginosa was conducted via the microdilution and crystal violet staining method, revealing Streptolactone A’s notable potency in inhibiting biofilm formation.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.465-2404-3193 Keywords Streptomyces sp. Streptolactone A antimicrobial antibiofilm DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) New Sulfureous Diketopiperazine from Roots of Moringa oleifera
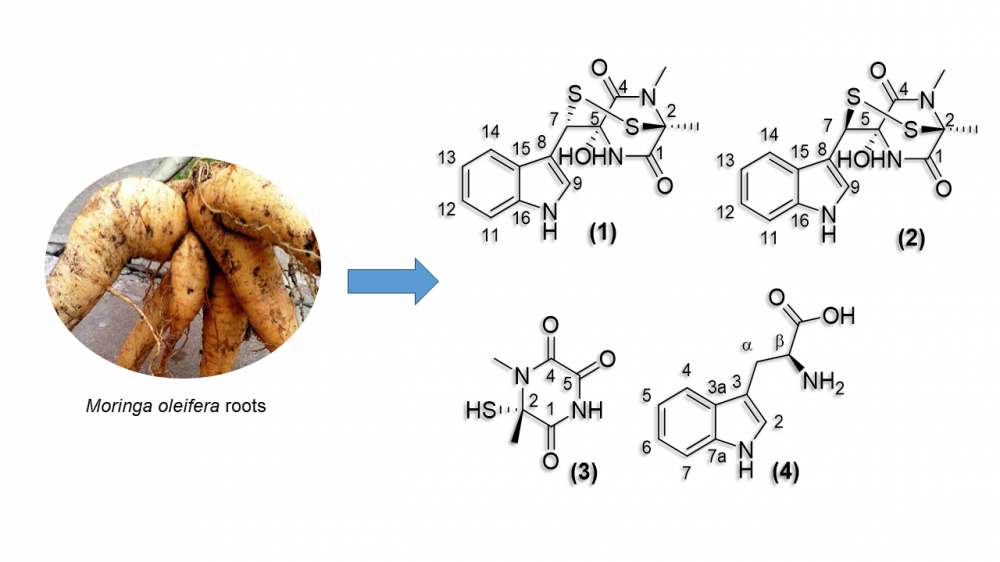
Phytochemical investigation of the roots of Moringa oleifera led to the isolation of a new sulfureous diketopiperazine, 7-epi lasiodipline D (1) together with its diastereomer, lasiodipline D (2), and two other known compounds. Structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated by HRESIMS, NMR, and ECD data. For the first time, sulfureous diketopiperazine derivatives (1-3) were obtained from the roots of M. oleifera.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.463.2403.3158 Keywords Moringa oleifera Moringaceae diketopiperazine 7-epi lasiodipline D lasiodipline D lasiodipline C DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Effect of Drying on the Quantity and Composition of Artemisia monosperma Essential Oil and Exploring the Bronchodilator Effect Using Guinea Pig Tracheal Muscles
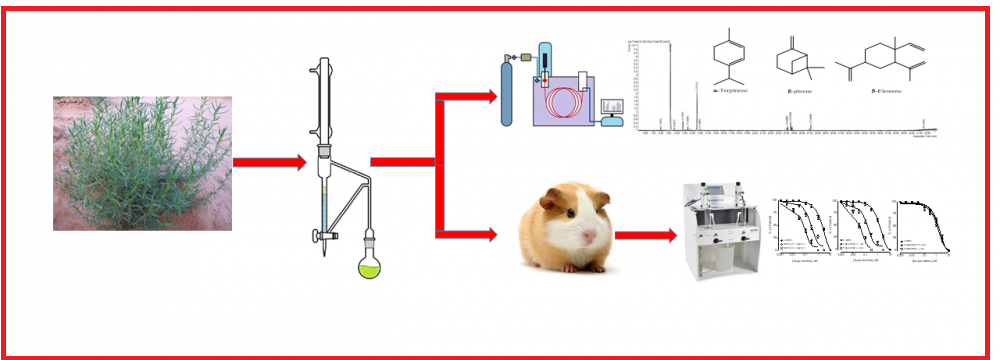
Artemisia monosperma is a plant with many traditional uses including some affecting smooth muscles. The A. momosperma essential oil (AMEO) prepared by hydrodistillation from fresh and dry aerial parts was compared qualitatively and quantitatively using GC/MS. The drying process affected the yield and composition of AMEO. The bronchodilator potential was explored using isolated guinea-pig trachea in ex-vivo organ bath setup. In the tracheal contractions induced by different spasmogens, AMEO was able to completely relax contractions induced by carbachol (CCh; 1 µM) and high K+ (80 mM) at closely related doses (p > 0.05) indicating a dual inhibition of phosphodiesterase enzyme (PDE) and voltage-mediated L-type Ca++ channels blocker (CCB) as papaverine. The current study provides scientific support to the medicinal use A. monosperma in respiratory disorders.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.470.2405.3233 Keywords Artemisia monosperma Essential oil GC/MS ex-vivo Guinea pig trachea mechanism DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.