Records of Natural Products
Year: 2025 Volume: 19 Issue:6 November-December
1) Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicity and structure-activity of Nerium oleander L.: A Systematic Review
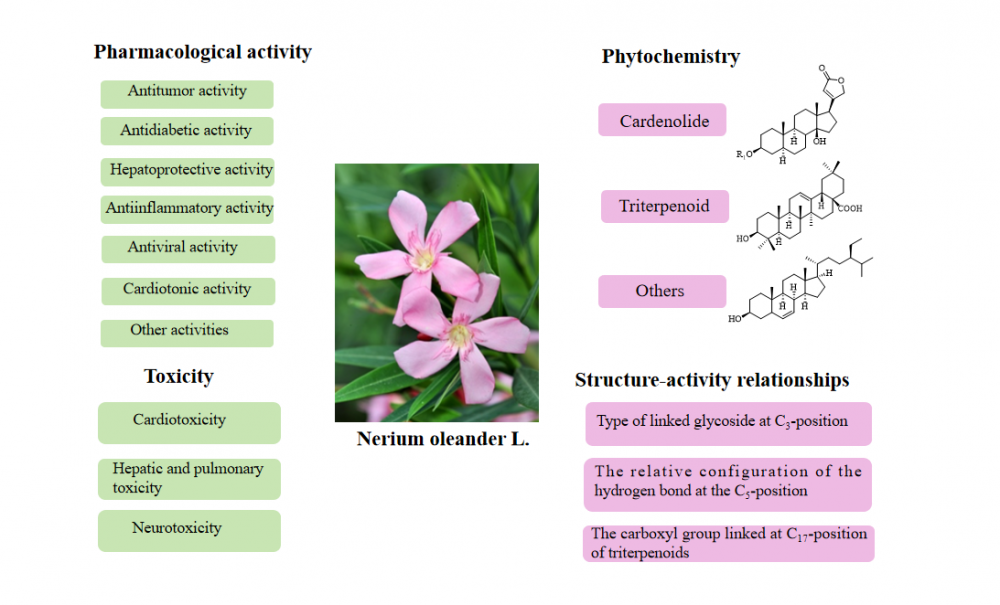
Nerium oleander L. is part of the Apocynaceae family and Nerium genus. Primarily found in subtropical areas, this plant is indigenous to the Mediterranean coast. It is also widely cultivated in China. To date, more than 146 compounds have been obtained from the plant, chiefly including cardiac glycosides, triterpenoids, phytosterols and other chemical constituents, of which cardiac glycosides are the main type of compounds with good pharmacological activity. Pharmacological studies have shown that N. oleander has anti-tumor, anti-diabetic, cardiotonic, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and other activities. This article provides important insights for future research, development, and use of this plant by summarizing the chemical contents, pharmacological properties, toxicity, and structure-activity connections of N. oleander over the previous 50 years.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.549.2506.3563 Keywords Nerium oleander L. phytochemistry pharmacology cardiac glycosides toxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Saganhaematenones: Novel Bioactive Natural Products, Derived from Haematococcus (Chlorophyceae) dSgH-K1 Strain, that Inhibit Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme
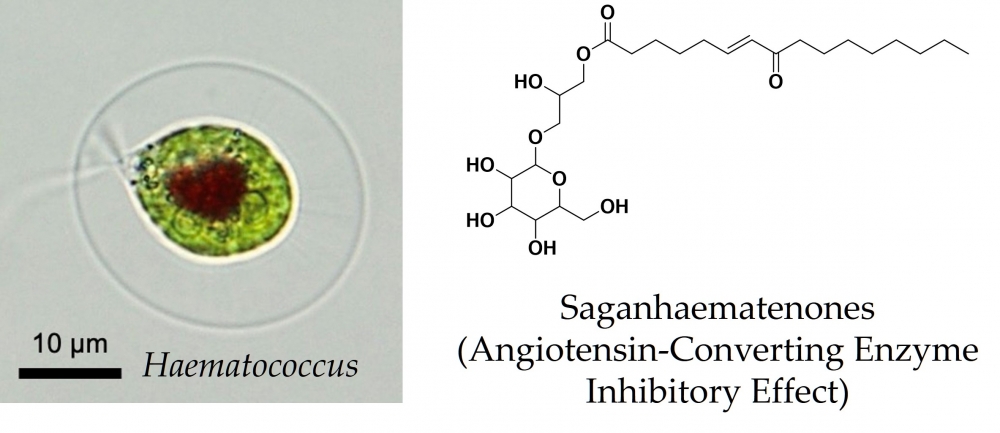
It is believed that microalgae biomass can be used in a variety of ways. However, their use is currently limited to specific fields, and there are a few applications of microalgae biomass in drug discovery. Numerous microalgae inhabit the world, and they likely produce unknown substances that contribute to human health. In this study, therefore, we used Haematococcus as a material to search for substances that were beneficial to human health. We tried to identify them using their blood pressure-lowering effect as an indicator, and then we succeeded in isolating two novel substances, saganhaematenone A and B. The structural analysis revealed that they belong to glyceroglycolipid and were analogues with a stereoisomeric relationship. Our findings suggest that microalgae biomass may also have beneficial effects on human health.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.550.2507.3585 Keywords Haematococcus microalgae angiotensin-converting enzyme bioactive molecules glyceroglycolipids saganhaematenone DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Phytochemical Variations in Ocimum basilicum L. Cultivars: Essential Oil Composition and Multivariate Chemotype Differentiation
