Records of Natural Products
Year: 2024 Volume: 18 Issue:3 May-June
1) Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of the Genus Nageia
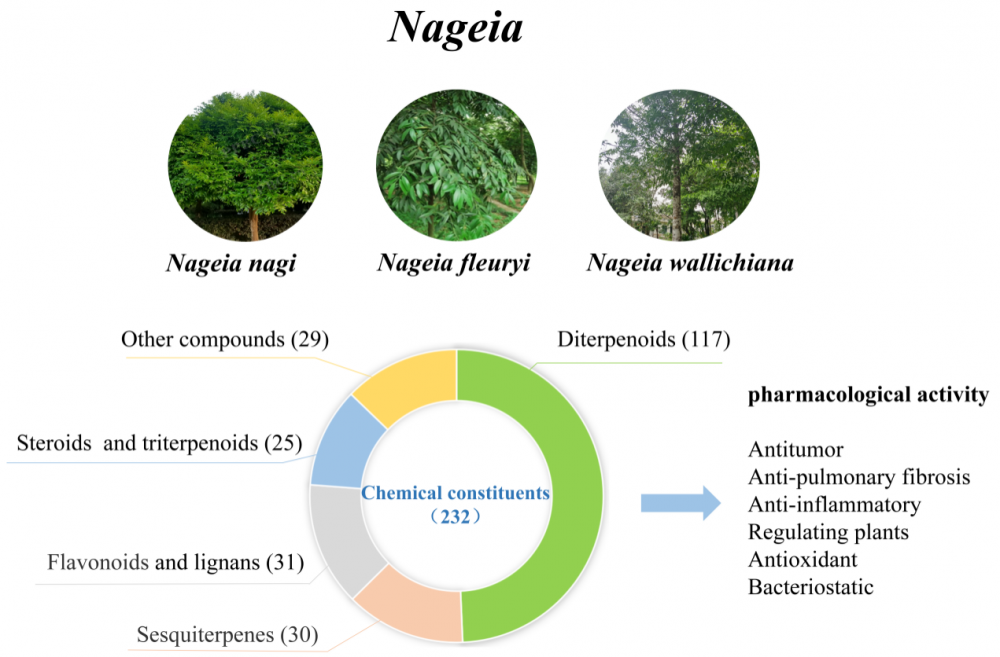
There are seven species in the genus Nageia, a member of the Podocarpaceae family; five are found in China. They are primarily found in eastern and southern Asia, close to the equator at the 30th parallel north and south, and in coastal mountainous areas and islands in the western Pacific. These herbs are extremely valuable for medicinal purposes. The three species of Nageia that are the subject of most current research on their chemical composition and pharmacological properties are N. nagi, N. fleuryi, and N. wallichiana. There are currently 232 known chemical components, which include steroids, flavonoids, sesquiterpenoids, and diterpenoids. Of these, 86 diterpenoid dilactones comprise most of the chemical components, and only plants of the Nageia genus contain C-ring decarbonized diterpenoid dilactones. These plants exhibit promising pharmacological activities such as anti-tumor, antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties. For the first time, an in-depth and systematic evaluation of the chemical constituents and pharmacological properties of plants in the Nageia genus is presented in the this article. This theoretical framework will help in the future investigation and development of medicinal resources and active ingredients within the genus.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.435.2311.2979 Keywords Nageia diterpenoids nagilactones antitumor antioxidants bacteriostatic DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) A New Sesquiterpene from the Fungus Penicillium sp. LPFH-hzw-zw1
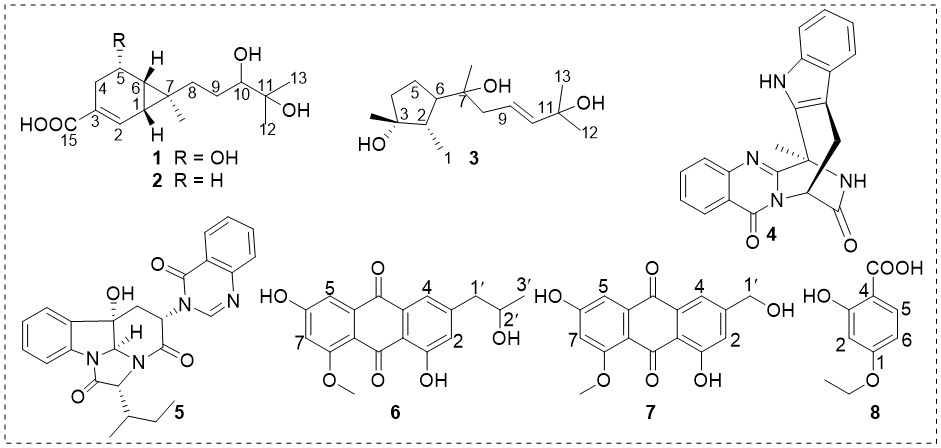 An investigation into the secondary metabolites of the sea sediment-derived Penicillium sp. LPFH-ZW-1 led to the isolation of a new compound, named penicipeneacid (1), along with seven known compounds. The structures of these compounds were identified through extensive analysis of the 1D and 2D NMR data, combined with HRESIMS data. The absolute configuration of 1 was determined by comparing the experimental and predicted ECD spectra. The bicyclo[4.1.0]heptane nucleus in compounds 1 and 2 was rarely found in nature. The known compounds were identified to be sesquicaranoic acid B (2), 9-cycloneren-3,7,11-triol (3), fumiquinazoline J (4), versiquinazoline H (5), penipurdin A (6), questinol (7), 2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzoic acid (8). Compounds 4 and 7 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and K562 tumor cell lines, with IC50 values ranging from 12.6 to 37.1 M.
DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.453.2402.3149
Keywords
marine fungus
Penicillium
sesquiterpene
penicipeneacid
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
An investigation into the secondary metabolites of the sea sediment-derived Penicillium sp. LPFH-ZW-1 led to the isolation of a new compound, named penicipeneacid (1), along with seven known compounds. The structures of these compounds were identified through extensive analysis of the 1D and 2D NMR data, combined with HRESIMS data. The absolute configuration of 1 was determined by comparing the experimental and predicted ECD spectra. The bicyclo[4.1.0]heptane nucleus in compounds 1 and 2 was rarely found in nature. The known compounds were identified to be sesquicaranoic acid B (2), 9-cycloneren-3,7,11-triol (3), fumiquinazoline J (4), versiquinazoline H (5), penipurdin A (6), questinol (7), 2-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzoic acid (8). Compounds 4 and 7 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and K562 tumor cell lines, with IC50 values ranging from 12.6 to 37.1 M.
DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.453.2402.3149
Keywords
marine fungus
Penicillium
sesquiterpene
penicipeneacid
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
3) Antimicrobial and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Compounds from the Branches of Uvaria siamensis
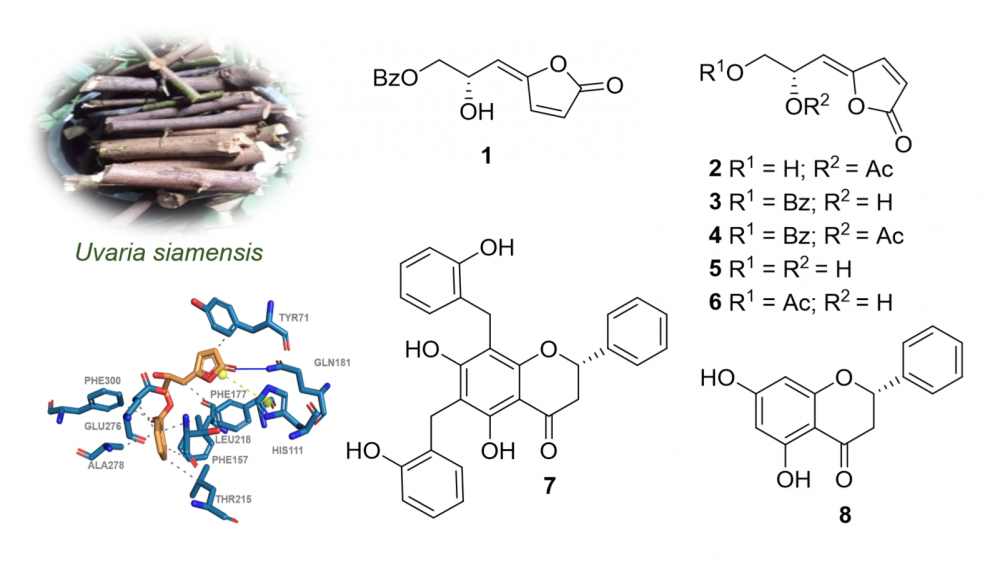
A new γ-butenoid, (Z)-6-acetylsphaerodol (2), along with seven known compounds, (4E)-7-benzoyloxy-6-hydroxy-2,4-heptadien-4-olide (1), (6S)-melodorinol (3), (6S)-acetylmelodorinol (4), (Z)-sphaerodiol (5), (Z)-7-acetylsphaerodol (6), dichamanetin (7), and pinocembrin (8), were isolated and structurally elucidated from Uvaria siamensis growing in Thailand. Their chemical structures were assigned by extensive spectroscopy (NMR and HRESIMS), as well as comparisons with the previous literature. Compounds 1-8 were evaluated for the antimicrobial activity against two multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains, 23Sa1 and SA-ATCC. Compounds 4 and 6 displayed moderate activity with inhibitory