Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Volume: 15 Issue:1 January-February
1) Chemical Constituents of the Seeds of Pharbitis purpurea and Laxative Effect of Methyl Caffeate on Rats
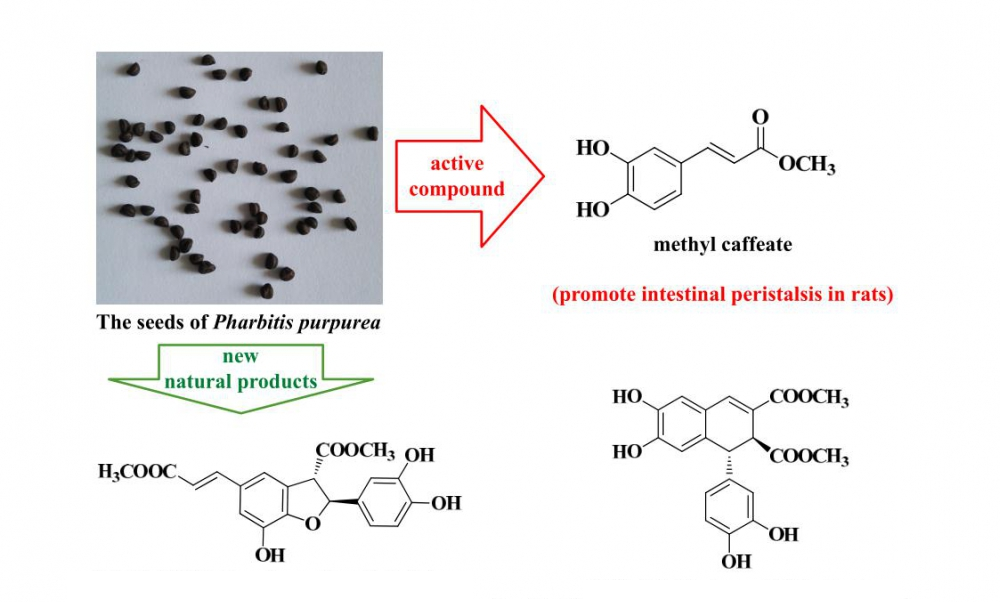
The chemical constituents of the seeds of Pharbitis purpurea belonging to the Convolvulaceae family were studied. The anti-tumor activities of all isolated compounds on A549 and HepG2 tumor cell lines and effect of methyl caffeate (8) on intestinal excretion in rats were also studied. Fourteen compounds were isolated from the seeds of P. purpurea by column chromatography using silica gel, ODS, Sephadex LH-20 and HPLC. Their structures were determined by 1D and 2D NMR and HRMS. They were identified as (2S,3S)-5-[(1E)-2-carboxyethenyl]-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-7-hydroxy-3-benzofurancarboxylic acid dimethyl ester (1), 8-epiblechnic acid (2), dimethyl (1R,2S)-6,7-dihydroxy-l-(3,4-dihydroxy)-phenyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene-2,3-dicarboxylate (3), dimethyl 6,9,10-trihydroxybenzo[kl]xanthene-1,2-dicarboxylate (4), syringaresinol-4’-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (5), (+)-syringaresinol (6), (+)-pinoresinol (7), methyl caffeate (8), ethyl caffeate (9), osmanthuside J (10), methyl 6β,7β,16β,17-tetrahydroxy ent-kauran-18-oate (11), β-sitosterol (12), 1-O-linoleoyl-glycol (13) and 1-O-linoleoyl-glycerol (14). Compounds 1 and 3 are new natural products. 4 is reported from the family Convolvulaceae for the first time and 8, 10 and 11 from P. purpurea for the first time. Methyl caffeate (8), 10 and 30 mg/kg, significantly promote intestinal peristalsis in rats. Methyl caffeate (8) has no acute toxicity to rats at 5000 mg/kg.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.178.19.12.1508 Keywords Pharbitis purpurea chemical constituents promoting intestinal peristalsis methyl caffeate DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) The Leaf and the Gall Volatiles of Salvia fruticosa Miller from Turkey: Chemical Composition and Biological Activities
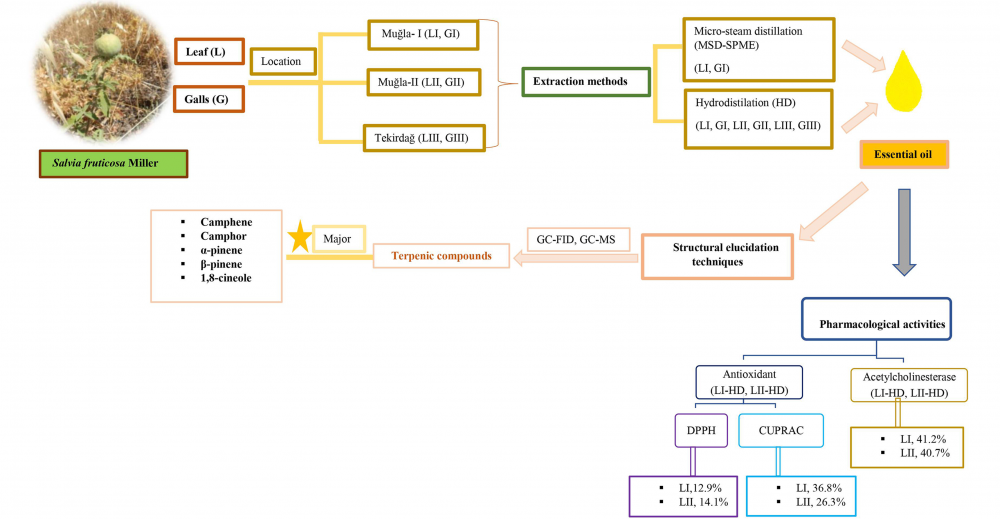
