Records of Natural Products
Year: 2024 Volume: 18 Issue:5 September-October
1) Schisantherin B: Review of Its Preparation, Biological Activities, Pharmacokinetics Analysis and Content Determination
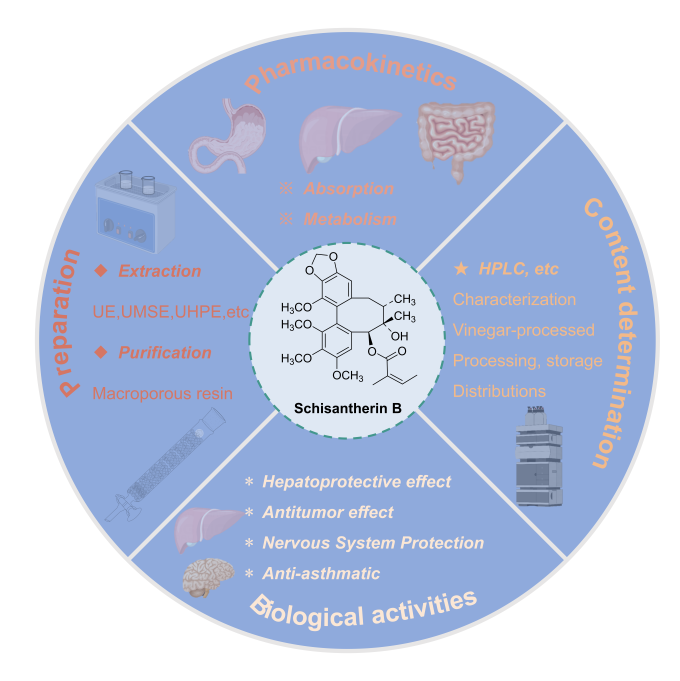 Schisandra chinensis (S. chinensis) is the dried mature fruit of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. Its primary active elements include polysaccharides, lignans, and other substances, and it is essential for neuroprotection, hepatoprotection, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and other functions. One of the components of lignan, schisantherin B (STB), is commonly extracted using ultrasonic extraction or a combination of ultrasonic and microwave techniques. The macroporous resin method is used to purify the extract at first. Pharmacological studies have shown that it has hepatoprotective, antitumor, and neuroprotective effects, among which hepatoprotective effects are more prominent, mainly by reducing the activity of intrahepatic ghrelin transaminase and improving liver damage. In addition, the pharmacokinetic analysis demonstrated that STB was well absorbed in vivo and was mainly in the form of passive transport in the gastrointestinal tract. The metabolic pathways in rats were also relatively diverse. At the same time, its content is related to the herb's traits, processing, storage methods, distribution, and other aspects. Therefore, the preparation, pharmacological effects, pharmacokinetic characteristics, and content determination of STB will be summarized, aiming to improve its knowledge system and provide a theoretical basis for subsequent more in-depth studies.
DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.462.2404.3192
Keywords
Schisandra chinensis
Schisantherin B
Preparation
Pharmacological effects
Pharmacokinetic
Content determination
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
Schisandra chinensis (S. chinensis) is the dried mature fruit of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. Its primary active elements include polysaccharides, lignans, and other substances, and it is essential for neuroprotection, hepatoprotection, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and other functions. One of the components of lignan, schisantherin B (STB), is commonly extracted using ultrasonic extraction or a combination of ultrasonic and microwave techniques. The macroporous resin method is used to purify the extract at first. Pharmacological studies have shown that it has hepatoprotective, antitumor, and neuroprotective effects, among which hepatoprotective effects are more prominent, mainly by reducing the activity of intrahepatic ghrelin transaminase and improving liver damage. In addition, the pharmacokinetic analysis demonstrated that STB was well absorbed in vivo and was mainly in the form of passive transport in the gastrointestinal tract. The metabolic pathways in rats were also relatively diverse. At the same time, its content is related to the herb's traits, processing, storage methods, distribution, and other aspects. Therefore, the preparation, pharmacological effects, pharmacokinetic characteristics, and content determination of STB will be summarized, aiming to improve its knowledge system and provide a theoretical basis for subsequent more in-depth studies.
DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.462.2404.3192
Keywords
Schisandra chinensis
Schisantherin B
Preparation
Pharmacological effects
Pharmacokinetic
Content determination
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
2) Two New Compounds from Arctium lappa Roots
.png)
A new caffeoylquinic acid, 1, 5-di-O-caffeoyl-3-O-(1-O-methoxy-2-O-caffeoyl-4-maloyl)-quinic acid (1), and a new 5-hydroxymethylfurfural dimer, 5-(((2-methoxymethyl) furan-5-methanol) methyl) furan-2-carbaldehyde (2), were discovered from Arctium lappa roots. A comprehensive HRMS, UV, IR, 1D and 2D NMR techniques were used for structural identification. These two compounds had Nitric Oxide (NO) inhibitory activity in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 inflammatory cell in a dose-dependent manner.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.474.2404.3187 Keywords Arctium lappa roots caffeoylquinic acid 5-hydroxymethylfurfural derivative anti-inflammatory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
3) Bronchodilator Monoterpenes from the Fruits of Trachyspermum ammi L
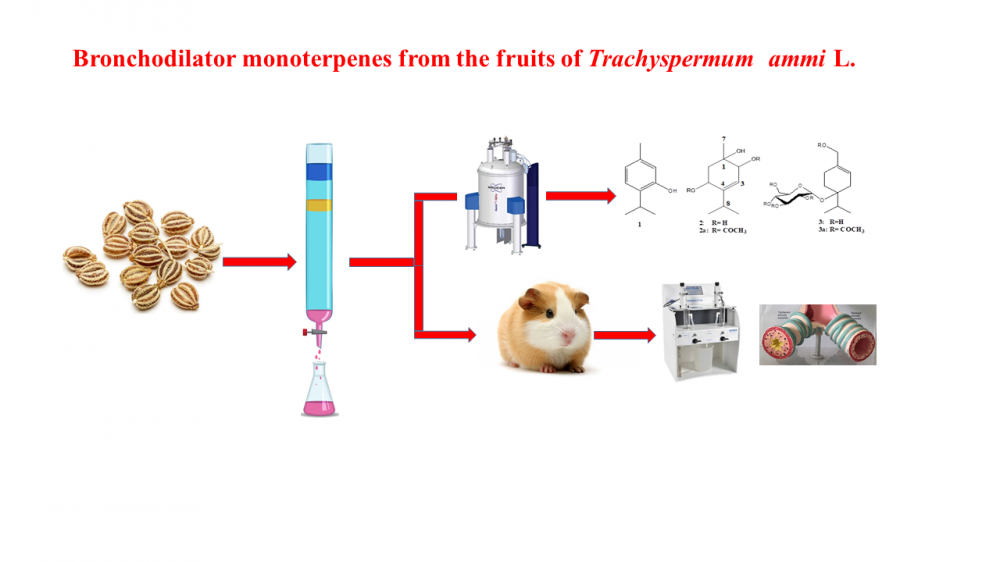
Trachyspermum ammi is widely used among the people in the Arabian Peninsula to treat general respiratory problems including bronchoconstriction. In this study, the fruit extracts and its fractions and purely isolated components obtained from the T. ammi were investigated for their possible bronchodilator potential in an ex vivo model using guinea pig trachea. It was observed that the ethanol extract (TAT) of the plant and its hexane (TAH) and chloroform (TAC) extract fractions completely inhibited carbachol (CCh, 1 µM)-induced contractions at a concentration of 1 mg/mL. As a result of the biological activity-guided purification studies of the chloroform extract (TAC), in which the highest activity was observed, eight sub-fractions were obtained between A-H. Of these, fractions A, D, G were found to have significant activity for tracheal relaxation with 100%, 55 ± 5% and 31 ± 3%, respectively, while the other five fractions were found not to have any activity. Three monoterpene compounds were isolated from the fractions with high activity and their structures were determined by 1D and 2D NMR and mass spectrometric techniques as well as by simple chemical derivatization. In this study, it was determined that the bronchodilator effect of compound 1 (thymol) was demonstrated by the activation of different subtypes of K+ channels. Reported data herein, demonstrated the scientific justification for the traditional use of T. amni species against asthma and bronchitis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.478.24.08.3285 Keywords Trachyspermum ammi L. thymol bronchodilator K+ channel opener ex-vivo DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Lyratin D, a New 4-Hydroxyisoflavan from the Whole Plant of Solanum lyratum Thunb
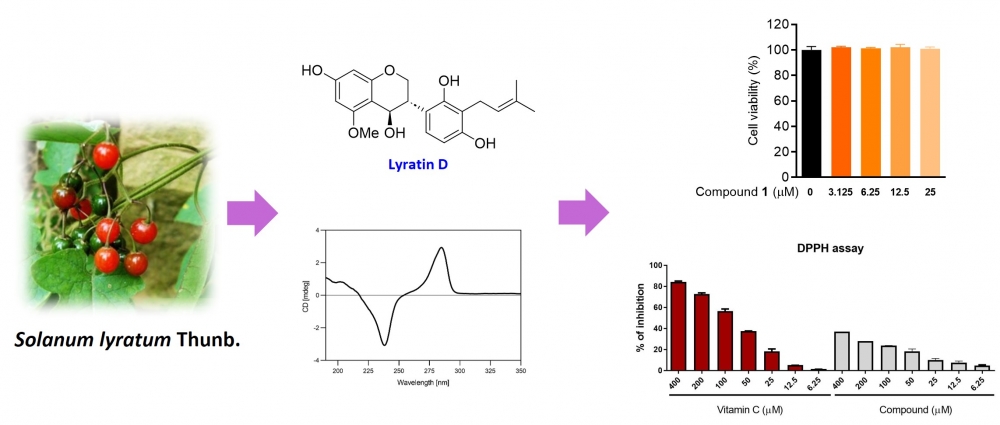
A new 4-hydroxyisoflavan, named lyratin D (1), was isolated from the whole plant of Solanum lyratum Thunb. Its structure and absolute configuration were elucidated through comprehensive analysis of its HR-ESI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR, and circular dichroism spectroscopy data. Compound 1 was then assessed for its cytotoxic effects on RAW264.7 murine macrophage cells, and its antioxidant activity was evaluated through DPPH assay.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.472.2406.3249 Keywords Solanum lyratum 4-Hydroxyisoflavan Antioxidant DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Potent Cytotoxicity and Nitric Oxide Suppression of Compounds Derived from Kaempferia elegans Rhizomes: Molecular Modeling on EGFR Inhibition