zones of 13 and 12 mm against 23Sa1 and SA-ATCC strains, respectively. Compounds 3 and 7 exhibited significant efficacy, displaying IC50 values of 157.7 and 94.2 µM, respectively, against α-glucosidase. According to the docking data, compounds 3 and 7 have a greater influence on binding contacts with the α-glucosidase active pocket, thereby affecting the inhibitory activity of the enzyme.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.452.2402.3145 Keywords Annonaceae Uvaria siamensis (Z)-6-acetylsphaerodol γ-butenoid antibacterial activity α-glucosidase inhibition DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Structure Characterization and Anti-tumor Activity of Polysaccharides from Rohdea chinensis
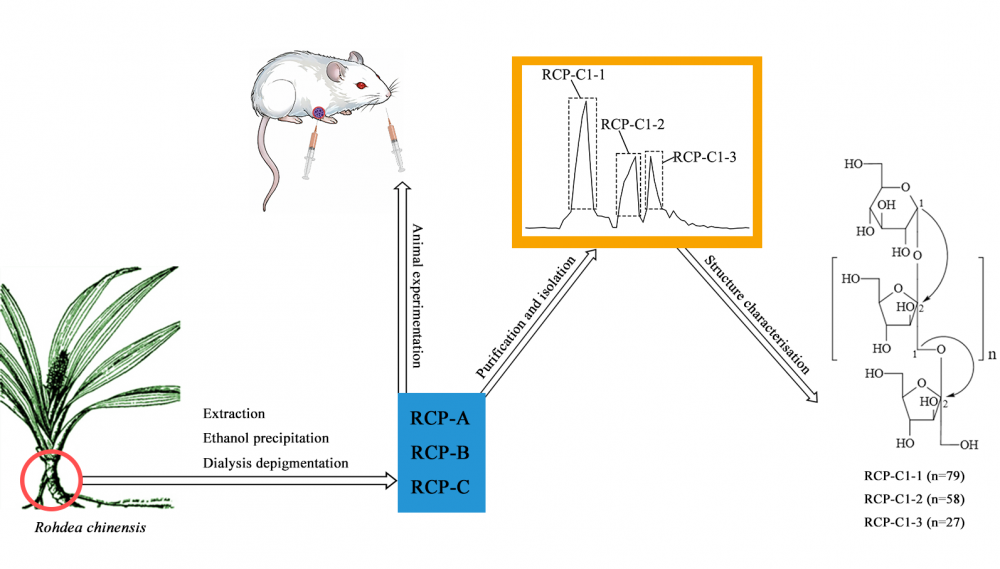
Three crude polysaccharides of RCP-A, B, and C were derived from the rhizome of Rohdea chinensis by means of hot water extraction, gradient ethanol precipitation and dialysis. Three different polysaccharides of RCP-C1-1, RCP-C1-2, and RCP-C1-3 were isolated using cellulose DEAE-52 and Sephadex G-200 chromatography from RCP-C. The average molecular weights of RCP-C1-1, RCP-C1-2, and RCP-C1-3 were measured as 1.51×104, 1.06×104, and 4.86×103 by means of MALDI-TOF MS and UHPGC, respectively. All three polysaccharides were found to consist of D-fructose and D-glucose following hydrolysis and comparison with literature data. Based on FT-IR and NMR analysis, the polysaccharides were identified as inulin-type fructans, with their backbone composed of α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-(β-D-fructofuranosyl)n-(1→2)-β-D-fructofuranoside (nRCP-C1-1=79, nRCP-C1-2=58, nRCP-C1-3=27). The anti-tumor activity of the polysaccharides (RCP-A, B, and C) was evaluated in H22 tumor-bearing mice. The results suggested that the polysaccharides (RCP-A, RCP-B, and RCP-C) inhibited the growth of H22 hepatocellular. Further, the treated groups of RCP-A, RCP-B, and RCP-C exhibited improvements in body weight as well as spleen/thymus indexes in H22 tumor-bearing mice.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.454.2403.3165 Keywords Rohdea chinensis polysaccharides anti-tumor activity inulin-type fructans DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) A Novel Limonoid from the Seeds of Chisocheton macrophyllus