In this study two different extraction techniques namely, conventional hydrodistillation (HD) and micro-steam distillation-solid-phase microextraction (MSD-SPME), were used to analyze the volatile constituents from the leaves and the galls of Salvia fruticosa Mill. by gas chromatography (GC-FID) and gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The oxygenated monoterpenes (62.4-69.3%) were found to be predominating compound group with 1,8-cineole and camphor as the main constituents in all the tested samples with the exception of the gall oil in which oxygenated sesquiterpenes (25.6%) and diterpenes (17.3%) were detected in high percentages. Qualitative differences of the volatiles obtained by HD and MSD-SPME techniques from the leaf and the galls are discussed. The resulting leaf essential oils were evaluated for their in vitro acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition potential. In vitro DPPH scavenging, and Cupric Reducing Antioxidant Capacity (CUPRAC) assays were used to evaluate the leaf essential oils. AChE inhibition 41.2% and antioxidant 36.8% assays results showed moderate levels of activity. In this present study, to the best of our knowledge comparative leaf and gall volatiles of S. fruticosa was reported for first time.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.185.20.03.1579 Keywords Salvia fruticosa galls acetylcholinesterase antioxidant SPME GC-MS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Salvianolic Acid B Attenuated Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Brain Injury in Mice by Inhibiting Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Inflammation

Salvianolic acid B (SAB) is one of main components of the dried roots and rhizomes of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (RSM), which is widely used as a medicinal herb in East-Asia. According to traditional Korean medicine, RSM promotes blood flow, and thus, we investigated the effects of administering SAB after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced brain injury in a mouse model. I/R-induced brain injury was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 2 h. SAB was orally administered to mice twice after 3 and 6 h of occlusion at 5, 15, or 45 mg/kg body weight. Administration of SAB at 45 mg/kg significantly reduced infarct volumes and edema indices and suppressed interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in brain ipsilateral hemispheres. SAB also down-regulated Mn-SOD protein expression in affected brain tissues after I/R-induced brain injury. Our results indicate the neuro-protective effects of salvianolic acid B are due to its anti-inflammatory effect mediated by intra-cellular superoxide scavenging..
