Records of Natural Products
Year: 2021 Volume: 15 Issue:2 March-April
1) A New Alkaloid Glycoside from the Stems of Zanthoxylum dissitum Hemsl.
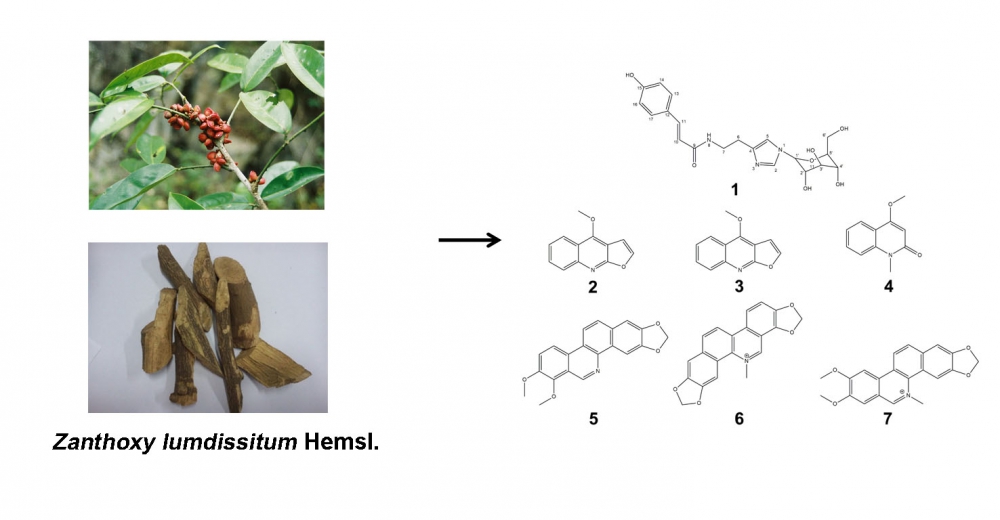
A new alkaloid glycoside (1) and six known alkaloids (2–7) were isolated from the stems of Zanthoxylum dissitum Hemsl.. The structure of compound 1 was resolved by spectrum data, including MS, IR, UV, and MS. All compounds obtained in this research were evaluated for their inhibitions against NO release from LPS-activated RAW264.7 macrophages. Compounds 1-3, 6 and 7 showed significant inhibition activities with IC50 values of 26.12±0.81, 8.41±0.23, 13.75±0.54, 6.97±0.77, and 5.78±0.42 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.191.20.05.1643 Keywords Zanthoxylum dissitum Hemsl. alkaloid macrophages NO DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
2) Identification and Structural Characterization of Anti-Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compounds from Ageratum conyzoides (L.)
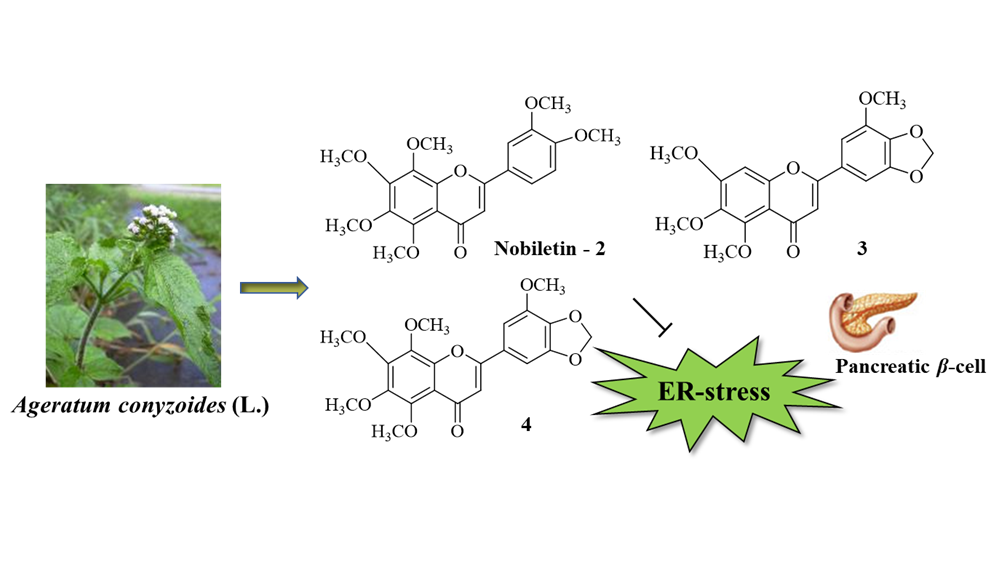
Ageratum conyzoides is an herbaceous plant widely used in traditional medicine against various diseases, and possesses anti-inflammatory, anti-ulcer, analgesic, and diuretic properties. However, its effects on endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, as observed in diseases such as diabetes, have not yet been characterized. In this study, using mouse pancreatic Beta-cells, we demonstrated that the ethanol extract of A. conyzoides effectively suppressed cell death induced by ER stress. Four polymethoxyflavones (PMFs) including (1) 5,6,7,3′,4′,5′- hexamethoxyflavone; (2) 5,6,7,8,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone (nobiletin); (3) 3′,4′-methylenedioxy-5′,5,6,7- tetramethoxyflavone; and (4) 5,6,7,8,5′-pentamethoxy-3′,4′-methylenedioxyflavone were isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction using reverse-phase chromatography. Their structures were elucidated using spectroscopic and mass-spectrometric analyses including 1D-, 2D-NMR, and HRESI-MS. All compounds were further evaluated for their ability to inhibit ER stress. Our results suggested that only compound 