Journal of Chemical Metrology
Year: 2021 Volume: 15 Issue:1 January-June
1) Preparation and value assignment of parabens and phenoxyethanol in cosmetic cream certified reference material
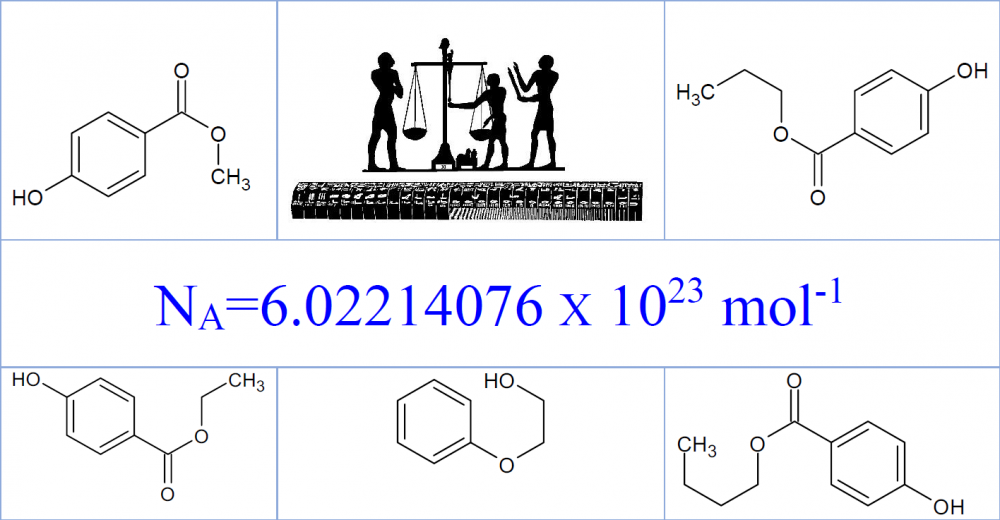
A new certified reference material has been developed by National Institute of Standards according to ISO Guides 30-35 and ISO 17034:2016 for preservatives in cosmetic cream to be used for validation and verification of analytical methods, proficiency testing and as internal quality control sample for quality assurance in testing laboratories. The material was prepared gravimetrically and mass fraction of each analyte was confirmed be validated liquid chromatographic method. The material along with analytes homogeneity and stability were completely evaluated. The certified value of phenoxyethanol, methyl, ethyl, propyl, and butyl paraben and their corresponding expanded uncertainties (k = 2.0) were found (0.500±0.017) %, (0.150±0.006) %, (0.051±0.003) %, (0.101±0.004) % and (0.050 ±0.003) %, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.59.21.04.2049 Keywords Cosmetic cream parabens phenoxyethanol value assignment reference material DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Preparation and certification of carbon monoxide gas reference material for the quality of CO emission measurements
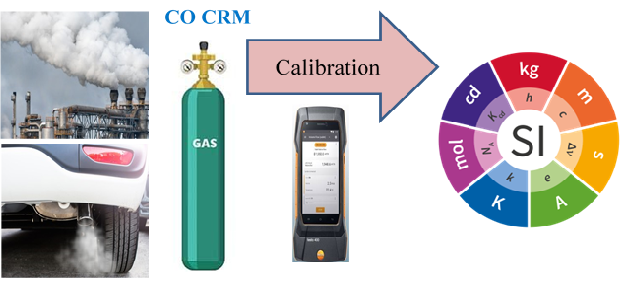
Carbon monoxide emissions in air are toxic and its monitoring is of great concern worldwide. The monitoring activities should rely on traceable measurement results to the SI units. To serve this monitoring purpose in Saudi Arabia, a primary gas mixture (200 mmol/mol) of Carbon monoxide (CO) in nitrogen has been gravimetrically prepared from pure CO and pure N2 in 5L aluminum gas cylinder based on ISO 6142. From this mixture, three diluted mixtures of concentrations 4.99, 7.49 and 10.01 mmol/mol were prepared also in 5L cylinders and the uncertainty of these gravimetric preparations was calculated. The mole fractions of the three mixtures were verified by GC-TCD in accordance with ISO 6143 and the uncertainty of the chromatographic measurements was calculated. The gravimetrically and chromatographically measured mole fractions together with their standard uncertainties were found compatible indicating good quality of the produced primary gas mixtures. Long term stability of the three gas mixtures was monitored along four years, and the results obtained showed very good stability of the gas mixtures. The relative uncertainty of the GC analytical results was found 0.52%, 0.51% and 0.52% which is small enough and advantageous for the calibration of CO emission measuring equipment.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.58.21.04.2055 Keywords CO N2 weighing GC-TCD uncertainty stability DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Uncertainty of small enthalpy effects measured by isothermal calorimetric titration
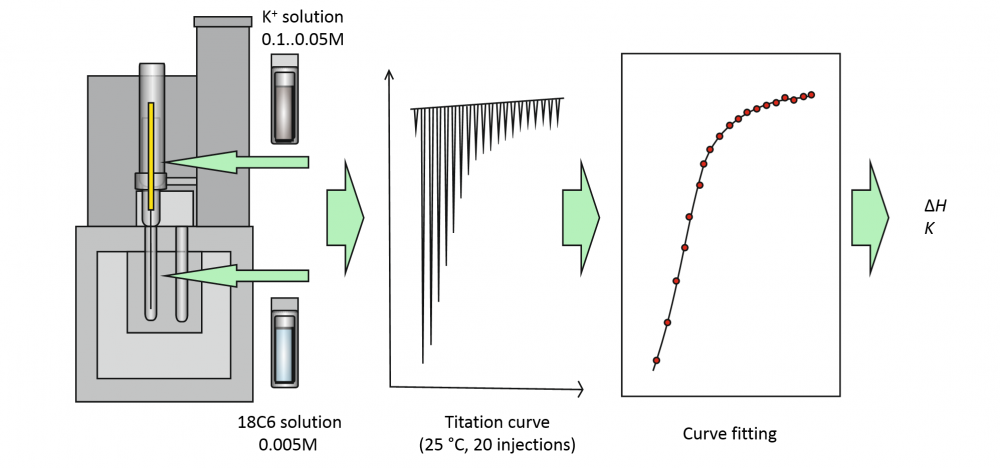