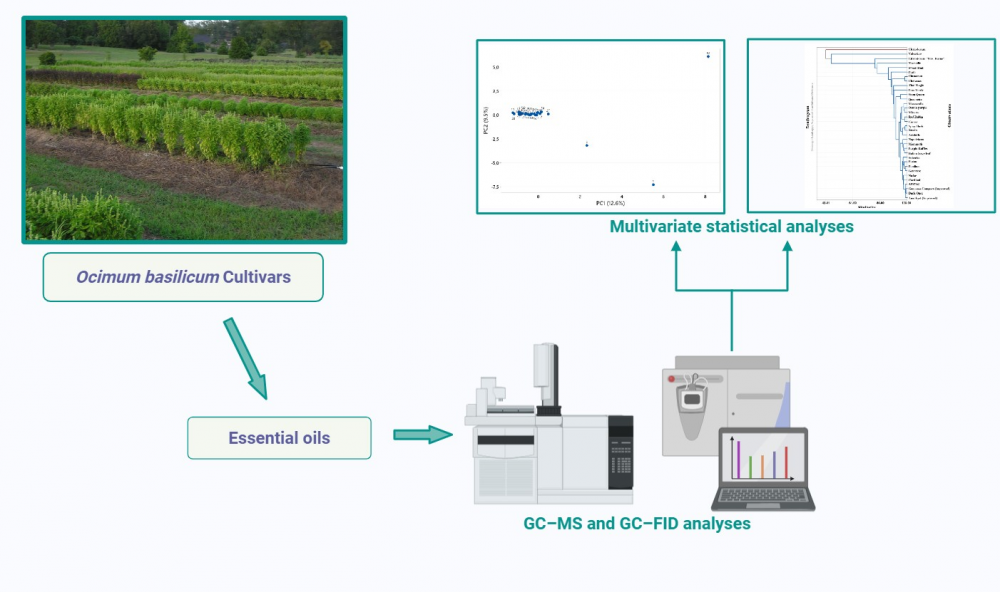
This study investigates the phytochemical variations among 34 cultivars of Ocimum basilicum to evaluate their essential oil composition and identify chemotaxonomic patterns. Understanding this variation is important for cultivar authentication, selection, and potential industrial or pharmacological applications. Essential oils were extracted via hydrodistillation and analyzed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS). To assess chemical variation and group cultivars based on their volatile profiles, principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) were applied. A total of 48 volatile compounds were identified across the cultivars. Linalool was the most abundant constituent, dominating in 28 cultivars with concentrations ranging from 24.2% to 81.1%. Methyl chavicol exhibited strikingly high levels in certain cultivars, reaching up to 82.0% in some samples. Cluster analysis revealed two major chemotype clades, with chemical similarity indices ranging from -33.07% to 90.84%, indicating substantial intra-specific variation and the potential for clear chemotaxonomic discrimination. The essential oil composition of O. basilicum cultivars exhibited marked variability, supporting classification based on chemotypic profiles. These findings enhance the understanding of chemotaxonomy within the genus and provide practical insights for cultivar selection in medicinal, aromatic, and commercial applications.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.545.2507.3597 Keywords Ocimum basilicum essential oils chemotaxonomy GC/MS multivariate analysis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Pearl Powder Exerts Antidepressant Effects by Modulating the GluN2A/BDNF/PSD-95 Signaling Axis
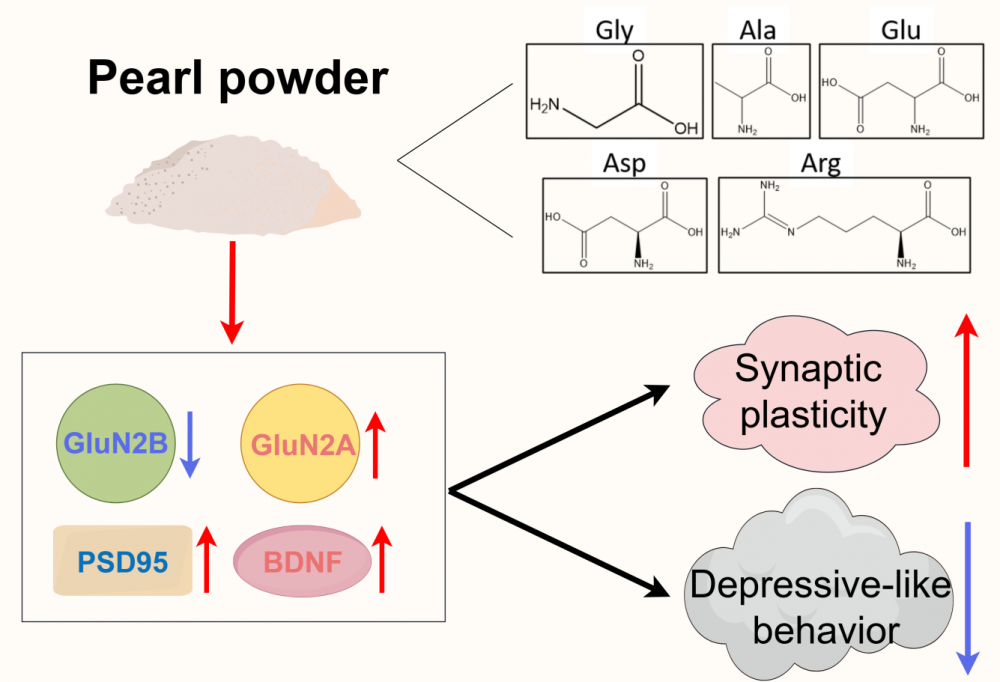