1 did not show an ability to rescue ER stress-induced cell death. Additionally, compound 2 as a nobiletin and its commercial product alleviated the tunicamycin-dependent chop mRNA expression induction. Notably, extremely low concentrations of both compounds exerted cytoprotective activity against tunicamycin-induced ER stress in pancreatic Beta-cells
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.194.20.06.1697 Keywords Ageratum conyzoides anti-endoplasmic reticulum stress pancreatic-cells nobiletin DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Chemical Constituents of Tibetan Herbal Medicine Pulicaria insignis and Their in vitro Cytotoxic Activities
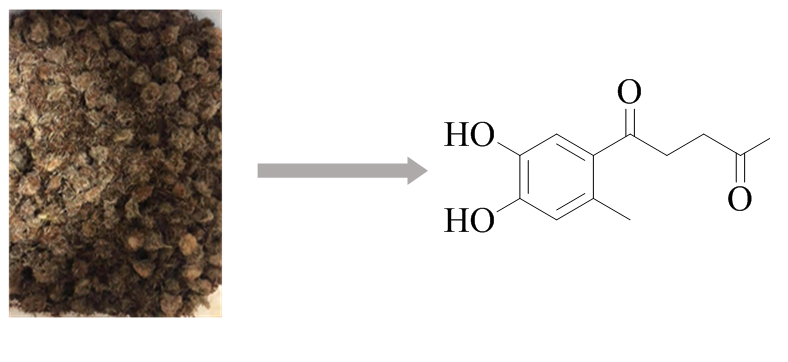
One new phenolic derivative, 1-(4',5'-dihydroxy-2'-methylphenyl)-pentane-1,4-dione (1), along with eighteen known compounds including eight sesquiterpenoids (2–9), one triterpenoid (10), one bisdpoxylignan (11), one coumarin (12), and seven flavonoids (13–19) were isolated from the dried inflorescence of Tibetan herbal medicine Pulicaria insignis. The structure of 1 was established by spectroscopic methods, including HRESIMS, IR, 1D, and 2D NMR. All isolates were assessed for the cytotoxic activities against MGC-803, T24, HepG2, and HeLa cell lines using the MTT assay. The results showed that compound 1 displayed moderate cytotoxicity against Hela and HepG2, and compounds 3, 4, 5, 6, and 13 exhibited potential cytotoxic activities against the four cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 3.05 to 14.37 μM. Notably, compound 5 exhibited significant anti-proliferative activities against HepG2 cell lines with the IC50 values of 3.05 ± 0.36 μM. Further bioactivity investigation showed that compound 5 could block HepG2 cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, thereby inhibiting the growth of HepG2 cells and inducing apoptosis in HepG2 cells.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.193.20.06.1692 Keywords Pulicaria insignis chemical constituent phenolic derivative cytotoxic activity sesquiterpenoid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) A New Cynaropicrin Derivative from Cynara Scolymus L.
