Organic Communications
Year: 2022 Volume: 15 Issue:4 October-December
1) A brief review on heterocyclic compounds with promising antifungal activity against Candida species
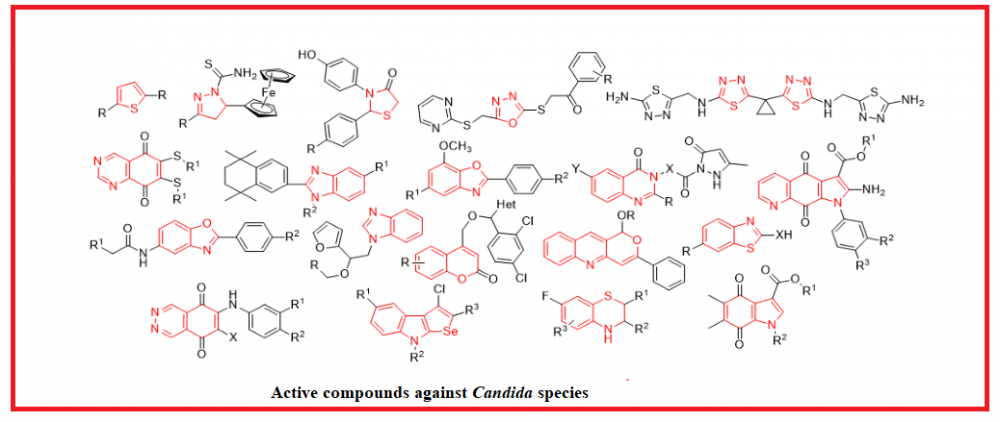
The most common reason for fungal infections is the development of Candida yeasts. Candida naturally is occurs on the skin and on most mucosal surfaces. It is proven that 90% of infections are caused by five Candida species: Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida krusei. Herein we’ve reviewed isolated and fused heterocyclic compounds that exhibit antifungal activity against Candida strains. Over 200 potential fungicidal agents were described, and some of the particularities which affect the action values were determined. Thus, it was noted that the presence of nitro-, methoxy-, trifluoromethyl-, and/or halogeno-containing groups at the specific positions in the benzene ring could significantly increase the inhibition of yeasts growth. That’s why using these patterns together with heterocycles while designing target compounds could speed up the search for new antifungal drugs.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.141.2210.2609 Keywords Candida sp. heterocyclic compounds fungicidal drugs MIC IC50 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Syntheses of some hydrazones derived from 2-(aryloyloxy) benzaldehydes and 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine and evaluation of their anticholinesterase and antioxidant activities
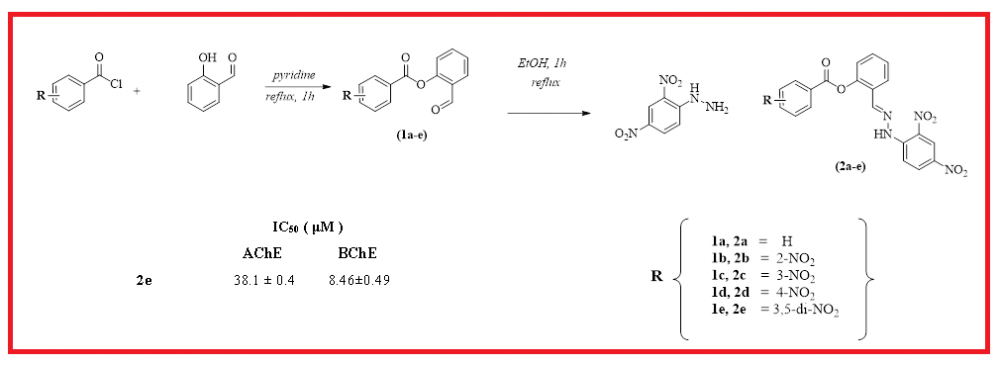
In this research, five novel hydrazone derivatives (2a-e) were obtained for the first time, characterized and investigated for their antioxidant properties, and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitory activities. The target molecules were easily synthesized by the condensation reaction of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH) with aryl esters (1a-e) derived from salicylaldehyde as a starting material. These molecules were fully elucidated by some spectroscopic techniques and elemental analysis. Antioxidant activities of newly synthesized molecules were examined by CUPRAC reducing, ABTS and DPPH radical scavenging assays. The IC50 values of the screened molecules were determined in the range of 72.54-221.52 µM against AChE and in the range of 8.46-48.28 µM against BChE. Among the tested molecules, compound 2e indicated the highest activity against both AChE and BChE. Also, the inhibitory capacities of all tested molecules were compared to the standard molecules galanthamine. On the other hand, In CUPRAC reducing assay, the target molecules exhibited antioxidant activities in the range of 30.29 and 59.43 µM. Among these compounds, compound 2b (IC50=30.29 µM) showed the closest activity to the standard compounds butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) (IC50=30.62 µM) and butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) (IC50=34.24 µM).