To evaluate the antidepressant-like effect of pearl powder in rats and explore its potential mechanism based on network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation. The chronic multiple mild stress (CMMS) rat model was applied to evaluate the effects of pearl powder on depression-like behaviors in rats through the sucrose preference test, forced swimming test, and tail suspension test. In addition, based on the identification of the major amino acid components of pearl powder, a network pharmacology analysis was performed to identify potential molecular targets of pearl powder. Subsequently, we compared the identified targets of pearl powder with depression-related targets by a Venn diagram and obtained the intersecting key genes. These genes were further used to construct PPI network and KEGG pathway analysis. Finally, Western blotting assay was applied to verify the protein levels of the relevant targets regulated by pearl powder to explore the underlying mechanisms. The behavioral tests showed that different doses of pearl powder (16.7 mg/kg, 83.3 mg/kg, and 166.7 mg/kg, administered once daily for one week by gavage) significantly improved the sucrose preference and alleviated depression-like behaviors in CMMS rats (FST: immobility time decreased by 12.34% ± 2.34%; TST: immobility time decreased by 12.03% ± 7.75%). After pretreatment of pearl powder with hydrochloric acid, the major amino acids in pearl powder were detected by an automatic amino acid analyzer, with top 5 (Gly, Ala, Glu, Asp, and Arg) accounting for more than 80% of the total amount. Network pharmacology analysis revealed that the top 5 active amino acids in pearl powder could regulate several targets such as CASP3, BDNF, MTOR, GluN2B, and MAPK1. The 84 key genes were also obtained after compared with depression-related target genes. In the following GO enrichment and KEGG pathway analysis, the top 10 items in the bubble plot indicated that pearl powder might exert anti-depression effects by regulating neuronal synaptic membranes and signal transmission. The next Western blot analysis verified that pearl powder could upregulate GluN2Aand synaptic-related proteins PSD-95 and BDNF, thereby improving the synaptic structure and function in the hippocampus. This study first clearly demonstrated that pearl powder significantly improved depressive-like behavior in CMMS rats. By combining network pharmacology and confirmatory experiments, it elucidated that the major active amino acids in pearl powder might participate in the repair of synaptic damage by regulating the expression of synaptic-related proteins, ultimately exerting its pharmacological activity against depression.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.551.2506.3569 Keywords CMMS rats depressive-like behavior pearl powder synaptic damage NMDAR DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