Combination of low concentration, low binding affinity and small solution volume is increasingly more common in calorimetric studies of host-guest interaction, but it leads to very small enthalpy and entropy effects, which are difficult to measure accurately. The aim of this study was to evaluate the reliability of enthalpy determination under such conditions using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) with a small-volume microcalorimeter and to evaluate the expected accuracy (expressed as measurement uncertainty) on the example of a simple 1:1 binding reaction of 18-crown-6-ether with K+ cation. The investigation focused on whether or not it is possible to get meaningful results from experiments on such a system with low binding constant, low concentration (logK ≈ 2), low Wiseman “c” parameter values (c < 1) and low total heat released in the studied system. A thorough estimation of measurement uncertainty was performed using the component-by-component (the “classical” GUM) approach to estimate the uncertainties of experimentally determined heat effects at individual titration points and applying those uncertainties to data fitting to obtain the K and ΔH values for the studied reaction. We found that it was possible to determine the reaction enthalpy ΔH of -26.6 kJ/mol with standard uncertainty of 1.1 kJ/mol. If we assume similar uncertainties for the other authors, the ΔH value found in this work is in good agreement with the majority of the literature ΔH values and those are in general in agreement with each other.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.57.21.03.1994 Keywords Isothermal titration calorimetry Wiseman c parameter measurement uncertainty studying the binding of low-affinity systems DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Measurement uncertainty evaluation for titrimetric determination of benzoic acid purity
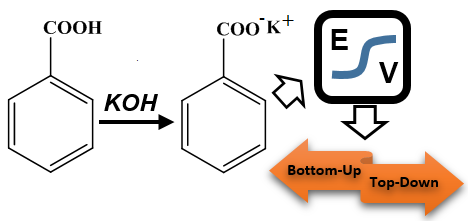
The uncertainty budget for the determination of benzoic acid purity by potentiometric titrimetry was proposed. For this purpose alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution was standardized with benzoic acid supplied from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) (SRM 39j), then the purity of the benzoic acid sample was determined by the same way. Measurement uncertainty evaluation of the method was exhaustively evaluated according to the EURACHEM/CITAC Guide CG 4, JCGM 100: 2008 and EUROLAB Technical Report No.1/2007, based on the bottom-up approach. Moreover, these results were compared with the results based on the top-down approach according to the EUROLAB Technical Report No.1/2007 and NORDTEST: NT TR 537. The measurement uncertainty was separately evaluated for the factor determination and the purity determination of one and six samples of benzoic acid for the bottom-up approach. The uncertainty sources for the purity determination of benzoic acid were carbon dioxide mole fraction, nominal concentration of benzoic acid, factor of alcoholic potassium hydroxide, amount of titrant consumption, the molar mass of benzoic acid and sample amount, respectively. Among these, the highest contributions to the uncertainty budget were found to be the factor of alcoholic KOH solution and the amount of titrant consumption for one and six samples, respectively. The expanded uncertainties for one and six measurements based on the bottom-up approach were found as 0.508% and 0.509%, and the expanded uncertainty for six measurements based on the top-down approach was found as 0.114%.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.54.20.11.1881 Keywords Benzoic acid traceability electrochemistry measurement uncertainty bottom-up approach top-down approach DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Investigation of aflatoxin and metal concentrations in animal feeds and feed ingredients from Turkey

