Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2022 Volume: 2 Issue:1 January-June
1) Mitigating Fluoride, Lead, Arsenic and Cadmium Toxicities in Laboratory Animals and Ruminants through Natural Products

Environmental pollutants are considered a serious health problem for humans and animals mainly ruminants in several regions of the world. Previously, many studies have investigated the mechanisms of toxicity of these pollutants on laboratory animals. Afterward, other studies have demonstrated that exposure to environmental pollutants may cause several adverse effects on the ruminant organs, influencing its performance and leading to socio-economic problems for breeders. Fluoride, lead, arsenic, and cadmium are the most common poisonings in ruminants, they can cause several irreversible toxic effects in many organs depending on the mode of action. The adverse effects of fluoride, lead, arsenic, and cadmium toxicities in laboratory animals and ruminants have been clearly summarized in this review. In addition, several results on protective or ameliorative effects by means of natural products against these toxicities in laboratory animals and ruminants have been illustrated.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.6.2202.2365 Keywords environmental poisonings laboratory animals ruminants toxicity mitigation natural products DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Development and validation of a primary IDMS method for the quantification of 12 sulfonamides in meat by using LC-MS/MS
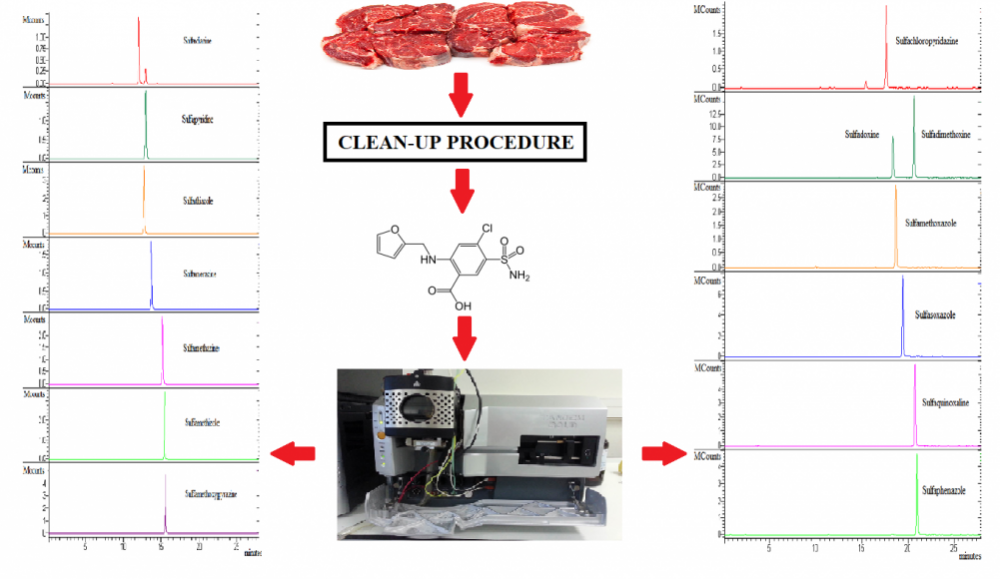
A new liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-IDMS) method was developed and validated for a simultaneous multi residue analysis of 12 sulfonamides (SAs) in beef meat. Sulfonamides were isolated from meat with a solvent extraction procedure. Reliable quantitative evaluation was accomplished by using each of the sulfonamides as the internal standart of their own isotopes. Matrix-matched calibration curves were used. Studied performance characteristics were linearity, recovery, precision, detection and quantification limits and robustness. Results were compatible to method performance acceptance criteria according to UME. Recovery results were 82-116%. Measurement uncertainty was calculated from “top down” approach”. Relative measurement uncertainty was between 7-14%.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.9.2204.2385 Keywords Sulfonamides IDMS method validation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Extraction of Cocoa Butter from by-product Cocoa Bean Shells by using SC-CO2 Extraction and Investigation of Flavour Profile and Antioxidant Capacities

Recently, sustainability in terms of making the life of humanity permanent is being by far the most important subject. In this study, the production of cocoa bean shell fat, a by-product obtained from supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) extraction, and cocoa butter were compared in terms of antioxidant capacity, fatty acid composition, and flavor profile. In addition, Soxhlet method was used for the comparison of extraction yield. Extract of cocoa bean shell was obtained by supercritical extraction method with 70% yield. Fatty acid composition and flavor profile were determined using Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) and Dynamic Headspace-GC/MS, respectively. The yield of the cocoa bean shell extract was 4.15% at Soxhlet and 15.09% and 10.31% at SC-CO2 extraction. The fatty acid constituents extracted using SC-CO2 ranged from 23.62% to 23.72% palmitic acid, 30.83% to 31.28% stearic acid, 32.19% to 32.41% oleic acid, and 9.35% to 9.61% linoleic acid. Physicochemical properties and fatty acid composition of SC-CO2 extracted cocoa bean shell fats content were found to be comparable to that of commercial cocoa butter. Antioxidant capacity of the obtained extract in terms of β-carotene linoleic acid method and total phenolic content were found to be lower than that of cocoa butter.