5) Trichothecene Sesquiterpenes with Anti-osteosarcoma Cytotoxicity from the Fungus Fusarium sp. XPW68
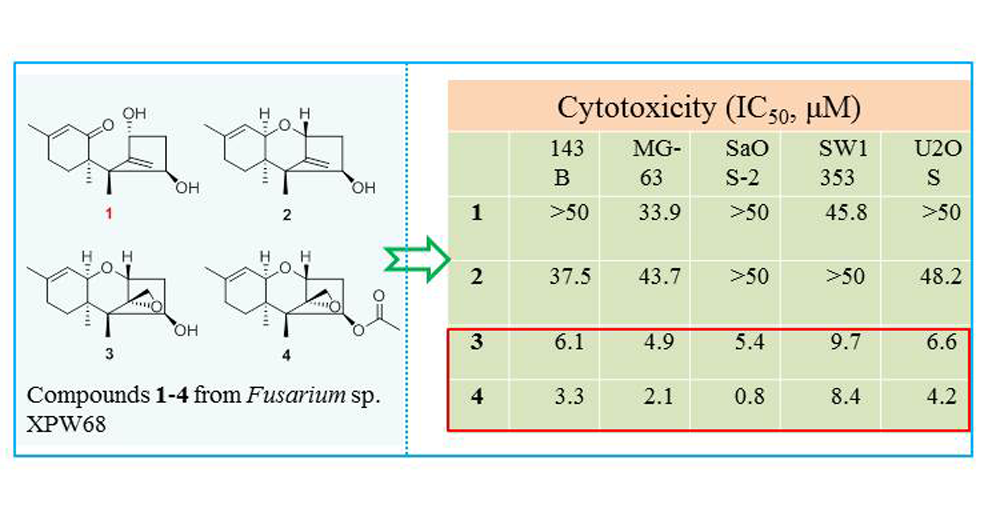
Fusarinene A (1), a previously undescribed trichothecene sesquiterpene, and three known compounds, 4β-hydroxytrichotheca-9,12-diene (2), trichodermol (3), and trichodermin (4), were isolated from the extract of Fusarium sp. XPW68. Their structures and relative configurations were identified by detailed analysis of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESIMS) data. In the cytotoxic assay, compounds 1-4 exhibited selective or potent inhibition against five human osteosarcoma cell lines including 143B, MG-63, SaOS-2, SW1353, and U2OS, with IC50 values ranging from 0.8 to 48.2 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.519.25.04.3479 Keywords Fusarium trichothecene sesquiterpene structure elucidation cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
6) A Novel Polyketide from the Endophytic Fungus Aspergillus puniceus
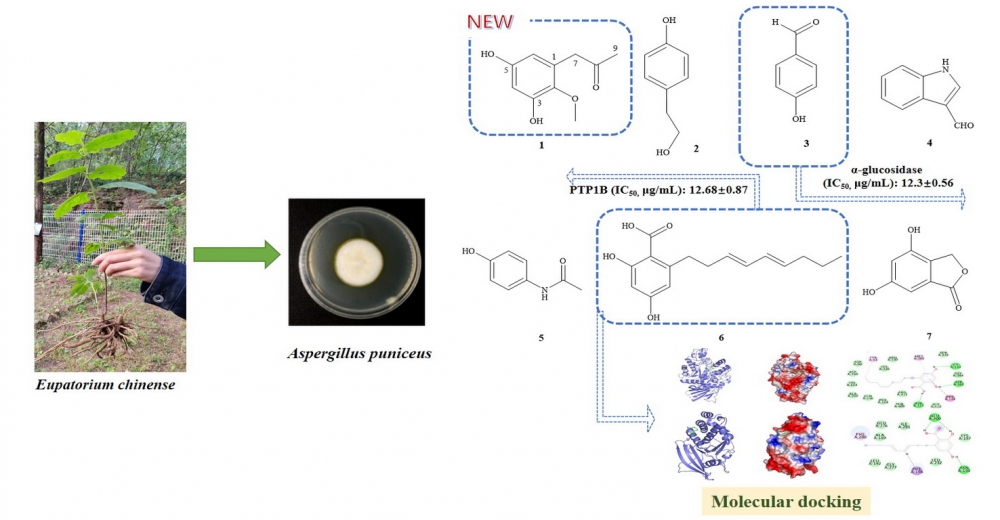
A novel polyketide, named Asperpropanol E, was found from the secondary metabolites of the endophytic fungus Aspergillus puniceus which was isolated from Eupatorium chinense L. In addition to this new compound, six known compounds were also identified. The structures of all compounds were elucidated through comprehensive chemical analysis utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) spectroscopic techniques. All isolated compounds were evaluated for biological activity by the MTT assay, compound 1 exhibited moderate inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), the IC50 (μg/mL) values of 31.63 ± 0.42 and 36.82 ± 0.54, respectively. Compound 3 demonstrated significant inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase (IC50 =12.3±0.56 μg/mL). Notably, compound 6 displayed potent dual inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase and PTP1B with the IC50 (μg/mL) values of 26.72 ± 0.63 and 12.68 ± 0.87, respectively. However, none of the tested compounds showed significant inhibitory effects on HGC-27 gastric cancer cells and HepG2 liver cancer cells.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.546.2504.3478 Keywords Aspergillus puniceus eupatorium chinense L endophytic fungi PTP1B Inhibition α-glucosidase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Heracleumate, A New Enynic Ester from the Roots of Heracleum rapula Franch