The contents of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), aflatoxin B2 (AFB2), aflatoxin G1 (AFG1) aflatoxin G2 (AFG2), aluminium (Al), arsenic (As), barium (Ba), calcium (Ca), cadmium (Cd), cobalt (Co), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), mercury (Hg), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), sodium (Na), nickel (Ni), phosphorus (P), lead (Pb), selenium (Se), tin (Sn) and zinc (Zn) in animal feed samples in Turkey were screened. Eighty animal feeds and feed ingredients were collected from different cities in Turkey. Aflatoxins were determined using the HPLC instrument after pre-separation using immunoaffinity column, and also the instrument of ICP-MS was used for metal determinations. All types of animal feed samples have led concentrations lower than the maximum EU and Turkey regulation limit, while 1.25% and 11.8 of mixed and feed additive samples had AFB1 and Hg concentrations higher than the maximum limits, respectively. A single correlation analysis was used to determine the relationship between AFB1 and total AFs and metal contents in mixed animal feed samples (p<0.05). A strong positive correlation was found between As and AFB1 and total AFs contents; whereas Cr was correlated negatively to AFB1 and total AFs, using single correlation analyses.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.56.21.01.1937 Keywords Animal feed; aflatoxins; metals; HPLC, ICP-MS; correlation analyses. © 2021ACG Publications. All rights reserved. aflatoxins metals HPLC ICP-MS correlation analyses DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Simultaneous quantification of teneligliptin hydrobromide and metformin hydrochloride: An improved HPTLC method with implementation of Plackett-Burman design

Simple, rapid, sensitive, robust, and validated high-performance thin-layer chromatography was developed for the simultaneous determination of anti-diabetic drugs Teneligliptin hydrobromide (TH) and Metformin hydrochloride (MH) in bulk and pharmaceutical formulation. HPTLC system equipped Camag Linomat V, TLC Scanner IV, Twin Trough chamber, Dual-wavelength UV Cabinet, and win CATS software V1.4.7 were used during the study. Separation of analytes were achieved using a pre-coated silica gel G60 F254 aluminum Sheets 10×10 cm2, with the thickness of 0.2 mm as stationary phase and a mobile phase comprising of Methanol: Ammonium sulfate (0.5 %w/v): Triethylamine (9: 2.7: 0.5 v/v/v). The detection wavelength was set at 237 nm. The Rf value of the TH and MH was 0.63 and 0.19, respectively. The method was validated using a dynamic linear range of 4-28 ng/band and 100-700 ng/band for TH and MH, respectively. The developed method was validated as per the ICHQ2 (R1) guideline. The statistical analysis proved that the method is accurate with 98.80–99.38 % w/v and 99.66–99.96 % w/v for TH and MH, respectively, and precise with less than 2 % RSD. The Plackett-Burman design was applied to check the robustness of the developed method. Finally, the method is termed as linear, precise, accurate, and robust. It can be implemented successfully for the routine analysis of pharmaceutical dosage forms comprising TH and MH and is appropriate for regulatory submission under regulatory flexibility.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.55.20.11.1893 Keywords : Teneligliptin hydrobromide metformin hydrochloride high-performance thin-layer chromatography ICH guidelines simultaneous estimation quality by design DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Increasing the production of some specific cytotoxic triterpenoids and evaluation of the morpho-physiological response associated with in vitro salt stress in Pistacia khinjuk Stocks.