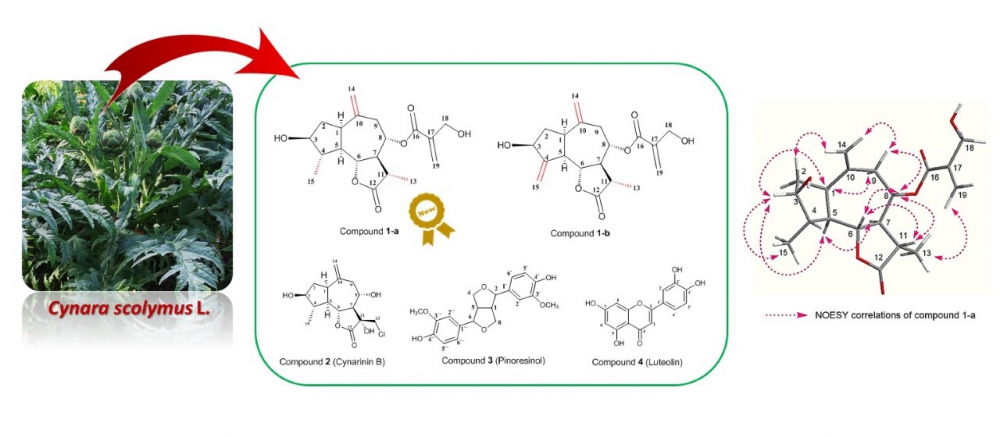
A new sesquiterpene lactone 1a along with other four known compounds 1b, 2, 3 and 4 were isolated from fresh leaves of Cynara scolymus L. using ordinary chromatographic techniques. The structures of the isolated compounds were determined via spectroscopic analysis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.198.20.07.1747 Keywords Cynara scolymus sesquiterpene lactones dihydrocynaropicrin etrahydrocynaropicrin pinoresinol luteolin DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Essential Oils of Three Hypericum Species from Colombia: Chemical Composition, Insecticidal and Repellent Activity Against Sitophilus zeamais Motsch. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
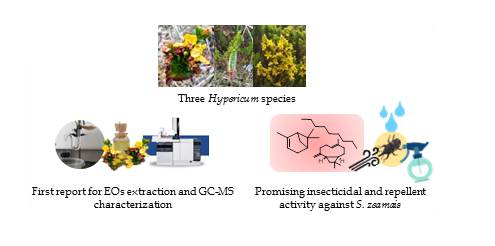
The maize weevil (Sitophilus zeamais) is one of the main insect responsible of significant losses in stored products, and to keep nutritional value of them to find effective and safe solutions are very important. The Hypericum genus might be a potential source of new bio-insecticides due to the chemical composition of essential oils. In this study, components of essential oils of three Hypericum species were investigated for first time by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) and, fumigant and contact toxicities as well as the repellent activity of essential oils of them were evaluated against S. zeamais adults. While the main components in H. mexicanum oil were determined as n-nonane (53.08%) and α-pinene (25.28%), the major constituents were determined as α-pinene (45.52%) and β-caryophyllene (13.59%) in the essential oil of H. myricariifolium. Chemical composition of essential oil of H. juniperinum were found to be n-nonane (12.0%), α-pinene (8.25%), geranyl acetate (7.93%), and β-caryophyllene (13.60%). The results revealed that H. mexicanum and H. myricariifolium oils have fumigant toxicity (LC50 < 500 µL/L air) and a potential action as repellents (RP > 70% at 6.2–22.7 μL/L air) for the control of the pest.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.192.20.05.1665 Keywords Sitophilus zeamais essential oil repellent Hypericum mexicanum Hypericum myricariifolium Hypericum juniperinum DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Isolation, Characterization and Antiproliferative Activity of Secondary Metabolites from Tanacetum alyssifolium (Bornm.) Grierson
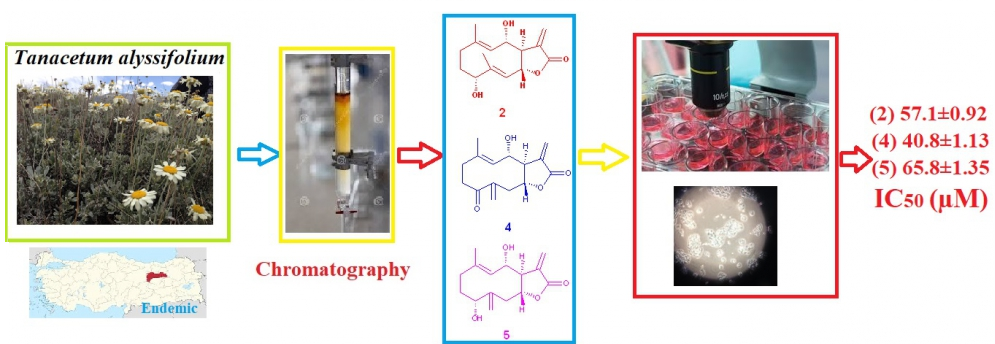
