Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2021 Volume: 1 Issue:1-2 January-December
1) Welcome to the First Issue of Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry

ACG Publications has international journals that have been serving as an open access since 2007 to our valuable scientists. Its goal is to make it possible for scientists to access their own knowledge, produced by their own efforts and financial sources, through their colleges and institutions. Now, we are delighted to welcome the launch of Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, a new peer-reviewed on-line journal, supporting open access.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.1.2112.2313 Keywords New Journal Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Allelopathic Effect of Aqueous Extracts of Stinkwort (Dittrichia graveolens L.) on Germination and Growth of Some Weed Species
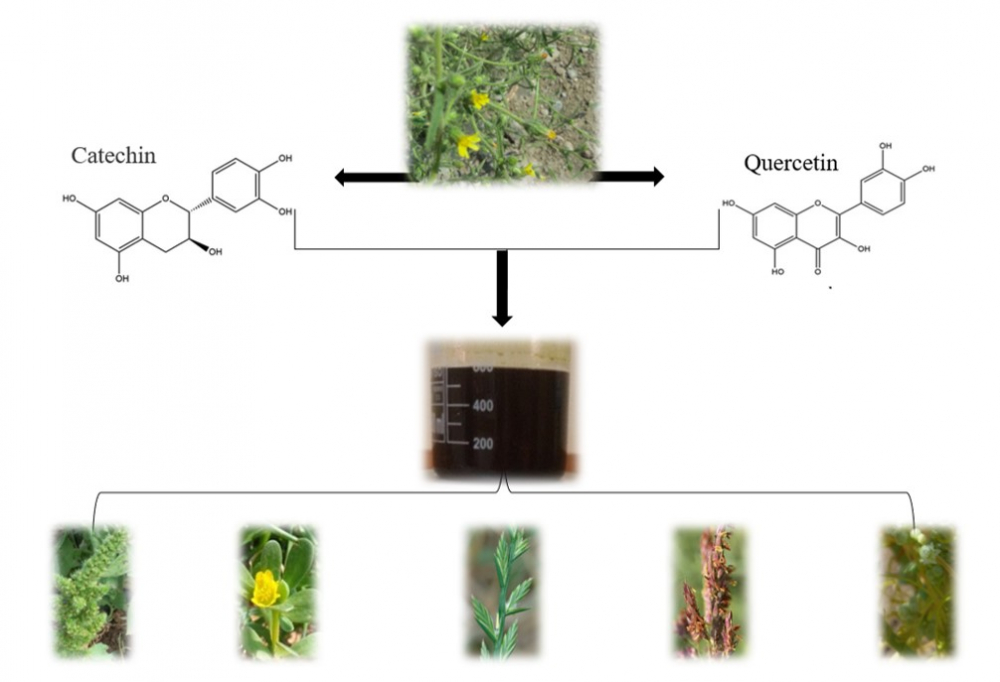
The experiment was implemented by CRD design with three replications and lasted for 40 days, from 5 October until 15 November 2020. Four extract concentrations of D. graveolens 0, 2, 6, and 10% were used. The concentration of 0% was considered as control. The allelopathic effect has been studied on five weed species; Amaranthus retroflexus L., Portulaca oleracea L., Lolium multiflorum Lam., Sorghum halepense L., and Cuscuta campestris Yunck. The research also aimed to determine the effect of Stinkwort extract on the growth of tomato seedlings. All concentrations affected seed germination for all studied weeds. The concentration of 10% was more influential in growth-related indicators compared to other concentrations. The seeds of L. multiflorum and rhizomes of S. halepense were more tolerant to D. graveolens allelochemicals in germination rate than A. retroflexus, P. oleracea, and C. campestris. All concentrations led to a reduction in the weed heights and the wet and dry weights compared with the controls. The effect of the extract with various concentrations was catalytic for the growth of tomato seedlings, as the average height of tomato seedlings was in direct proportion to the concentration.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2.2107.2151 Keywords Allelochemicals weeds seeds rhizomes concentration DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Environmentally Friendly Extraction of Antioxidants from Elettaria cardamomum seeds with Glucose-Citric Acid-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent
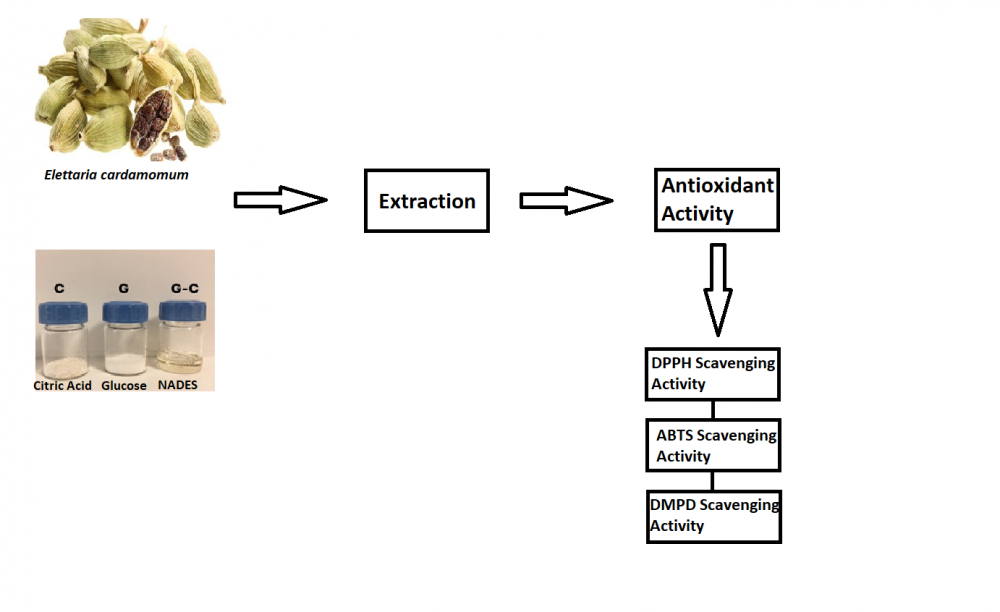
Elettaria cardamomum belongs to the Zingiberaceae family. It contains components (phenolic compounds, alkaloids, terpenoids) it has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. The purpose of this study is to research the effect of glucose-citric acid based natural deep eutectic solvent (NADES) on the antioxidant activity of Elettaria cardamomum. In this study, glucose-citric acid was used as a NADES and methanol-water was used as a conventional solvent. The radical scavenging activities, phenolic compound and tannin amounts of the extracts obtained as a result of extraction with two different solvents were found. Antioxidant activities of extracts prepared with natural deep eutectic solvent were found to be higher. It has been shown that NADES, which are less harmful on the health and environment, have low toxicity and are environmentally friendly, can be used in extraction instead of traditional solvents such as hexane, benzene, and methanol.