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.137.2209.2570 Keywords Aryl ester hydrazone anti-cholinesterase activity antioxidant activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Synthesis of some 2-alkyl-5-(4-vinylphenyl)-2H-tetrazole compounds via the Wittig reaction and investigation by X-ray crystallography
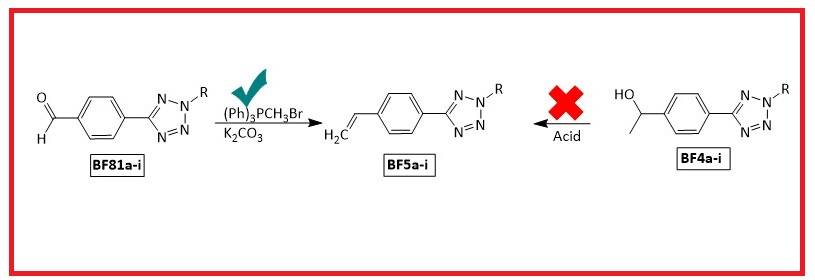
Tetrazoles are frequently used in industry and medicine. However, molecules that have both tetrazole and alkenyl groups are rare. For this purpose, new 2-alkyl-5-(4-vinylphenyl)-2H-tetrazole (BF5a-i, 63-99%) derivative compounds containing both styrene and tetrazole were synthesized with a high yield under mild conditions by the Wittig reaction. Their structures were verified by spectroscopic methods (FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C-APT NMR, HRMS, and X-Ray crystallography (for BF5a).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.139.2211-2633 Keywords Tetrazole styrene X-ray crystallography Wittig dehydration DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Post-synthetic sulfonation of a diphenylanthracene based porous aromatic framework
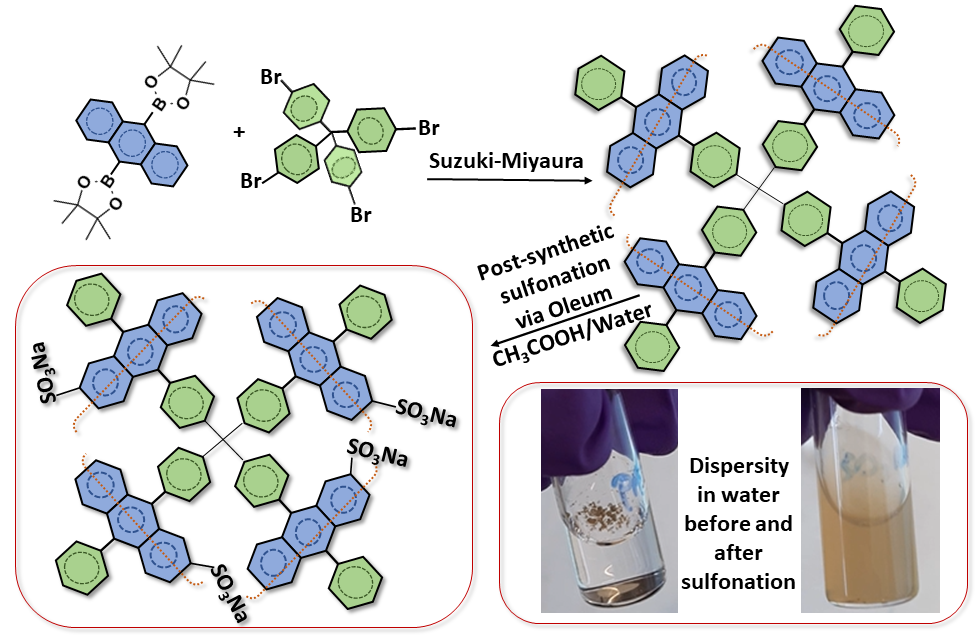
Post-synthetic modification is an alternative pathway to introduce functionalities into the backbone of porous materials. Sulfonation of porous organic polymers is one of the frequently applied post-functionalization since the sulfonate groups are interesting for various applications such as carbon dioxide storage, proton conduction, ion removal. Moreover, sulfonation drastically improve hydrophilicity of the hydrophobic materials, therefore, makes the final compounds more processable in aqueous media. In this article, a procedure for post-synthetic sulfonation of a diphenylanthracene (DPA) based porous aromatic framework (DPA-PAF) is presented. Oleum (fuming sulfuric acid) was used as the sulfonation agent in acetic acid+water media instead of the conventionally used chlorosulfonic acid in the chlorinated solvents. Aside from macroscopic (visual) observations such as improved dispersibility in water when compared to the parent compound, the introduction of sulfonate groups was confirmed by using infra-red spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and gas sorption (surface area) measurements.