Records of Natural Products
Year: 2020 Volume: 14 Issue: 1 January-February
1) Roselle Seed Oil and its Nano-Formulation Alleviated Oxidative Stress, Activated Nrf2 and Downregulated m-RNA Expression Genes of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in Paracetamol-intoxicated Rat Model
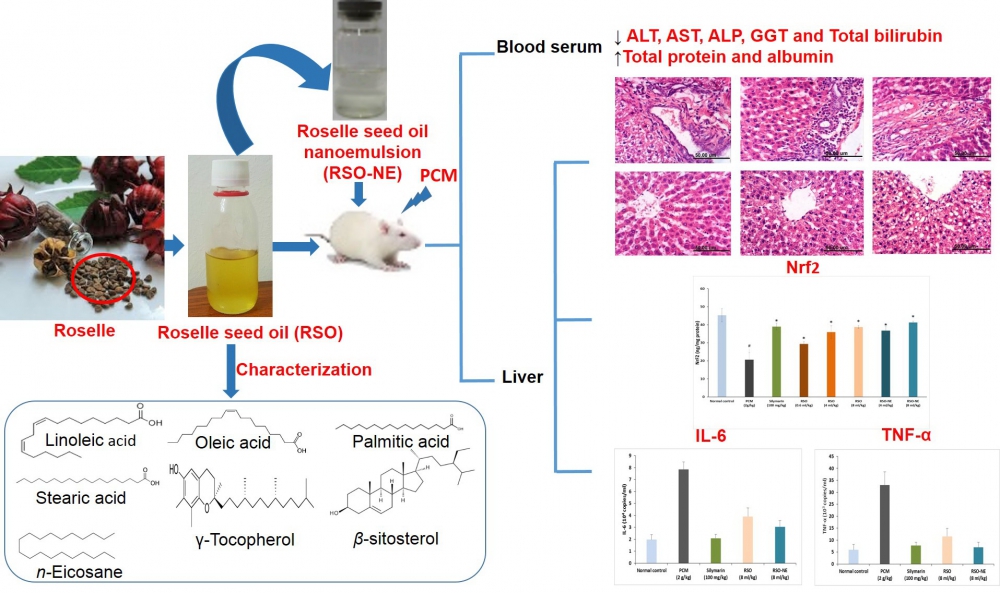
Abstract: Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) seeds, traditionally used in liver disorders, have recently attracted more attention as a new source of healthy edible oil with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. However, its hepatoprotective effect has not been explored yet. In the current study, the hepatoprotective potential of roselle seed oil (RSO; 0.6, 4 and 8 ml/kg) and its nano-formulation (RSO-NE; 4 and 8 ml/kg), and their possible underlying mechanism were investigated in a paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity rat model, compared to silymarin. RSO and RSO-NE protected the liver against paracetamol-intoxication and maintained the overall architecture of liver tissues in a dose dependent manner. Additionally, hepatic nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor2 (Nrf2) and glutathione (GSH) increased significantly in pre-treated groups, while malondialdehyde (MDA) decreased. Moreover, RSO and RSO-NE significantly inhibited paracetamol-induced mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6). Chemical analysis of RSO showed fatty acids (mainly linoleic, oleic, palmitic and stearic acids), n-eicosane, β-sitosterol and tocopherols as the major constituents, which contributed synergistically to its protective effect. The efficacy of RSO-NE (8 ml/Kg) was superior to its corresponding unformulated oil (0.6 ml/kg), indicating its enhanced bioavailability. These findings encourage the use of RSO in development of health promoting products such as food supplements, functional food and nutraceuticals for the prevention of liver disease.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.133.19.03.1220 Keywords Hepatoprotective Hibiscus sabdariffa Nanoemulsion Nrf2 Pro-inflammatory cytokines Tocopherols DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Aspterrics A and B, New Sesquiterpenes from Deep Sea-derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10

Two new sesquiterpenes, namely aspterric A (1) and aspterric B (2), together with aspterric acid (3), were isolated from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10. The structures of aspterrics A and B were determined by NMR and HRESIMS data. Biogenetically, aspterrics A and B were assumed to be the intermediates to derive aspterric acid.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.131.19.04.1247 Keywords Aspergillus terreus deep-sea-derived fungus sesquiterpenoids aspterrics A and B DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Docking Studies and Antiprotozoal Activity of Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Scrophularia Syriaca Benth. Growing in Saudi Arabia
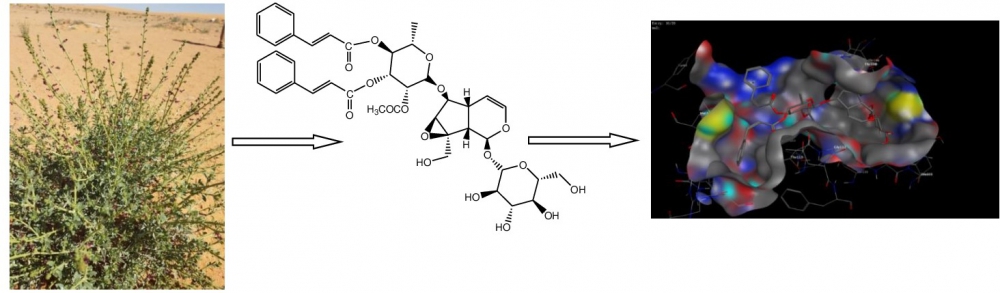