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.3.2107.2149 Keywords Elettaria cardamomum antioxidant activity NADES DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Biological Activities of Medlar (Mespilus germanica) Extracts Obtained Using Different Solvents
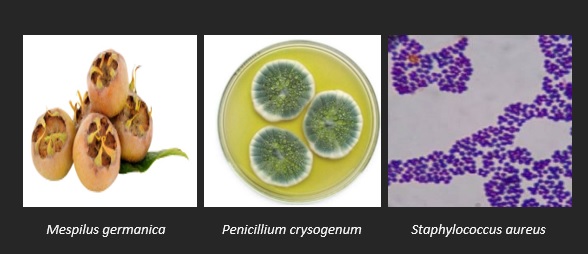
In this study, antibacterial and antifungal properties of four medlar extracts obtained using four different solvents, ethanol, methanol, acetone and water, were investigated. The disk diffusion method was used to determine the antimicrobial effects of the extracts. In addition, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) and minimum fungicidal concentration (MFC) values were determined. The antibacterial effect of the pure water extract of medlar on S. aureus bacteria was found to be high (11.46 mm). In addition, the MIC and MBC values of the pure water extract were determined as 35.15 and 23.39 µg/mL for S. aureus bacteria. When the antifungal effect was examined, the antifungal effect of the pure water extract of medlar against P. crysogenum was found to be high (14.00 mm). The MIC and MFC values of the pure water extract of medlar are 23.43 and 11.72 µg/mL for P. crysogenum, respectively. Therefore, it was concluded that the pure water extract had the highest antimicrobial effect.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.4.2112.2294 Keywords Medlar extract antifungal; bactericidal DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Ixiolirion tataricum (Pall.) Schult. & Schult.f. var. tataricum.

The role of plants in human life and the importance of plants in the food, drug and cosmetics industry have been increasing nowadays. This study investigates biological and chemical properties of root, branch, leaf, flower and aerial ethanol extracts of Ixiolirion tataricum (Pall.) Schult. & Schult. f. var. tataricum species, consumed as food in the population. The chemical composition of the species has been determined by the LC-MS/MS by specifying total phenolic and flavonoid contents. Antioxidant activity, cholinesterase, urease, tyrosinase, elastase and collagenase inhibitory activities have also been studied. According to the results of LC-MS/MS, quinic acid, protocatechuic acid, p-coumaric acid, and rutin have been detected. The branch ethanol extract contained higher amounts of quininic acid (12.101 µg analyte/g extract) than extracts of leaves, flowers, roots and aerial parts. On the other hand, the leaves ethanol extract exhibited high antioxidant activity in all tests (ABTS: IC50= 57.47±0.86 µg/mL, CUPRAC: A0.5= 66.76±1.86, DPPH: IC50: 119.2±1.52). The species has the potential to be used in the food industry due to its high antioxidant capacity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.5.2112.2301 Keywords Ixiolirion tataricum LC-MS antioxidant enzyme activities collagenase elastase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2021 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
