Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2024 Volume: 4 Issue:1 January-June
1) Terpenoid Composition of Salvia plebeia R. Br.: Its Antioxidant and Antifungal Potential
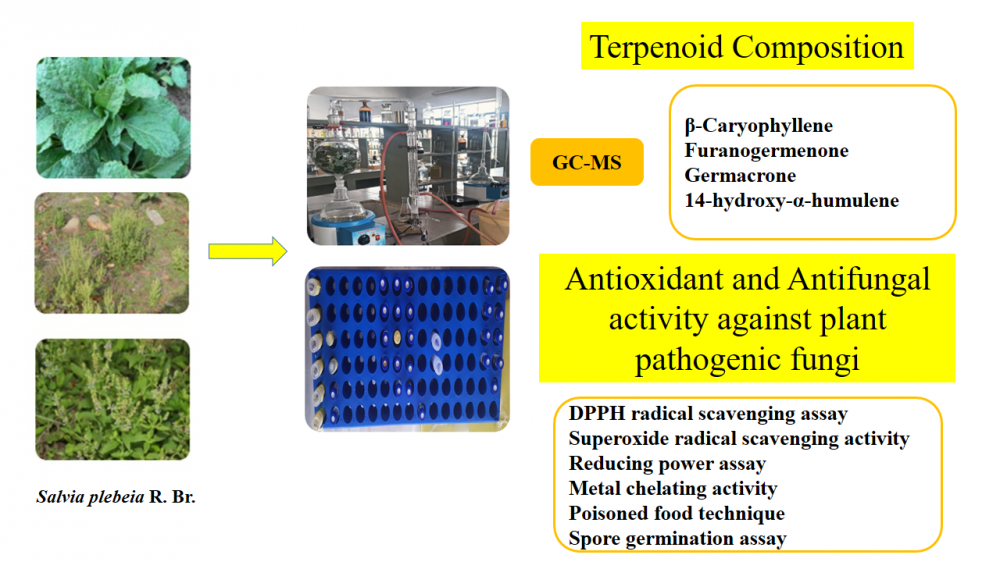
The GC-FID and GC-MS analysis of the essential oil of areal parts of Salvia plebeia, led to identification of 32 compounds constituting 93.8 % of the essential oil (EO). EO of this plant was dominated by sesquiterpenoids (49.4%) with major presence of β-caryophyllene, furanogermenone, germacrone and 14-hydroxy-α-humulene. Antioxidant activity determined by DPPH and super oxide radical scavenging, metal chelating and reducing power assay, though the EO showed lower activity than the standard antioxidants but possessed significant reducing power. The in vitro antifungal activity of EO against phytopathogens was determined by poisoned food method. EO showed strong inhibitory effect on the mycelial growth against all phytopathogens with an IC50 values ranging from 180.5 to 372.9 µg/mL and MIC ranging from 1500 to 3000 µg/mL. Among the test fungi, three fungi, viz., Helminthosporium maydis, Curvularia lunata and Albugo candida were highly susceptible for the oil in spore germination assay with their IC50 value 246.9, 263.8 and 316.8 µg/mL, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.84.2402.3108 Keywords Salvia plebeia Chemical composition antioxidant activity antifungal activity essential oils β-caryophyllene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Validation of a UV-VIS-NIR Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Sodium Benzoate in Water

Abstract: Sodium benzoate is a widely used food preservatives and its determination receives much interest. This article describes the development and validation of a method using a UV-VIS-NIR Spectrophotometer at 225 nm to determine the mass fraction of sodium benzoate in water for the purpose of characterization of a reference material. The study was carried out in accordance with the ICH and EURACHEM guides using a primary reference material of sodium benzoate of purity 99.98±0.22%. The studied performance characteristics were the limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), selectivity, linearity, accuracy, precision, recovery and bias. The results obtained were statistically analyzed and the method showed very good linearity in the selected calibration range. The LOD and the LOQ were found 0.19 and 0.57 mg/kg respectively. This method demonstrated very good accuracy ranging from 99.54 to 100.08% and precision, 0.39% RSD, signifying its high reliability in producing precise and accurate results. The validation results also revealed that the method is fit-for-the purpose of determination of sodium benzoate in water.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.83.2403.3167 Keywords Sodium benzoate UV-VIS-NIR Spectrophotometer validation linearity precision accuracy DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Research on the Characteristic Properties of Viburnum opulus Nectar Fermented with Water Kefir Grains§
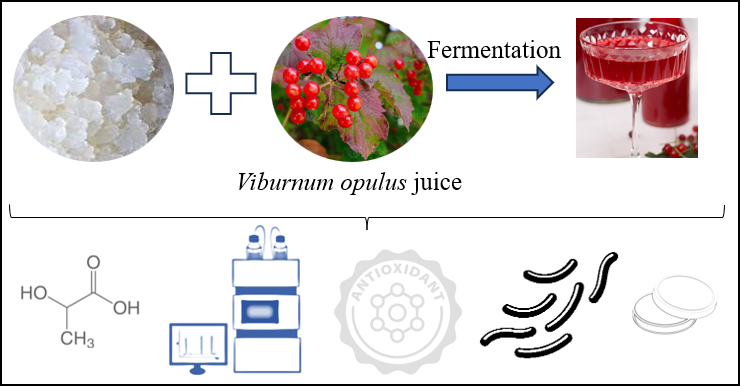
Water kefir is produced by fermenting a plant-based carbon source with water kefir grains under favorable conditions. The resulting drink had unique sensorial properties, high antioxidant capacity, and probiotic microorganism content. In this study, water kefir grains were used for fermentation of nectar obtained from Viburnum opulus for 24 hours at 25°C. The study investigated the fermented beverage's organoleptic, physico-chemical, antioxidant capacity, and microbiological content. The results showed that the sensory evaluation of the water kefir beverage obtained by fermenting V. opulus was generally low, but the product's color and fermented odor were highly appreciated. Lactobacilli