Phytochemical study of the ethanolic extract of Scrophularia syriaca Benth. was attained by chromatographic and spectroscopic procedures, which resulted in isolation of eight compounds; 6-O-α-L- rhamnopyranosylcatalpol (1), scropolioside B (2), gmelinoside-L (3), 8-acetyl harpagide (4), scropolioside D (5), scropolioside D2 (6), quercetin (7) and kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside (8). The antiprotozoal activity was evaluated against Trypanosoma brucei brucei (s427-WT), Trypanosoma brucei brucei (TbAT1-B48), Leishmania major and Leishmania mexicana. Compounds 2, 5, 7 and 8 exhibited mild to moderate activities against kinetoplastid parasites compared to pentamidine positive control, the mechanism of antiprotozoal activity was predicted by the molecular docking studies on the target enzyme Trypanosoma brucei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (TbGAPDH).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.19.03.1224 Keywords docking iridoids Leishmania Trypanosoma Scrophularia syriaca DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Chemical Constituents of Croton thurifer Kunth as α-Glucosidase Inhibitors

Phytochemical investigation of Croton thurifer, collected in Loja-Ecuador, led to the isolation of seven known compounds identified as: (3R, 20S) -3-palmitate-20-hydroxydammar-24-ene (1); (3R, 20S)-3-acetoxy-20-hydroxydammar-24-ene (2); trans-phytol (3); vomifoliol (4); β-sitosterol (5); trans-tiliroside (6) and sparsifol (7). The structures of the isolated compounds were determined by NMR, MS, as well as by comparison with literature data. The hypoglycemic activity of the crude extracts and isolated compounds was assessed by their ability to inhibit α-glucosidase activity. The hexane and methanol extracts did not show any inhibitory activity on α-glucosidase, while the ethyl acetate extract (EtOAc) showed very low inhibitory activity with IC50= 1.77 mg/mL. Two of the seven isolated compounds exhibited good inhibitory activity with IC50 values much higher than acarbose (377 μg/mL). trans-tiliroside was the compound with the highest inhibitory activity (IC50 = 114.85 μg / mL), while (3R, 20S)-3-Acetoxy-20-hydroxydammar-24-ene had moderate inhibitory activity (IC50=292.87). Trans-tiliroside exherted a non-competitive inhibition with Km values between 368 and 358 μM and Vmax value from 695 and 325 nM/min for unhibited and inhibited reaction, respectively and a Ki of 163,6 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.136.18.11.1069 Keywords Croton thurifer α-glucosidase trans-tiliroside (3R, 20S)-3-Acetoxy-20-hydroxydammar-24-ene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Induced Lipase Inhibitors from Endophytic Phomopsis sp. 0391
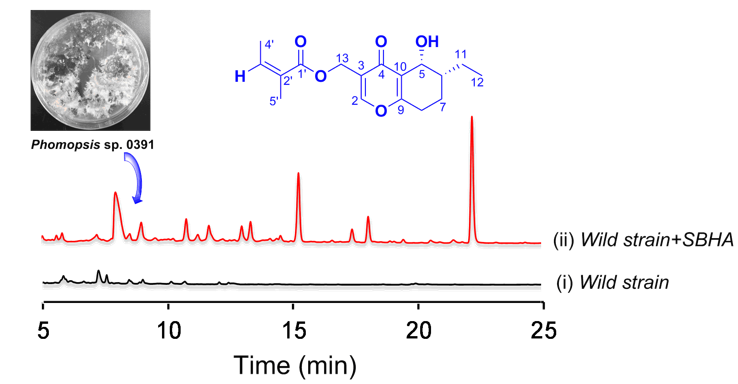
Abstract: Seven compounds including a new one named as 13-angeloyloxy-diplosporin (1) were isolated from the endophytic Phomopsis sp. 0391 cultivated in the presence of a histone deacetylase inhibitor. All of these isolates were evaluated for lipase suppressive activities and we firstly found that compounds cytosporone B (5) and dothiorelone A (6) displayed significant lipase inhibited activities compared to the positive control (Orlistat, IC50 = 43 μg/mL) with the IC50 values at 115 and 275 μg/mL, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.134.19.01.1243 Keywords Natural products Endophytic fungi Chemical epigenetics approach Lipase inhibitor DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Bioassay-guided Isolation and Identification of Anti-inflammatory Sesquiterpene Lactones from Chrysophthalmum montanum (DC.) Boiss.