Secondary metabolites of Tanacetum alyssifolium (Bornm.) Grierson (Asteraceae) were investigated for the first time. Thirteen compounds including axillarin (1), Luteolin-7-O-β-glucoside (8) and rutin (13) as flavonoids, fraxetin (7), isofraxidin (9), isofraxidin-7-O-glucoside (11) and fraxidin (12) as coumarins, tatridin A (2), altissin (3), tamirin (4) and tanachin (5) as sesquiterpene lactones and 2,4-dihydroxy-6-methoxy acetophenone (6) and picein (10) as acetophenone derivatives were isolated from the methanol extract of the species. The structures of all isolated compounds were elucidated by 1D and 2D-NMR techniques and by comparing with the literature data. In addition, in vitro cytotoxic activity of all isolated compounds was evaluated against breast cancer MCF-7 cell line by XTT assay. Sesquiterpene lactones; tatridin A (2), tamirin (4) and tanachin (5) were found to be the most cytotoxic molecules against MCF-7 cell line.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.201.20.07.1702 Keywords Tanacetum alyssifolium sesquiterpene lactones cytotoxicity MCF-7 cell line DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Chemical Investigation of a Co-Culture of Aspergillus fumigatus D and Fusarium oxysporum R1
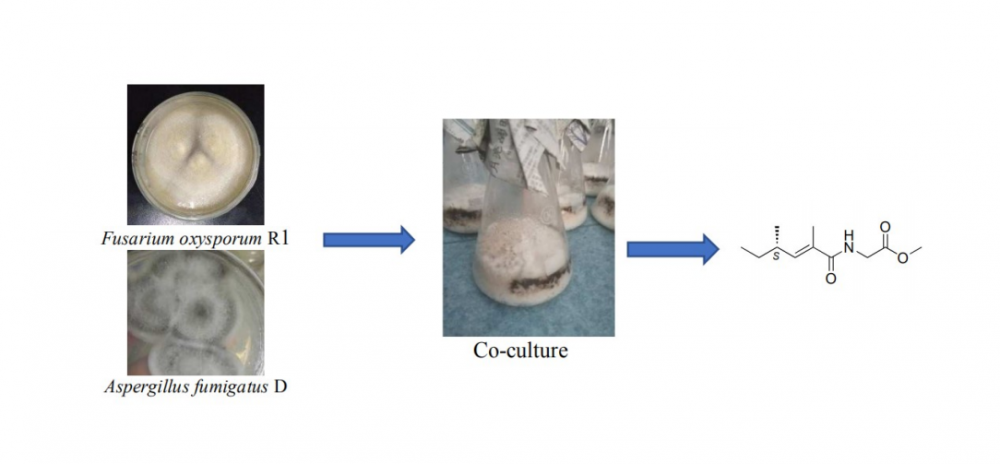
Chemical investigation of a co-culture of two endophytic fungi Aspergillus fumigatus D and Fusarium oxysporum R1 from two traditional medicinal plants, Edgeworthia chrysantha Lindl. and Rumex madaio Makino, led to isolation of a new amide 1 and six known compounds, including neovasinin (2), neovasifuranone B (3), N-(2-phenylethyl)acetamide (4), α-linolenic acid (5), α-elaeostearic acid (6), palmitoleic acid (7). On the basis of extensive spectroscopic analysis including 1D and 2D NMR, HR-ESI-MS and optical rotation measurement as well as comparison of literature data, chemical structure of 1 was unambiguous elucidated as (S, E)-methyl-2-(2,4-dimethylhex-2-enamido)acetate. Bioassay results indicated that none of these compounds exhibited strong inhibitory effect on three human pathogens Escherichia coli, Staphyloccocus aureus and Candida albicans with MIC values of ≥25 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.199.20.07.1728 Keywords Endophytic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus D Fusarium oxysporum R1 co-culture amide antimicrobial effect DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Novel Pharmacological Effects of Syringin on Anxiety Behavior and Autonomic Nervous System Activity
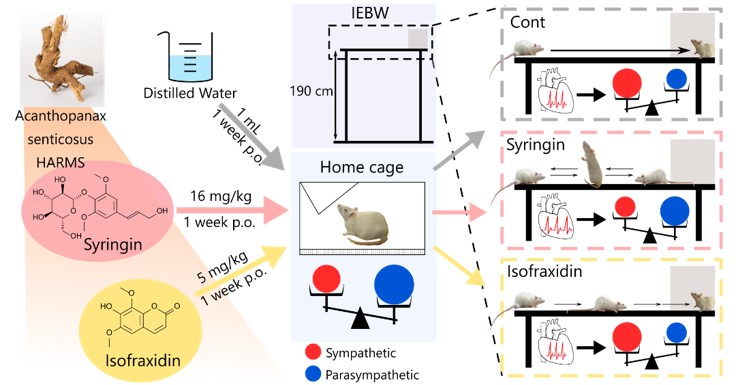
Acanthopanax senticosus HARMS (ASH), a traditional Chinese herbal medicine, has been used to treat arthralgi, muscle weakness of the lower body, hypertension, and impotence. ASH was also reported to increase resistance to stress and fatigue. Recently, the efficacy of ASH against depression and stress-induced gastric ulcer was demonstrated in a rodent model. Previously, we also reported that ASH exerted anxiolytic effects and modulated