Organic Communications
Year: 2024 Volume: 17 Issue:4 October-December
1) Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of 2-thioxoimidazolidinone derivatives
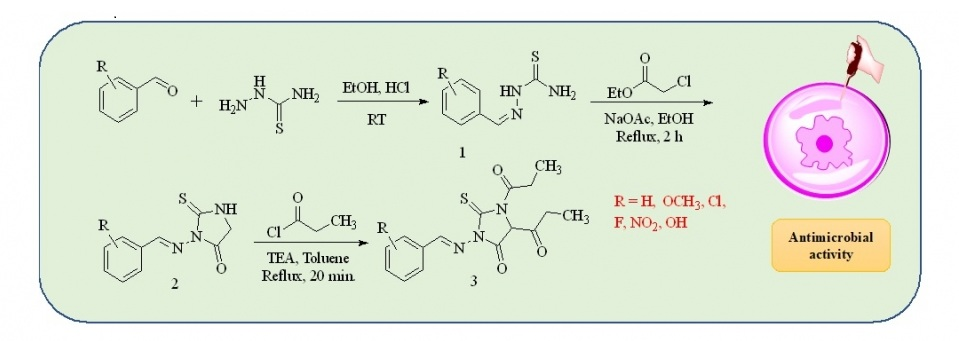
The infectious diseases caused by antimicrobial pathogens are often difficult to treat and thwarted by resistance to drugs. Therefore, designing new drugs to treat antimicrobial infections is a challenge in drug discovery research. A series of 2-thioxoimidazolidinone derivatives were synthesized in high yield from N'-arylideneamino-2-thioxoimidazolidin-4-ones using propionyl chloride and triethyl amine in toluene medium. The compounds were screened for the in vitro antifungal and antibacterial activities. The studies revealed that compounds (±)1,1'-(3-(((1E,2E)-3-(2-methoxyphenyl)allylidene)amino)-4-oxo-2-thioxoimidazolidine-1,5-diyl)-bis(propan-1-one) and (±)1,1'-(3-((2,4-dichlorobenzylidene)amino)-4-oxo-2-thioxoimidazolidine-1,5-diyl)bis-(propan-1-one) possess antifungal properties comparable to the reference drug ketoconazole. This study highlights the importance of substituted 2-thioxoimidazolidinone derivatives, and their potential as antimicrobial agents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.174.21.3340 Keywords 2-Thioxoimidazolidinone in-vitro studies molecular docking nitrogen heterocycles antifungal agents DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Microwave-assisted acetylation of alcohols, phenols, and amines using phthalimide-N-sulfonic acid as an organo-catalyst under solvent-free conditions
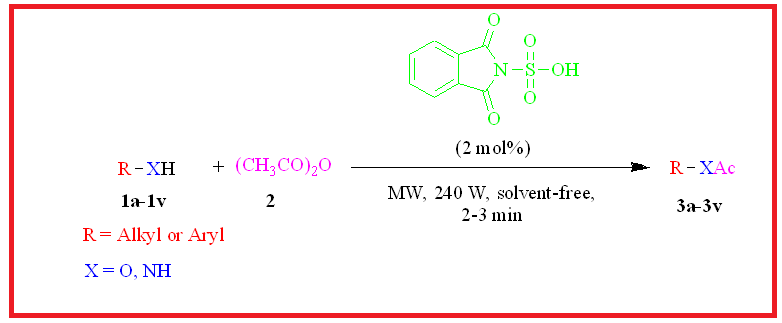
An efficient, environmentally benign, and simple procedure has been developed for acetylation of various alcohols, phenols and amines. In this method, Phthalimide-N-sulfonic acid is used as a new and effective organo-catalyst in catalytic amount. This procedure was carried out under solvent-free conditions at room temperature as well as at microwave irradiation. Microwave-assisted reaction gives improved yields with a reduced reaction time. The present method provides noteworthy advantages of microwave irradiation and organo-catalyst such as simple work-up procedure, short reaction time with excellent yields and environmentally benign procedure. All compounds have been confirmed by 1H NMR, 13C NMR and IR spectroscopy.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.175.2410.3349 Keywords Microwave, phthalimide-N-sulfonic acid, organo-catalyst, protection, acetylation, solvent-free DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Synthesis of novel sulfamides derived from dopamine analogues with their in silico studies against hyperprolactinemia
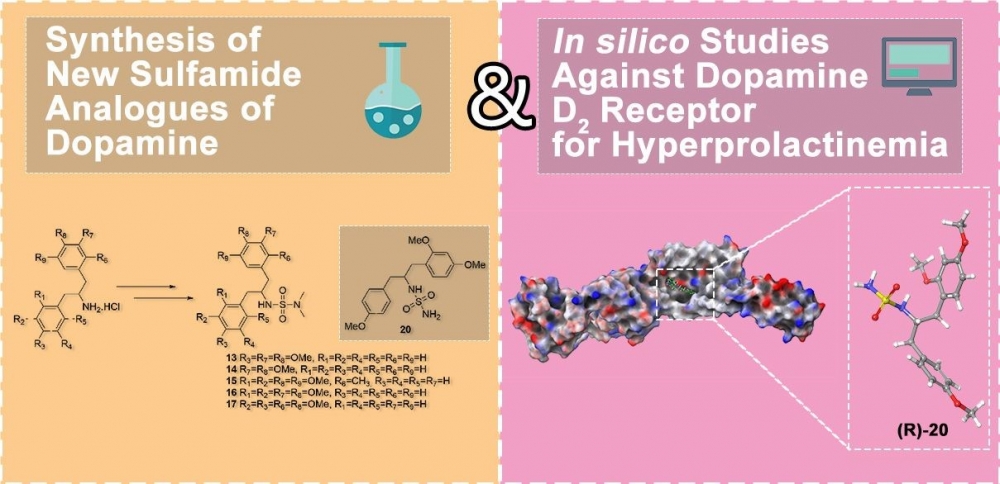