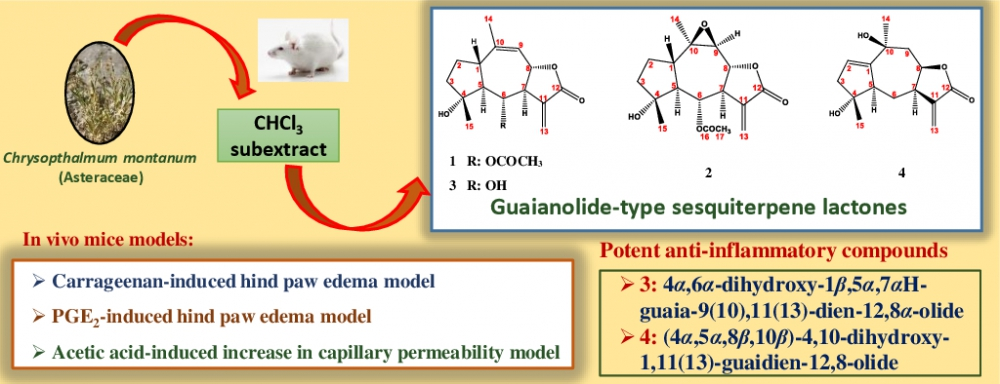
The aerial parts of Chrysophthalmum montanum (DC.) Boiss. (Asteraceae) is traditionally used for wound healing, as well as for the treatment of common cold, sinusitis, and other inflammatory diseases. The objectives of this study were to identify potential anti-inflammatory effects of the methanol extract, and its different polarity subextracts (n-hexane, chloroform, n-butanol, and remaining aqueous), and guaianolide-type sesquiterpene lactones [6α-acetoxy-4α-hydroxy-1βH-guaia-9.11(13)-dien-12.8α-olide (1), 6α-acetoxy-4α-hydroxy-9β.10β-epoxy-1βH-guaia-11(13)-en-12.8α-olide (2), 4α,6α-dihydroxy-1β,5α,7αH-guaia-9(10),11(13)-dien-12,8α-olide (3), and (4α,5α,8β,10β)-4,10-dihydroxy-1,11(13)-guaidien-12,8-olide (4)] from the aerial parts of C. montanum. In order to evaluate the anti-inflammatory activity of C. montanum, carrageenan- and PGE2-induced hind paw edema, and acetic acid-induced increase in capillary permeability mice models were used. The methanol extract, the chloroform subextract, and compounds 3, and 4 were shown to possess anti-inflammatory activity in in vivo models at 100 mg/kg dose. The results provide a biological, and phytochemical basis for the traditional use of C. montanum aerial parts for inflammatory conditions in Turkish folk medicine.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.135.18.11.1074 Keywords Asteraceae Chrysophthalmum montanum sesquiterpene lactones anti-inflammatory carrageenan prostaglandins DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Two Novel Sesquiterpenes and A New Pregnane Derivative from the South China Sea Gorgonian Subergorgia suberosa
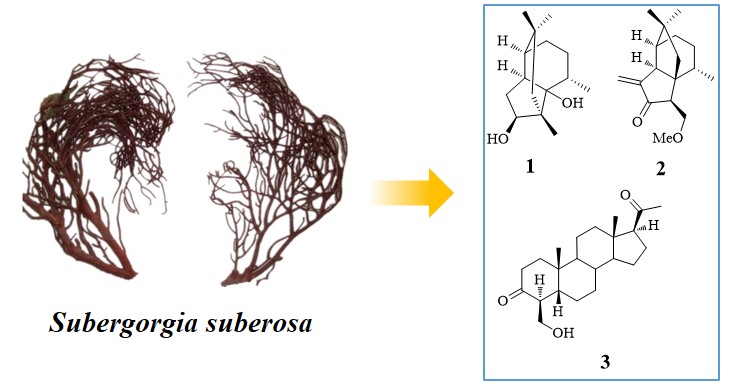
Two novel sequiterpenes isosuberosenol A (1), suberosain A (2), and a new pregnane derivative 4-hydroxymethyl-5β-pregnan-3, 20-dione (3) have been isolated from the South China Sea gorgonian Subergorgia suberosa. Their structure and relative stereochemistry were established based on the detailed spectroscopic analysis, including HR-ESI-MS, 1D- and 2D NMR spectra. The skeleton of isosuberosenol A (1) have been previously undescribed. The discovery of isosuberosenol A (1) provides some strong support for the plausible biogenetic pathway of quadrone type sesquiterpenes.