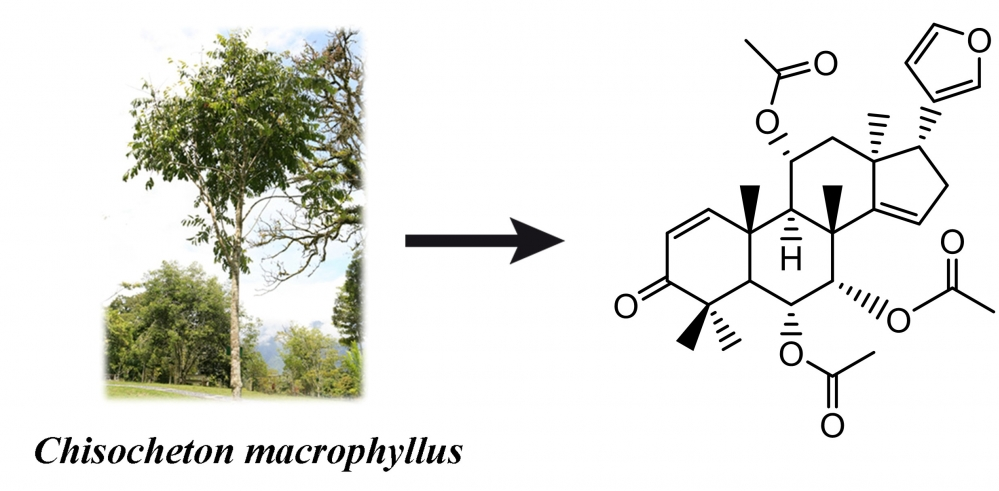
This study aimed to isolate a novel limonoid compound, (6R,7S, 8R, 9R, 10R, 11R, 13S, 17R)-17-(furan-3-yl) -4, 4, 8, 10, 13-pentamethyl-3-oxo-4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-6,7,11-triyltriacetate (11α-acetoxydysobinin) (1), and 3 pre-existing limonoids, namely dysobinin (2), dysobinol (3), and 7-deacetylepoxyazadiradione (4) from the seeds of Chisocheton macrophyllus (Meliaceae). In addition, the structure of the isolated compounds was determined using various spectroscopic techniques, including UV, IR, HRTOFMS, 1D, and 2D NMR. The cytotoxic effects of each compound were then evaluated against breast cancer cells of the Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 (MCF-7), but no significant activity was observed.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.451.2311.2960 Keywords Chisocheton macrophyllus Meliaceae limonoid cytotoxic activity MCF-7 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) 9,11-Cycloneren-3,7-diol: a New Cyclonerane Sesquiterpene from the Marine-Sediment-Derived Fungus Trichoderma harzianum WH-22
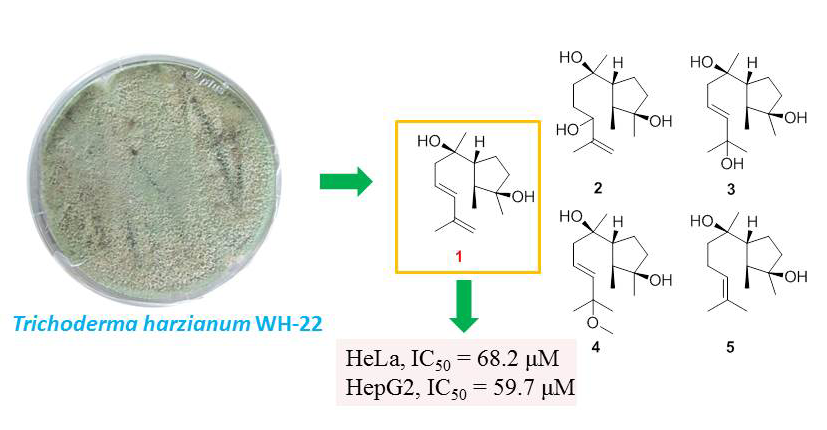
One new cyclonerane sesquiterpene, 9,11-cycloneren-3,7-diol (1), along with four known ones, 11-cycloneren-3,7,10-triol (2), 9-cycloneren-3,7,11-triol (3), 11-methoxy-9-cycloneren-3,7-diol (4), and cyclonerodiol (5), were obtained from the extract of marine-derived fungus Trichoderma harzianum WH-22. The structure of 9,11-cycloneren-3,7-diol (1) was elucidated by comprehensive spectroscopic analysis, including 1D/2D NMR and HRESIMS data. 9,11-Cycloneren-3,7-diol (1) exhibited weak cytotoxicity against HeLa and HepG2 cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 68.2 and 59.7 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.456.2403.3175 Keywords Cyclonerane sesquiterpene Trichoderma harzianum structure elucidation cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) A New Sterol-Related Metabolite from the Soft Coral Capnella imbricata