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.184.20.03.1573 Keywords Salvianolic acid B Salvia miltiorrhiza ischemia/reperfusion injuryi nflammationb rain edema DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Myrica gale L. Leaf and Flower Essential Oils and Hydrolates
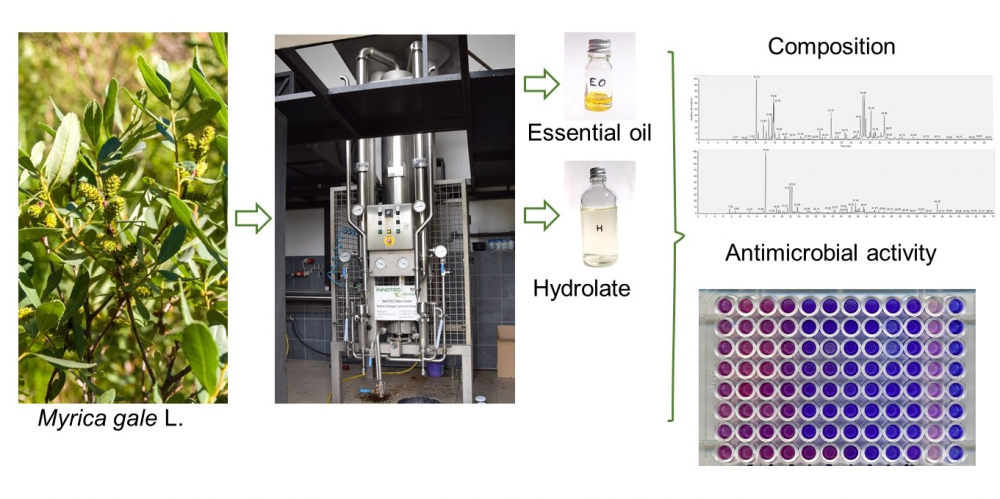
Myrica gale L. (sweet gale) leaves and flowers were subjected to industrial steamdistillation in order to obtain essential oil and hydrolate. Obtained products were investigated to determine their chemical composition and antimicrobial activity. The main components found in both leaf and flower essential oils were monoterpene hydrocarbons: α-pinene (12.3, 23.5.%), p-cymene (12.8, 4.9%), and limonene (11.0, 5.6%), respectively. While oxygenated monoterpenes: 1,8-cineole (28.6, 44.2%), terpinen-4-ol (14.3, 13.4%), and α-terpineol (15.6, 11.3%) were dominant compounds in leaf and flower hydrolates. Essential oil and hydrolate from M. gale leaves exhibited antimicrobial activity against obligatory and opportunistic bacterial pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Enterococcus faecalis. Interestingly, the leaf essential oil, but not the hydrolate, was also active against Candida albicans and Candida glabrata – yeast included in human skin and mucous membrane microbiota and simultaneously important fungal pathogens.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.190.20.04.1628 Keywords Sweet gale monoterpenes antimicrobial activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Two New Ecdysteroid Glycosides from the Rhizomes of Silene tatarinowii Regel
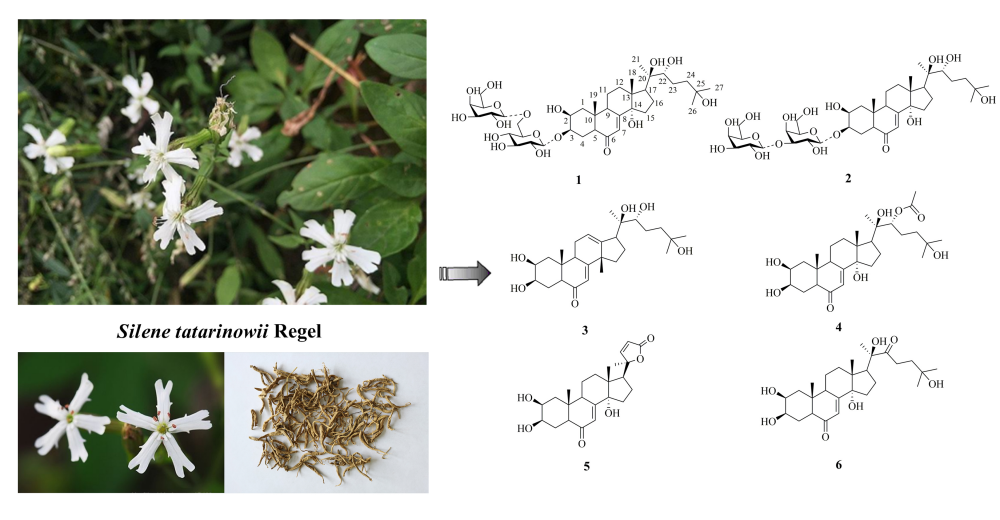
Two new ecdysteroid glycosides, sileneosides I and J (1 and 2), along with four known ecdysteroids (3–6) were isolated from the rhizomes of Silene tatarinowii Regel. Their structures were determined based on physicochemical properties and spectroscopic methods. In addition, the cytotoxicity of compounds 1–6 was evaluated in vitro in human SGC790, HCT116, A549, and BEL7404 tumor cell lines. The results showed that compounds 1 and 2 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against SGC790 (IC50 82.58 ± 0.53 μM) and A549 cells (96.62 ± 0.58 μM), respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.195.20.07.1726 Keywords Silene tatarinowii ecdysteroids sileneosides I sileneosides J cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Chemical Constituents from Typhonium giganteum Rhizome and Their Antioxidant, Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activities