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.137.19.04.1257 Keywords sesquiterpene pregnane derivative Subergorgia suberosa DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Comparative Effects of Flavonoids from Fructus Sophorae on Rat Osteoblasts in vitro
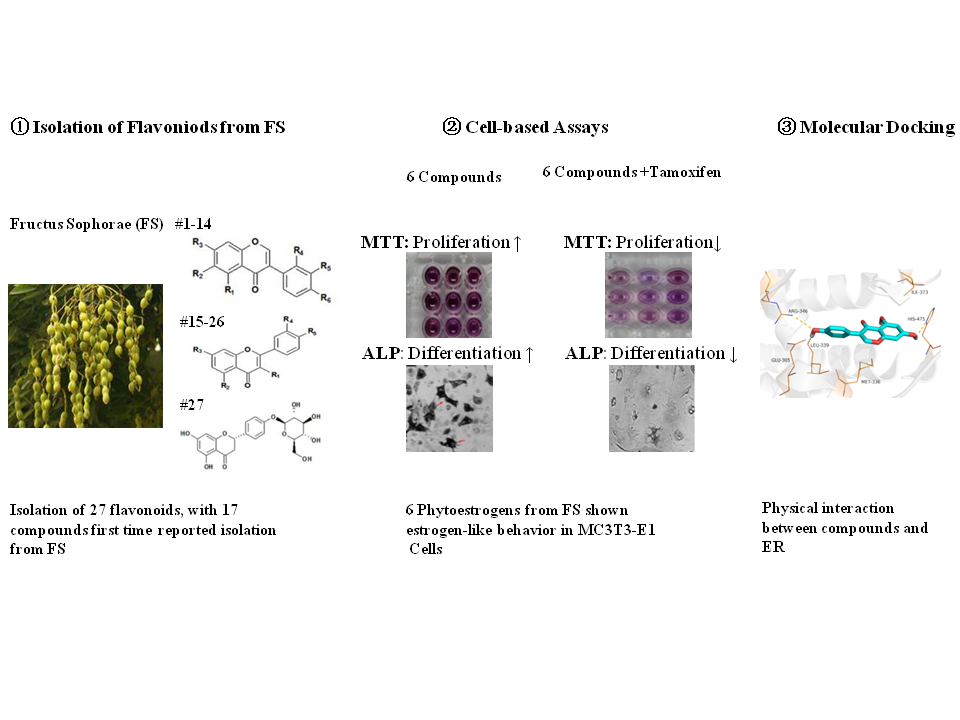
Fructus Sophorae (FS), the dry mature fruit of Sophora japonica Leguminosae, is a valuable traditional Chinese medicine resource with flavonoids as the major active ingredients. To identify the plant-derived estrogen-like flavonoids serving as potential osteoporosis chemopreventive agents, we isolated and identified 27 flavonoids compounds, including 17 compounds obtained for the first time from FS. To screen out the flavonoids with estrogen-like biological behavior from the 11 high yield compounds, we set up an in vitro screening system in rat osteoblast MC3T3-E1 cells including MTT assay, alkaline phosphatase staining and Alizarin red S staining assay to examine the effects on cell proliferation, differentiation and mineralization of osteoblast cells respectively. Six flavonoids, including genistein, sophoricoside, sophorabioside, sophoraflavonoloside, nicotiflorin and rutin, significantly increased the cellular activity of MC3T3-E1 cells. Furthermore, blocking the estrogen receptor signaling by tamoxifen compromised the effects above significantly, suggesting the 6 compounds behave as estrogen-like reagents. Moreover, the interaction between the six flavonoids from FS and estrogen receptor was clarified by molecular docking method from Glide XP. Collectively, being used as food and medicine in China, FS is rich in flavonoids with estrogen-like effects, may be used as healthy supplementary in treating postmenopausal women osteoporosis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.138.19.04.1262 Keywords Fructus Sophorae Flavonoid Phytoestrogens Estrogen Receptor Osteoporosis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Inhibition of iNOS Induction and NF-κΒ Activation by Taste Compounds from the Edible Mushroom Tricholoma caligatum (Viv.) Ricken