Triterpenoids are a class of secondary metabolites that are known to exhibit and possess various biological activities. Using plant biotechnological tools, a novel approach for producing these compounds offers opportunities not only to produce such bioactive secondary metabolites but also to increase the quantities of these essential phytochemicals. Therefore, this study was aimed to elucidate the biosynthesis of some cytotoxic triterpenoids through in vitro micropropagation of Pistacia khinjuk Stocks with the application of different NaCl concentrations (0 to 250 mM) and to evaluate the triterpenoids content as well as synchronize the morpho-physiological properties of plant materials during the salt application. The effects of these salt concentrations were investigated on P. khinjuk seedlings grown for four weeks by using the MS medium supplemented with 100 mg/L L-ascorbic acid and NaCl of given concentrations. LC-MS/MS results showed that the amount of all triterpenoid types from different plant parts was increased while root-shoot lengths, RWC, total Chl, Chl-a/b, and carotenoid values were decreased significantly at high salinity concentrations (150 mM). The reduction of the quantitative and qualitative morpho-physiological parameters was due to the production of an increased amount of secondary compounds, i.e., triterpenoids rather than primary compounds in response to the increased salt concentrations.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.53.20.10.1883 Keywords Pistacia khinjuk stocks LC-MS/MS alt stress triterpenoid in vitro plant physiology DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A comparative view to heavy metal pollution in soil and rainwater in Çanakkale, Turkey

On Earth, atmosphere interact with crust and thus simultaneously monitoring of environmental pollution in both parts of the environment is important. Soil and rainwater samples were taken in different parts of Çanakkale, Turkey, in two seasons. Study sites laid along with the prevailing wind direction (from NE to SW) as wind has the potential to distribute pollutants emitted into the air throughout its path. The concentrations of selected elements were determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Also, physical parameters such as pH, temperature, electrical conductivity of the rainwater and temperature and pH value of the soil samples were measured together with the meteorological parameters. Seasonal differences for the selected elements were insignificant in the soil samples (p>0.05), while some elements showed seasonal variations in the rainwater samples (p<0.05). The highest average heavy metal levels were found for Zn > Pb > Mn> Cu> Cd > Ni> Cr in the rainwater samples and Mn > Zn > Cu > Pb > Cr > Ni > Co in the soil samples, respectively. The highest enrichments were found for Pb in the rainwater and As in the soil samples. Elevated As levels occurred in the samples can pose a great risk for public health and agriculture.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/jcm.52.20.09.1817 Keywords Atmospheric pollution Çanakkale ICP-MS meteorological parameters rainwater soil pollution DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.