autonomic nervous system activity under stress. However, no research has examined the anxiolytic effects of isofraxidin and syringin, two constituents of ASH. Thus, we investigated the anxiolytic constituents of ASH. The rats were administered distilled water, isofraxidin or syringin for 1 week. Autonomic nervous system activity was estimated using heart rate variability and anxiety behavior in the improved elevated beam walking (IEBW) test. The syringin increased the time spent in the open arm in the IEBW test. The syringin blocked the significant decrease in normalized high-frequency power, indicative of parasympathetic nervous system activity, in the IEBW test. The isofraxidin exerted no significant effects on behavior and autonomic nervous system activity. These results indicated that syringin partially contributes to the anxiolytic and autonomic nervous system-modulating effects of ASH.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.200.20.08.1775 Keywords Acanthopanax senticosus isofraxidin syringin anxiolytics autonomic nervous DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Computational Study and Biological Evaluation of Isolated Saponins from the Fruits of Gleditsia aquatica and Gleditsia caspica

Phytochemical study of the ethanolic extract of the fruits of Gleditsia aquatica and Gleditsia caspica resulted in the isolation of the triterpene saponins; aquaticasaponin A (1), aquaticasaponin B (2), caspicaoside L (3) and caspicaoside M (4). Compound (1) showed good activity against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (IC50 =16.3 μg/mL) and Staphylococcus aureus (non-MRSA), (IC50 =12.2 μg/mL) and it expressed considerable cytotoxic activity against BT-549 (Human Ductal Carcinoma, Breast), KB (Human Epidermal Carcinoma, Oral) and SK-MEL (Human Malignant Melanoma) with IC50 values of 8.3, 10.0 and 3.3 μg/mL, respectively. Compounds (2) and (3) showed potent cytotoxicity against BT-549 with IC50 values of 5.3 and 7.3 μg/mL, and against SK-MEL with IC50 values of 4.3 and 3.1 μg/mL, respectively. Compound (4) showed good cytotoxicity against KB with IC50 value of 7.3 μg/mL. In consistent, the study of molecular determinates of cytotoxic activity of these new scaffolds showed close high docking scores to CD81 (Cluster of Differentiation 81) human antigen which could be of great importance for the development of new cytotoxic candidates. The structure identification of isolated metabolites was carried out using 1D and 2D NMR and mass spectra.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.202.20.08.1764 Keywords Triterpenoidal saponins cytotoxicity CD81 human antigen computational study MRSA DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.