.jpg)
Exploratory research was carried out on the ethyl acetate extract derived from the soft coral Capnella imbricata, sourced from the southeastern waters of Taiwan. This investigation yielded the isolation of three sterol-related compounds (1–3). Among these compounds, one previously unidentified metabolite, designated as 4β-hydroxy-24-methylene-5-cholesten-7-one (1), was discovered, along with two known metabolites, namely, 3β-hydroxy-24-methylene-5-cholesten-7-one (2) and gorgostan-5,25-dien-3β-ol (3). The structures of these isolated metabolites were determined through comprehensive spectroscopic analyses. Furthermore, the relative stereochemistry of metabolite 3 was established for the first time in this study using single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The potential anti-inflammatory properties of metabolites 1–3 were evaluated by investigating their ability to suppress the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) proteins in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.455.2402.3141 Keywords Capnella imbricata sterol X-ray iNOS COX-2 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Polyscias serrata Roots in a Parallel Study of Network Pharmacology
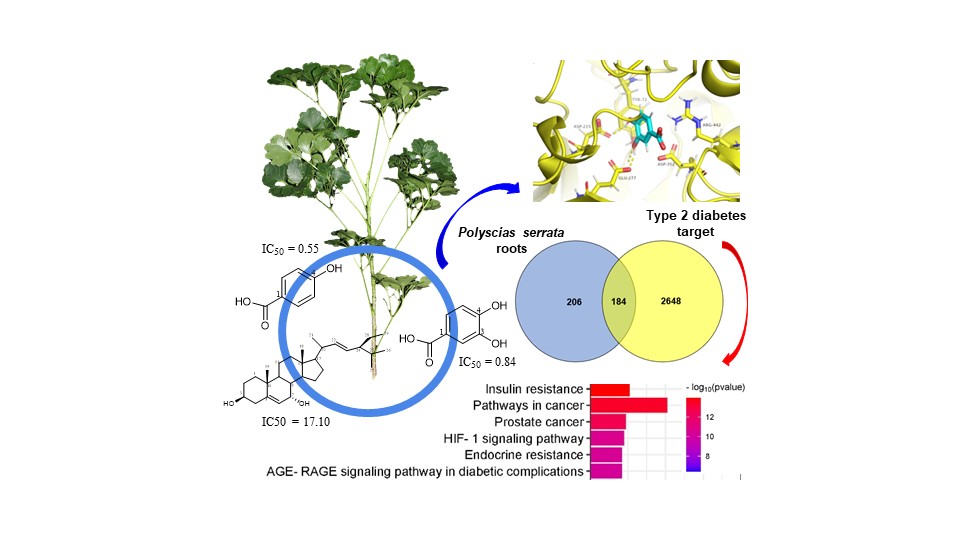
Nine known compounds were isolated from the P. serrata roots and showed promising inhibitory activity against α-glucosidase. The molecular docking study of them was exhibited the 4-hydroxyl group in the aromatic ring of benzoic acid derivatives improves the bioactivity. Network pharmacology was performed to investigate the molecular mechanisms of isolated compounds and suggested that the insulin resistance pathway would be a primary mechanism of action. This is the first time the α-glucosidase inhibitors of P. serrata roots were reported.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.457.2401.3038 Keywords Polyscias serrata α-glucosidase inhibitor molecular docking network pharmacology DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Chemical Components of the Extracts and Essential Oil of Sanguisorba minor Scop. subspecies muricata (Spach) Briq.