Because of the important biological properties of sulfamides, in the present work six novel sulfamides were synthesized from dopamine derivatives and their insilico studies were carried out against hyperprolactinemia. Five sulfamides were synthesized via the reaction of known dopamine derivatives with N,N-dimethyl sulfamoyl chloride in the presence of NEt3. For comparison of biological activity, a sulfamide without N-alkyl at the terminal nitrogen was also synthesized. For this synthesis, firstly benzyl alcohol was reacted with chlorosulfonyl isocyanate (CSI). Then, new sulfamoyl carbamate was obtained by the reaction of the formed carbamate derivative with a dopamine analogue in the presence of NEt3. As a result of the hydrogenolysis of the formed sulfamoyl carbamate under Pd-C catalyst, a new sulfamide was obtained. Molecular docking simulations and ADME predictions were employed to assess the binding affinity and drug-like properties of sulfamide derivatives at the dopamine D2 receptor, aiming to identify potential contributors to hyperprolactinemia. In the in silico docking studies, it was determined that the binding affinity of the R enantiomer of unsubstituted sulfamide 20 to the D2 receptor was higher than that of Cabergoline and Quinagolide used as standards and there was no deviation from the Lipinski rule of five in the ADME evaluation.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.176.2411.3361 Keywords Dopamin derivatives dopaminergic hyperprolactinemia molecular docking sulfamides DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Synthesis, characterization, antioxidant, in silico-based virtual screening and anti-cancer potential of substituted 2-(4-acetyl-5-methyl-1h-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-n-phenylacetamide derivatives
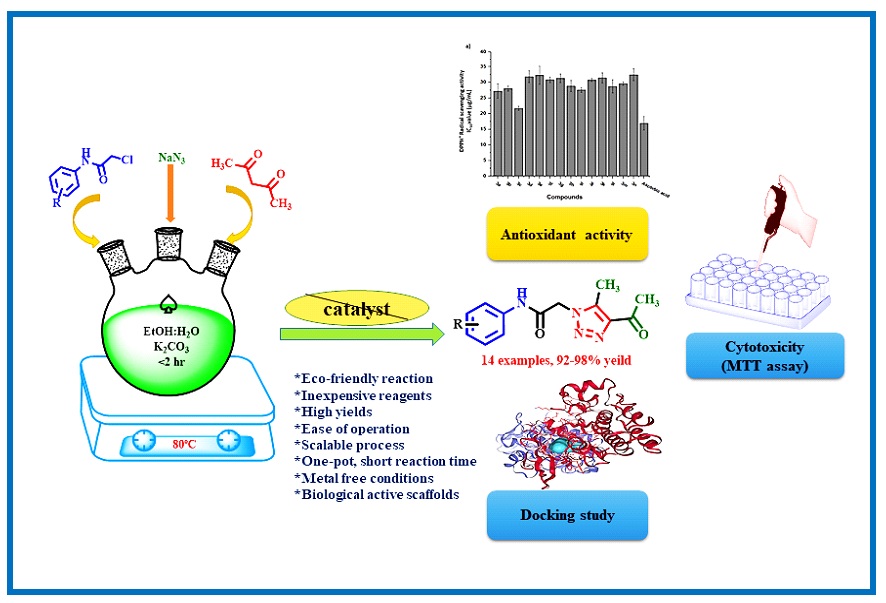
Cancer has been a widespread disease for decades in various of types for decades, and the search for effective treatments continues. Researchers are exploring various new drugs, including natural compounds and small organic molecules, for their potential to combat cancer. One promising approach involves hybrid structures that combine different pharmacophore units with known biological activities. These structures have gained popularity due to their encouraging results. In this study, we synthesized several new hybrid compounds containing 1,2,3-triazole units. We confirmed the structures of these compounds using methods like ¹H NMR, ¹³C NMR, and LC-MS. We then evaluated their antioxidant properties and in vitro anticancer activities. The results showed that these new compounds demonstrated having good radical scavenging activity and potential agents for anticancer activity. Notably, compounds 3b, 3d, 3a, 3m, and 3i exhibited low concentrations of IC50 values (14.08±0.6, 14.3±0.8, 15.82±0.4, 18.12±0.86 and 19.7±0.88 μg/mL, respectively) when compared to the standard drug Cisplatin (IC50: 21.13±1.6 µg/mL). Computational analysis has been performed like ADMET evaluation and Molecular docking studies revealed the compounds having good binding affinity with cancer target proteins like HIF-1α ranging from -8.1 kcal/mol to -7.0 kcal/mol and HER2 ranging from -10.0 kcal/mol to -8.8 kcal/mol respectively when compared with standard drug Cisplatin showed binding affinity ranging from -4.2 kcal/mol to -3.9 kcal/mol.