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.7.2204.2419 Keywords Cocoa bean shell cocoa butter antioxidant capacity supercritical extraction sustainability green chemistry DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Determination of Fatty Acids Profile, Antioxidant, and Anticholinesterase Inhibitory Activities of Ganoderma lucidum collected from Swat, Pakistan
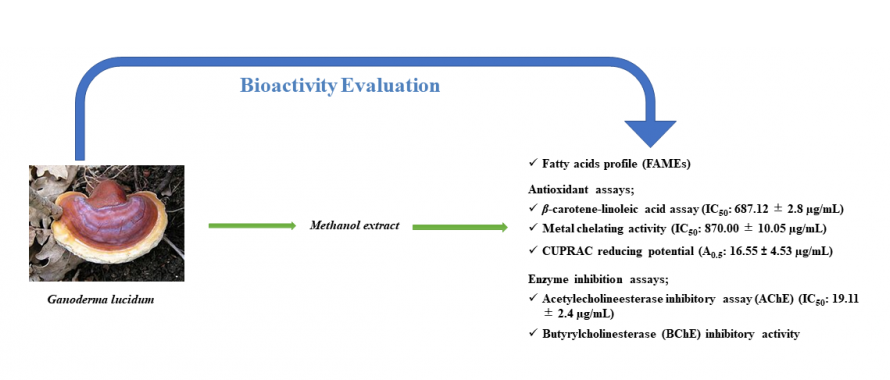
The current study was conducted on methanol extract of Ganoderma lucidum to evaluate its antioxidant, enzyme inhibition activities, and fatty acids profile. The dominant fatty acids were found to be linoleic acid (53.6 %), oleic acid (24.2 %), and palmitic acid (11.5 %) among the 10 different fatty acids detected in the methanol extract using GC/MS techniques. Fatty acids groups like C14:0, C15:0, C16:1, C17:0, C17:1, C18:0, and C18:3 were also found from trace to middle amount (0.15 %, 0.15 %, 1.11 %, 0.26 %, 0.27 %, 2.85 %, and 5.9 %) respectively. Polyunsaturated fatty acids concentration of G. lucidum exposed the significance for lowering the blood cholesterol level. Methanol extract of G. lucidum showed significant antioxidant potential against β-carotene-linoleic acid assay (IC50: 687.12 ± 2.8 µg/mL), metal chelating activity (IC50: 870.00 ± 10.05 µg/mL), and CUPRAC reducing potential (A0.5: 16.55 ± 4.53 µg/mL) respectively. The CUPRAC assay supports the lipid peroxidation inhibitory activity results. Against AChE enzyme, methanol extract of G. lucidum demonstrated IC50 value 19.11 ± 2.4 µg/mL, while exhibited weak butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitory activity (IC50 > 100 μg/mL). Thus, Ganoderma lucidum may defend people in contradiction of free radical damage, and may be an important source of potential new acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory drugs.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.10.2202.2368 Keywords Ganoderma lucidum fatty acids profile antioxidant anticholinesterase inhibitory activity medicinal edible mushroom DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Optimization of Assay Conditions for t-RNA by Experimental Design
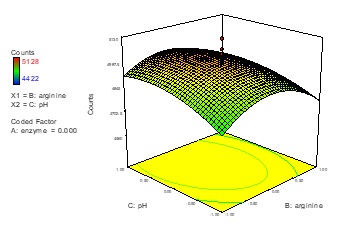
A design of an experiment is generally to fictionalize an execution of an experimental process and the term of experimental design strategy usually refers to a two-stage modeling. The first of all named as working strategy is the determination of the experimental execution model and the last one is that a mathematical model for response surface function to define the relationship between the experimental factors. In this work, it was selected optimization of assay conditions for t-RNA using Central Composite Design, the influence of three factors, namely pH, enzyme concentration and amino acid concentration as an experimental design application, and improved an experiment strategy in order to optimize the effective operation factors on this chemical reaction and mathematical solution techniques of the response surface function. As examining of the coefficients of the response surface equation and its graphics, we can say that the most effective parameter on the esterification process is enzyme concentration alone and together with pH.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.8.2204.2430 Keywords Experimental design statistics optimization response surface t-RNA DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.