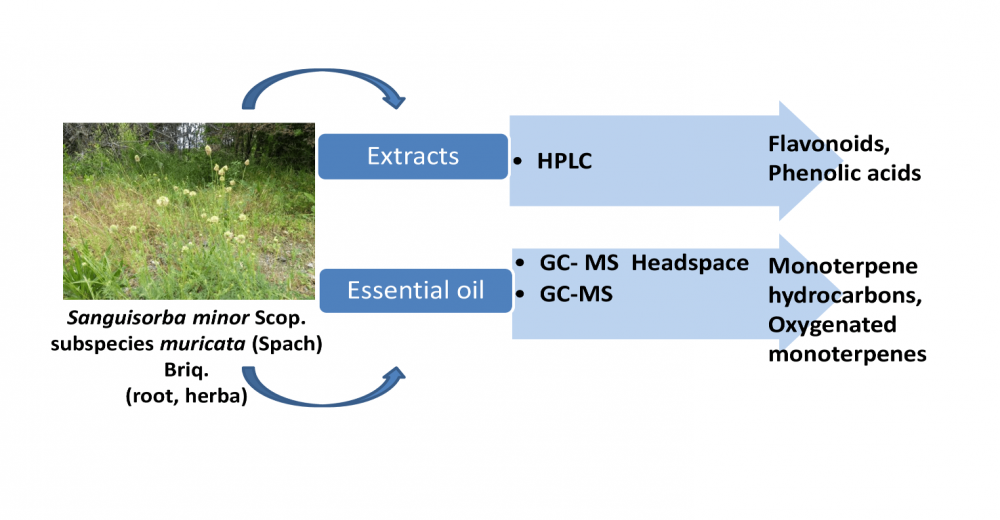
The aim of this study is to investigate the chemical composition of ethanol, acetone extracts and essential oil of the roots and aerial parts of Sanguisorba minor subsp. muricata. Flavonoids and phenolic acids were identified as the main components in the studied extracts herein. Rutin and quercetin-3-sophoroside were found to be dominant flavonoids in both extracts. Although it was observed that the determined chemical compositions of the essential oil obtained from the aerial parts and roots of the plant species were quite different from the data obtained by Headspace measurement, as expected, the essential oils obtained from the species were found to be rich in mainly monoterpene hydrocarbons and oxygenated monoterpenes. While salicylaldehyde, carvacrol and linalool were determined as the main components in the essential oil obtained from the aerial parts of the species, the main components in the essential oil obtained from the roots were observed as borneol, myrtenol and α-campholenol.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.459.2401.3008 Keywords Essential oil extracts GC-MS headspace HPLC DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Calkbisabenacid, A New Bisabolane Sesquiterpenoid from the Leaves of Callicarpa kwangtungensis
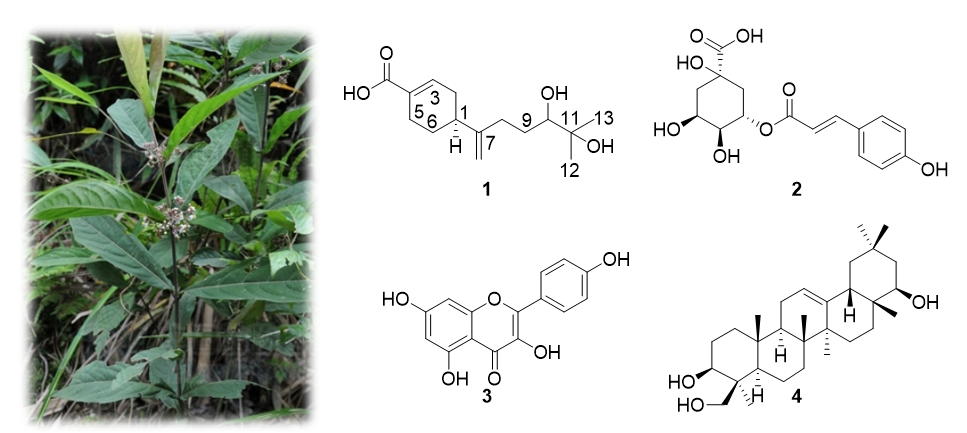
A new bisabolane sesquiterpenoid, named calkbisabenacid (1), was isolated from the leaves of Callicarpa kwangtungensis, along with four known compounds: 5-O-coumaroylquinic acid (2), kaempferol (3), and soyasapogenol B (4). The structure of compound 1 was determined by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, COSY, HSQC, and HMBC spectra, in combination with the HRESIMS data. The absolute configuration of C-1 in compound 1 was determined by comparing the experimental ECD spectrum with the calculated ECD spectra of the two possible stereoisomers. The known compounds were identified by comparing their NMR data with those reported in the literature. Compound 4 was isolated from this species for the first time. None of these compounds demonstrated any inhibitory effects against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.461.2404-3196 Keywords Calkbisabenacid sesquiterpene Callicarpa kwangtungensis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.