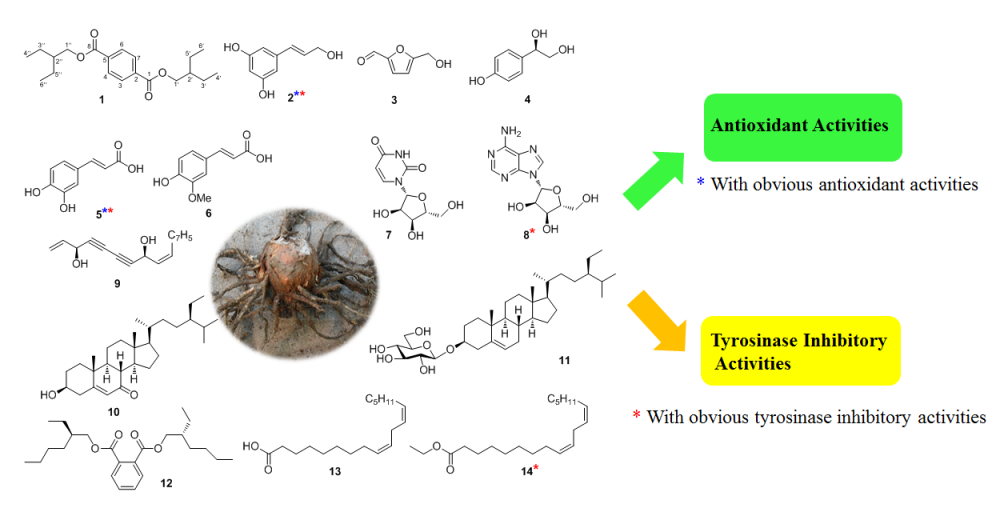
Fourteen constituents were isolated from the rhizome of Typhonium giganteum, which included two new compounds, trans-3,5-dihydroxy-cinnamyl alcohol (1), bis(2-ethylbutyl) terephthalate (2), along with twelve known compounds (3–14). The structures of these compounds were elucidated by physical data analyses such as 1D NMR, 2D NMR and HRESIMS. All compounds were tested for their antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitory activities. Compounds 1, 5 exhibited obvious DPPH radical scavenging activities, while compounds 1, 5, 8, and 14 showed significant tyrosinase inhibitory activities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.196.20.07.1741 Keywords Typhonium giganteum terephthalate DPPH tyrosinase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Chemical Constituents of Gymnosporia stylosa and Their Anti-inflammatory Activity
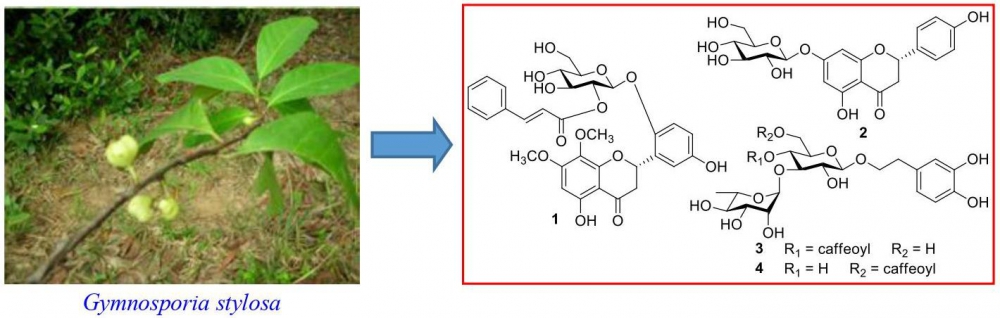
A new flavanone glycoside, gymnosporioside (1), and three known compounds (2-4) were isolated from the leaves of Gymnosporia stylosa. The structure of gymnosporioside (1) was determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS), and circular dichroism (CD) spectral data. The known compounds were identified as prunin (2), acteoside (3), and isoacteoside (4), by comparing the NMR data from this study with those reported in the literature. These known compounds, 2-4, have not been previously isolated from G. stylosa. Their anti-inflammatory activities were evaluated against lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced activation of nitric oxide (NO) production in RAW264.7 cells, in vitro. Compounds 3 and 4 showed significant inhibitory activities against LPS-induced NO production in RAW264.7 cells, with IC50 values of 17.8 ± 0.4 and 19.3 ± 0.3 mM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.179.20.03.1578 Keywords Gymnosporia stylosa Celastraceae Flavanone Anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Essential Oil from the Leaves of Lindera fragrans Oliv.