Abstract
Tricholoma caligatum (Viv.) Ricken is an edible mushroom that belongs to matsutake group. The first chemical investigation of the three different extracts of Tricholoma caligatum resulted in two new compounds, 8-demethoxylascivol (1) and 8-epi-lascivol (2) and six known compounds, lascivol (3), trametenolic acid (4), ergosterol (5), ergosterol peroxide (6), 5a, 6a-epoxyergosterol (7), and cerebroside B (8). Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic analyses including 1D and 2D NMR data. The biological activities of all the compounds were evaluated toward multiple targets related to inflammation and metabolic disorder such as NF-κΒ, iNOS and ROS. The findings of this study reveal that the edible mushroom Tricholoma caligatum could be a potential source for anti-inflammatory bioactive metabolites.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.139.19.04.1263 Keywords Tricholoma caligatum iNOS NF-κΒ anti-inflammatory lascivol DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Natural Glycosides from Indigofera stachyoides radix
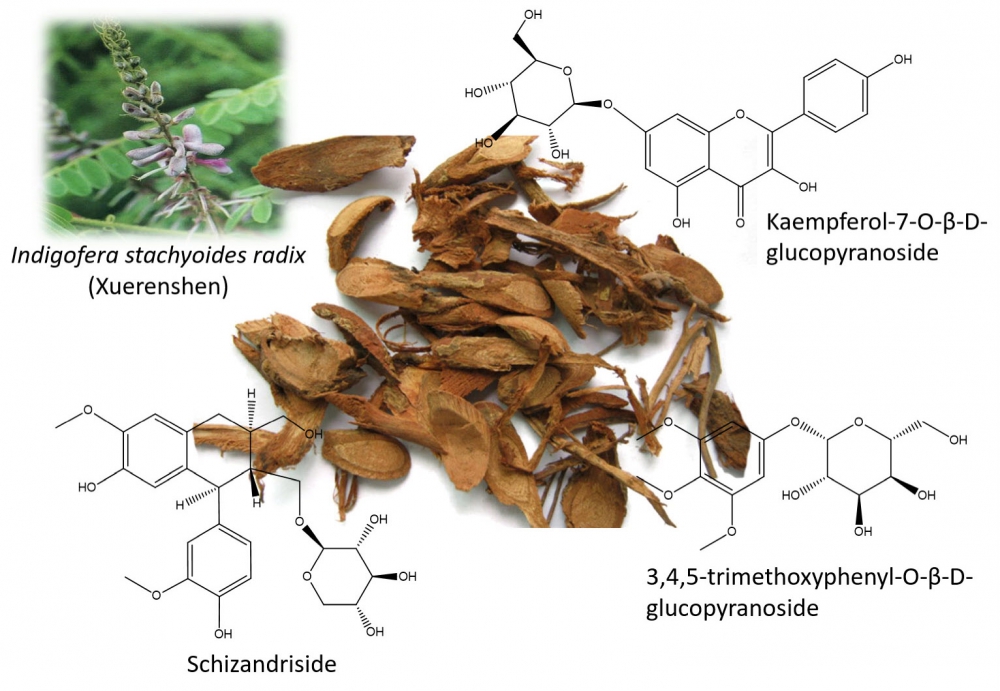
Six natural polar glycosides were isolated and identified from indigofera stachyoides radix, they were identified as β-sitosterol-D-glucoside (1), schizandriside (2), kaempferol-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (3), 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (4), 2-methoxy-4-(2'-hydroxyethyl)–phenol-1-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (5) and 2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl) ethyl 1-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6). Meanwhile, four flavonoids including 7, 4'-dihydroxyl-3'-methoxyisoflavone (7), calycosin (8), 7-hydroxyl-4'-methoxyflavanone (9), maackiain (10) and one steroid compound, stigmasterol (11) were also reported herein.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.141.19.04.1240 Keywords Indigofera stachyoides radix glycoside schizandriside kaempferol-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside natural medicine DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2020 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.