spp., Lactococci spp., and yeast counts were approximately 6 log cfu/mL after fermentation. Even though the total soluble solids amount value was as low as 1.0, the microbial development in the plant nectar was favorable. Following the fermentation, there was a significant increase in the concentrations of malonic acid, lactic acid, citric acid, and propionic acid (P<0.05). Our sample color had a slightly red-yellow mixture based on instrumental color analysis. The total antioxidant capacity was determined as 937 mg GAE/L based on the results of the antioxidant capacity analysis. The conclusion was that V. opulus is a suitable substrate for fermentation with water kefir grains despite the low overall sensorial evaluation of the product.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.85.24.03.3155 Keywords Antioxidant capacity fermentation Viburnum opulus water kefir DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Comparision of Nutritional Value of Salmon and Sturgeon Caviar

This review examines the differences physical and nutritional properties of sturgeon and salmon caviar. When examining their physical characteristics, sturgeon caviars are characterized as smaller and blackish color roes, while salmon caviars are characterized as larger and reddish-hued roes. There is no similarity between salmon caviar and sturgeon caviar in terms of both color and size. Considering the nutritional value, salmon roe has higher protein composition than sturgeon roe. Although sturgeon caviar has a higher total lipid composition, salmon caviar has higher omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) like EPA and DHA. Salmon caviar which is a caviar substitute, has a more favorable profile in terms of nutrition. Additionally, it appears as a cheaper alternative for caviar consumption.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.86.2403.3161 Keywords Caviar sturgeon salmon fatty acid protein DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Cellular Seafood: Current Challenges to Overcome for the Development of Cellular Seafood
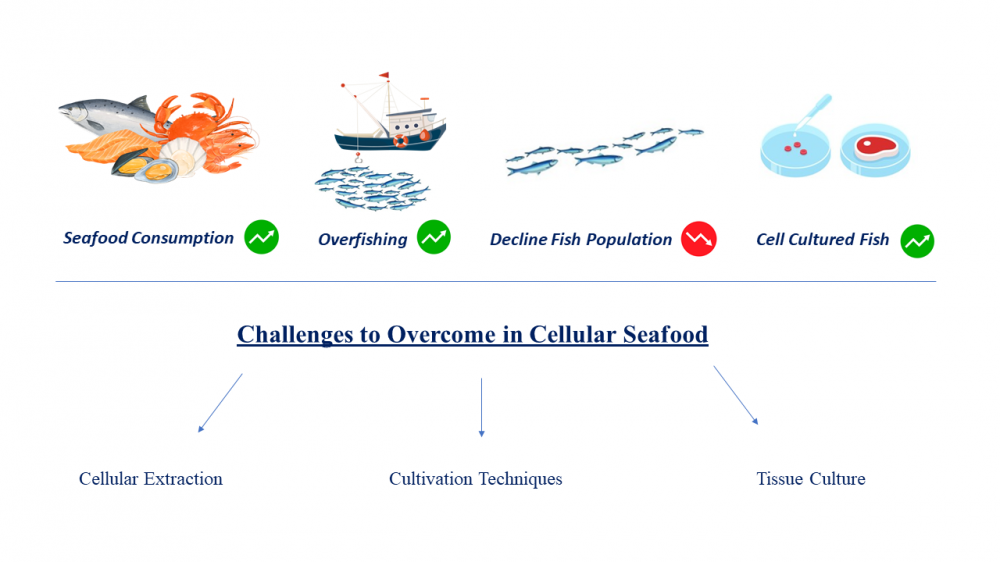
Worldwide, seafood accounts for nearly 20% of annual animal protein consumption, and its production is critical to ensure global food and nutrition security. The increase in seafood demand has resulted in overfishing and caused a decrease in aquatic species. Aquaculture or fish farming, includes breeding, growing, and harvesting fish and aquatic products in a controlled environment; It is the first solution to overfishing. To supply sufficient seafood for the growing demand, the alternative seafood industry provides promising opportunities. Cell-based seafood refers to seafood that is produced using cell and tissue culture without slaughtering the animal. This method, called cellular agriculture, has been adopted from regenerative medicine that uses advanced isolation and cultivation techniques of tissue culture. To serve as a credible alternative to traditional seafood, cellular seafood should be efficiently produced and should mimic seafood in all its physical sensations, such as visual appearance, smell, texture and of course, taste. The efficient culture of cells used for production of cellular seafood primarily depends on stem cells, cell culture conditions including incubation temperature and medium composition. Many of these variables should be known and optimized for each species. Overall, this review underscores the importance of further research in cell culture to advance the field of cultured seafood and promote sustainable seafood production.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.24.2403.3162 Keywords Cellular seafood stem cells cultivated meat lab-grown meat cell culture DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.