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.138.2210.2605 Keywords Porous organic polymers porous aromatic frameworks PAF-1 post-synthetic modification sulfonation oleum DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Synthesis and evaluation of antiproliferative and mPGES-1 inhibitory activities of novel carvacrol-triazole conjugates
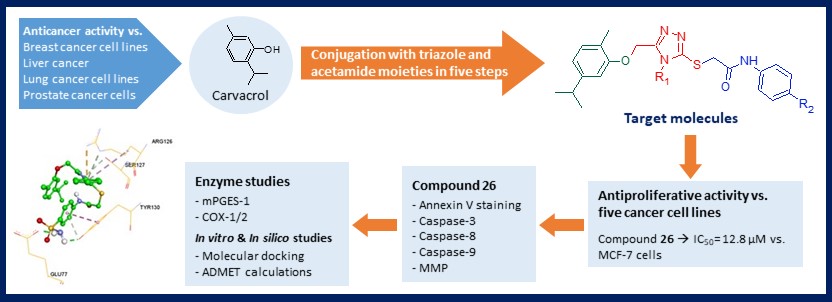
Some novel triazole-bearing acetamide derivatives 9-26 were synthesized starting from carvacrol. All synthesized compounds were characterized by FTIR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, HMBC and MS data. In vitro cytotoxic activities of all synthesized molecules against five cancer lines (human breast cancer MCF-7, human lung cancer A549, human prostate cancer PC-3, human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562, human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell lines) were evaluated by MTT assay. Compounds were also tested on mouse embryonic fibroblast cells (NIH/3T3) to determine selectivity. Eighteen target compounds 9-26 were screened for their mPGES-1 and COX-1/2 inhibitory activities. Of these compounds, 26 (KUC16D425) showed the highest mPGES-1 inhibition at 10 µM. This compound have also been observed to induce apoptosis and inhibit cell migration in MCF-7 cells. In silico molecular docking calculations were performed to understand the binding interactions of compounds with target proteins. ADMET predictions were also done to evaluate drug-like properties of the novel compounds.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.142.2212.2651 Keywords Carvacrol 1,2,4-triazoles cancer apoptosis mPGES-1 in silico studies DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Zn(OAc)2•2H2O: An efficient catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of 2-substituted benzothiazoles
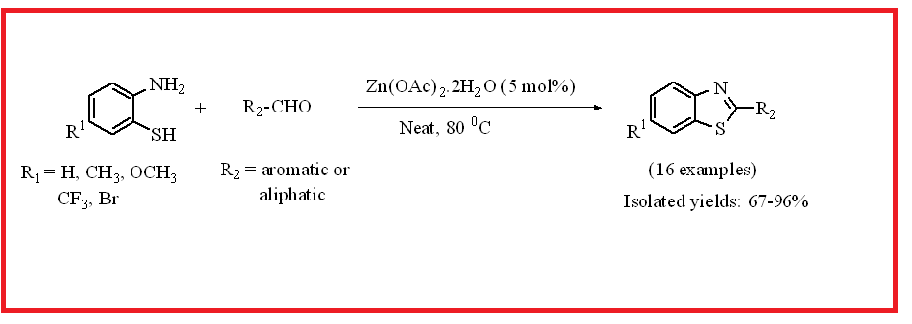
By condensation from aldehyde and 2-aminothiophenol at 80 0C, environmentally friendly, easily accessible, and inexpensive Zn(OAc)2.2H2O (5 mol%) was used to synthesize electronically and structurally divergent benzothiazoles in moderate to good yields (67-96%). All the 2-substituted benzothiazole analogues were thoroughly characterized by IR, NMR and mass spectral analyses.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.140.2210.2618 Keywords Catalysis aldehydes 2-aminothiophenol benzothiazoles zinc acetate solvent-free condition DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.