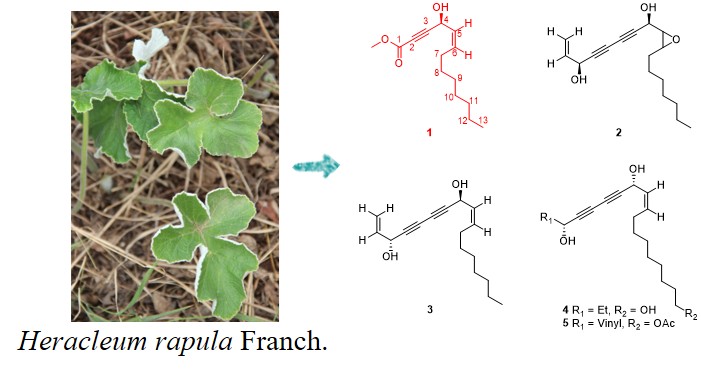
To discover new secondary metabolites and reveal the anti-inflammation effective ingredients of Heracleum rapula, a phytochemical investigation was performed, leading to one new enynic ester, heracleumate (1), and four polyacetylene diols, 9-epoxyfalcarindiol (2), 3(R), 8(S)-falcarindiol (3), oplopantriol B (4), and 18-Oacetyloplopantriol B (5) were isolated and identified. Their structures were established by spectroscopic analysis. Compounds 1, 2, 4, and 5 exhibited NO inhibition activities with IC50 values of 48.1 ± 1.9, 95.8 ± 6.2, 18.9 ± 2.0, and 88.7 ± 7.1 μM in RAW 264.7 cells treated with lipopolysaccharide. Among them, oplopantriol B (4) exhibited the best NO inhibition activity. Additionally, compounds 1, 2, and 4 can significantly reduce the levels of inflammatory cytokines, including COX-1, IL-6, iNOS, and TNF-α.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.547.2506.3552 Keywords Heracleum rapula Franch. enynic ester polyacetylene diol anti-inflammation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) An Undescribed Ingenane Glucoside Isolated from the Roots of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud and Its Anti-inflammatory Activity
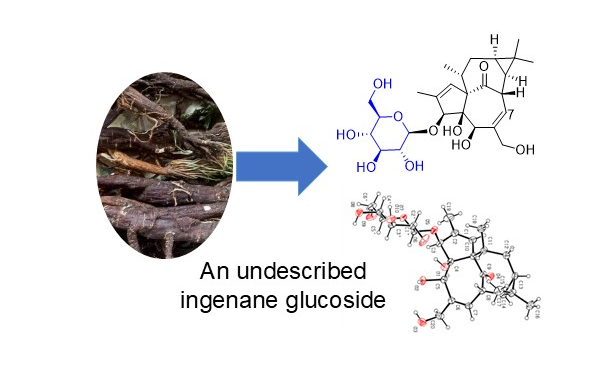
Abstract: A new compound, ingenol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (1) was isolated from the roots of Euphorbia fischeriana Steud. (Euphorbiaceae), together with four known compounds (2−5). The structure of compound 1 was characterized by a combination of spectroscopic techniques and X-ray crystallography. Moreover, biological evaluation revealed that compound 1 exhibited potent inhibitory effect on NO production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, with IC50 value of 25.24 ±3.48 μM.
DOI https://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.548.2507.3589 Keywords Euphorbia fischeriana Steud. Ingenol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside Anti-inflammatory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2025 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.