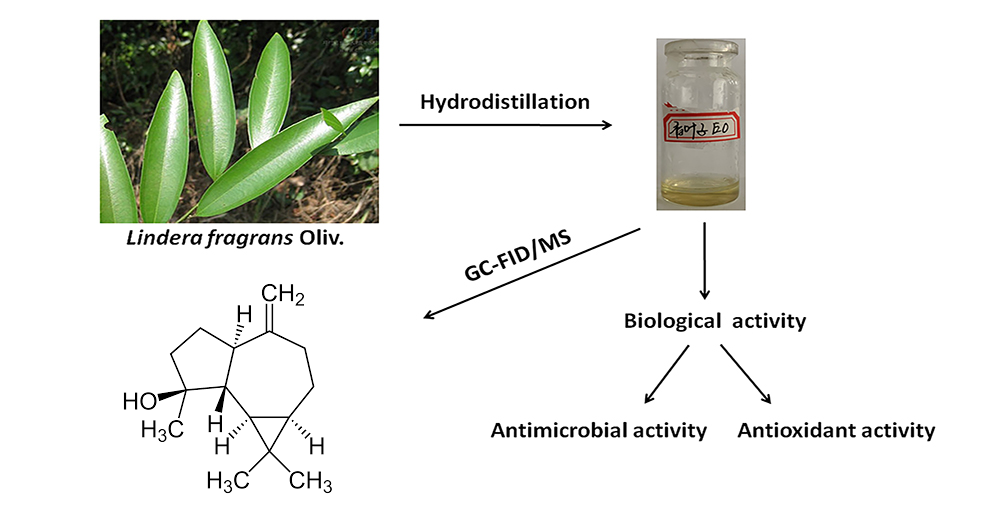
The chemical composition of the essential oil obtained by hydrodistillation from the leaves of Lindera fragrans Oliv. was determined by gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Sixty two compounds accounting 76.45% of the essential oil were identified. The main constituents found to be spathulenol (27.63%), ledol (6.81%), β-caryophyllene (4.01%), (+)-cis-limonene oxide (3.69%), α-cadinol (3.24%). The disc diffusion method on antimicrobial activities revealed that it has remarkable inhibition effect against Escherichia coli (CP009072.1), Staphylococcus aureus (CP009361.1), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CP015117.1) and Candida albicans (FJ159643.1). Antioxidant capacity of the essential oil was evaluated by 2,2'-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) and β- carotene bleaching assay, and it did not show effective antioxidant activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.189.2004.1618 Keywords Lindera fragrans Oliv. essential oil antimicrobial antioxidant GC-MS spathulenol DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Cytotoxic Activity and Phytochemical Constituents of Macrosolen bidoupensis Tangane & V.S. Dang
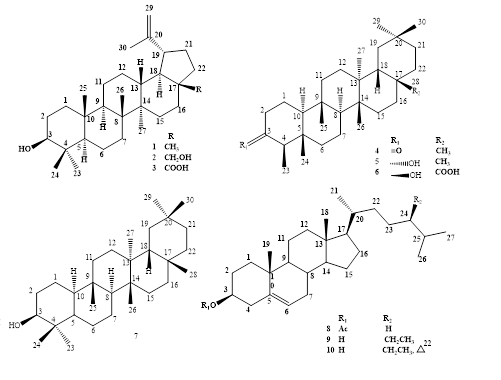
Phytochemical investigations of the whole plants of Macrosolen bidoupensis Tangane & V.S. Dang, a new species discovered in Viet Nam were conducted and led to the purification of ten compounds, comprising three lupane-type (1-3), three friedelane-type (4-6), and one glutinane-type (7) triterpenoids and three cholestane-type steroids (8-10) using various chromatographic methods. Their structures were characterized by HR-ESI-MS, NMR experiments and comparison with previous literature. Compounds 1, 3 and 5 expressed moderate cytotoxicity against two tested cell lines - MDA-MB-231 and RD (IC50 ranged from 34.19 to 74.25 μM), whereas compounds 4 and 6 exhibited selective cytotoxic activity (IC50 ranged from 29.07 to 45.20 μM).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.197.20.02.1545 Keywords Macrosolen bidoupensis Loranthaceae cytotoxic activity triterpenoid steroid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.