A new naturally occurring diarylheptanoid, (1E,4Z,6E)-5-hydroxy-1,7-diphenylhepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (3), was isolated from the rhizomes of K. elegans along with six known compounds, flavokawain B (1), 5,6-dehydrokawain (2), pinocembrin (4), cardamonin (5), alpinetin (6), and crotepoxide (7), among which compound 6 had not previously been isolated from this plant species. Two chalcones, flavokawain B (1) and cardamonin (5) were active against nitric oxide (NO) radicals released from LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages, resulting in 91.58% and 98.68% inhibition of NO production, respectively. Furthermore, compounds 1 and 5 showed superior cytotoxicity against MCF-7 (IC50 = 23.07 and 20.84 mM) and MDA-MB-231 (IC50 = 21.77 and 26.64 mM) cell lines, respectively. In silico molecular modeling studies of the most active compounds 1 and 5 against epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) suggested that π–π interactions with residues on the EGFR protein contributed to their anticancer properties. The results suggest that cardamonin (5) could be a promising candidate for further development of anti-inflammatory and anticancer agents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.472.2406.3250 Keywords Kaempferia elegans flavokawain B cardamonin anti-inflammation human cancer cell molecular modeling DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Heptaelliptoic Acid A, a New Betulinic Acid Saponin from the Leaves of Heptapleurum ellipticum

One new 3-O-glycoside of betulinic acid, named heptaelliptoic acid A (1), together with one known betulinic acid analogue (2), and four other compounds (3‒6) were separated by combinatively chromatographic techniques. For the first time, all of the purified compounds (1‒6) were reported from the H. ellipticum species. Their structures were obviously elucidated basing exhaustive and pervasive UV-VIS, FT-IR, HR-MS-ESI, and NMR experiment data. Compounds 2-4 were significantly displayed the in vitro a-glucosidase inhibition (IC50 values of 11.53, 28.75, and 10.90 μM, respectively) better than the acarbose positive drug (IC50 value of 214.50 μM).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.476.2407.3265 Keywords Araliaceae Heptapleurum ellipticum heptaelliptoic acid A α-glucosidase inhibition betulinic acid saponin DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Aspilactonol J: A New Cytotoxic Polyketide Isolated from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. w2-13

Marine-derived Aspergillus sp. strain w2-13, isolated from Dongshan Island in Fujian Province, produced five compounds through solid-state fermentation. This included a new polyketide, aspilactonol J (1), and four previously identified compounds (2–5). The structure of the new compound was determined using NMR, HR-MS, and ECD, supported by theoretical calculations. A plausible biosynthetic pathway for polyketides 1–3 was also proposed. Cytotoxicity tests on various cancer cell lines revealed that aspilactonol J (1) exhibited significant selectivity and efficacy, especially against HepG2 cells, suggesting its potential for pharmaceutical development. This study highlights the role of marine fungi as valuable sources of bioactive natural products with therapeutic potential.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.477.2406.3552 Keywords Aspergillus polyketide NMR ECD TDDFT cytotoxic DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Evaluation of Essential Oil Components in Genetically Modified Poaceae Plants: A Comparative Study of Their Whitening and Antioxidant Activities In Vitro

This study aimed to modify the essential oils of Cymbopogon flexuosus (Nees ex Steud.) W.Watson, hereafter referred to as CF, and Cymbopogon martini (Roxb.) W.Watson, hereafter referred to as CM, utilizing an acid-distillation protocol. The modification resulted in a significant reduction in the aldehyde components, Neral and Geranial, in CF, subsequently leading to the formation of the monoterpene, Cymene. Conversely, the alteration in CM decreased the proportions of the monoterpenol, Geraniol, and the ester, Geranyl acetate. These modifications enhanced the cellular safety of both CF and CM essential oils towards B16-F10 cells in vitro, increasing it by 4 to 8-fold, and concurrently improved their melanin suppression and antioxidant properties.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.473.2404.3209 Keywords Essential Oil Safety Acid-distilled Whitening Antioxidant DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Chemical Composition and Evaluation of the Antibacterial, Synergistic Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities of the Essential Oil of Macrothelypteris torresiana (Gaudich.) Ching

In this study, we evaluated the chemical composition, antioxidant, cytotoxic, and antibacterial activities of the essential oil extracted from the aerial parts of Macrothelypteris torresiana (Gaudich.) Ching (MT-EO), as well as its synergistic antibacterial effect in combination with commercial antibiotics. Fifty-seven compounds were identified in MT-EO, representing 97.9% of the total oil content. The compounds bicyclogermacrene (12.9%), spathulenol (11.9%), β-elemene (5.7%), and hexyl hexanoate (5.0%) were detected as the main constituents. The microdilution and checkerboard assays were used to evaluate the antibacterial and synergistic properties of the essential oil. It was found that MT-EO possessed bactericidal activity against all tested bacteria, with MIC values between 0.625 to 1.250 mg/mL, which was the same as MBCs. Additionally, synergistic effects were detected in both M. torresiana essential oil -chloramphenicol and -streptomycin combinations. Besides, according to the MTT test, MT-EO possessed broad-spectrum cytotoxicities on various cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 15.12 ± 0.96 to 47.07 ± 1.96 μg/mL, including the MCF-7, A-549, HCT-116, HepG2, and LO2 cell lines. Furthermore, MT-EO showed moderate antioxidant activities in DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays, with IC50 values of 434.5 ± 9.6 and 98.1 ± 1.1 μg/mL, and Trolox equivalent of 97.11 ± 3.37 μmol Trolox × g-1, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.479.2407.3723 Keywords Macrothelypteris torresiana essential oil antibacterial synergistic antioxidant cytotoxic DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Insight into Chemical Composition and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Essential Oil from Flowers, Leaves and Vine Stems of Cissampelopsis volubilis Miq.

Fresh flower, leaf, and vine stem materials of Cissampelopsis volubilis Miq., collected from the wild in Lao Cai province of Vietnam, were hydrodistilled to obtain essential oils. The oil yields were 0.49%, 0.82% and 0.28% (v/w) for flowers, leaves, and vine stems, respectively, calculated on a dry weight basis. The major components of these essential oils, that were analyzed using gas chromatography-flame ionization detector (GC-FID) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), included: α-pinene (32.4%) and β-pinene (39.6%) in flower oil; α-pinene (55.8%) and β-pinene (23.2%) in leaf oil; α-pinene (65.7%) and α-copaene (5.9%) in vine stem oil. The essential oil from leaves exhibited strong anti-inflammatory effect, with IC50 of 22.07 ± 2.01 µg/mL in inhibiting nitric oxide (NO) production in RAW 264.7 (ATCC®-TIB-71TM) cells. This finding paves the way for further research into the potential use of this plant's leaves in treating inflammation-related diseases. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity of essential oils of C. volubilis flowers, leaves, and vine stems.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.480.2408.3307 Keywords Anti-inflammatory activities α-pinene β-pinene Cissampelopsis volubilis essential oil composition DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.