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.177.2412.3374 Keywords Nucleophilic substitution 2-chloro-N-arylacetamide 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition 1,2,3-triazoles MTT assay DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Synthesis of β-enaminoesters from β-ketoesters and amines by solvent-drop grinding approach in PEG 400

An effective catalytic system for the synthesis of β-enaminoesters from β-ketoesters under mechanochemical conditions using mortar and pestle in recyclable PEG 400 as solvent-drop approach was developed. This method has a number of benefits, including shorter reaction times, use of inexpensive recyclable solvent cum catalyst system, compatible reaction conditions, and high product yields. ©2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.178.2409.3334 Keywords β-ketoesters β-enaminoesters grinding solvent-drop PEG 400 mechanochemical catalysis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of α-aminophosphonates using nano ZnO catalyst: evaluation of their anti-diabetic activity
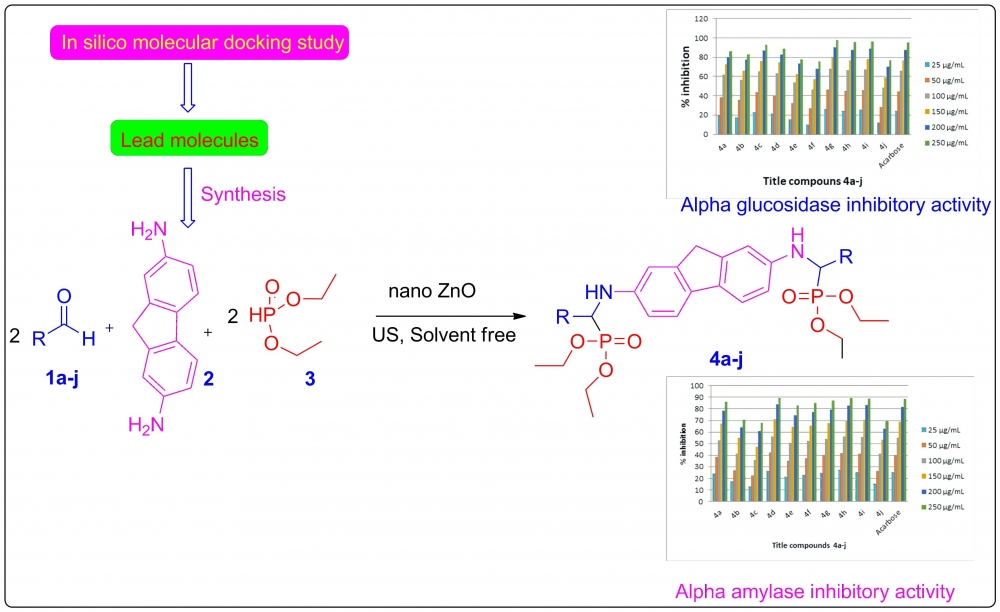
A more efficient and environmentally friendly way of synthesizing α-aminophosphonates is achieved by employing nano-ZnO to catalyze the Kabachnik-Fields reaction under ultrasonication within a solvent-free environment. Before synthesis, molecular docking and in silico ADME analysis were used to assess each molecule's drug-like characteristics and ability to inhibit α-amylase and α-glucosidase. The newly synthesized compounds' in vitro inhibitory effects on α-amylase and α-glucosidase were also evaluated, and their structure was confirmed using spectroscopic investigation. The target enzyme was effectively inhibited by most of the substances. In comparison to the reference drug, acarbose (IC50, 106.5±0.6 μg/mL), compounds 4d (IC50, 102.2±0.3 μg/mL), 4h (IC50, 102.9±0.4 μg/mL), which contained a 2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl moiety, and 4i (IC50, 103.9±0.5 μg/mL) showed the strongest inhibitory activity. The enzyme inhibition of the remaining compounds ranged from moderate to good.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.180.2412.3384 Keywords Kabachnik-Fields reaction α-aminophosphonates ADMET molecular docking α-amylase α-glucosidase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
7) Heat gun-assisted rapid and efficient synthesis of tetra-substituted Zinc(II) phthalocyanines functionalized with alkylthio or alkoxy chains
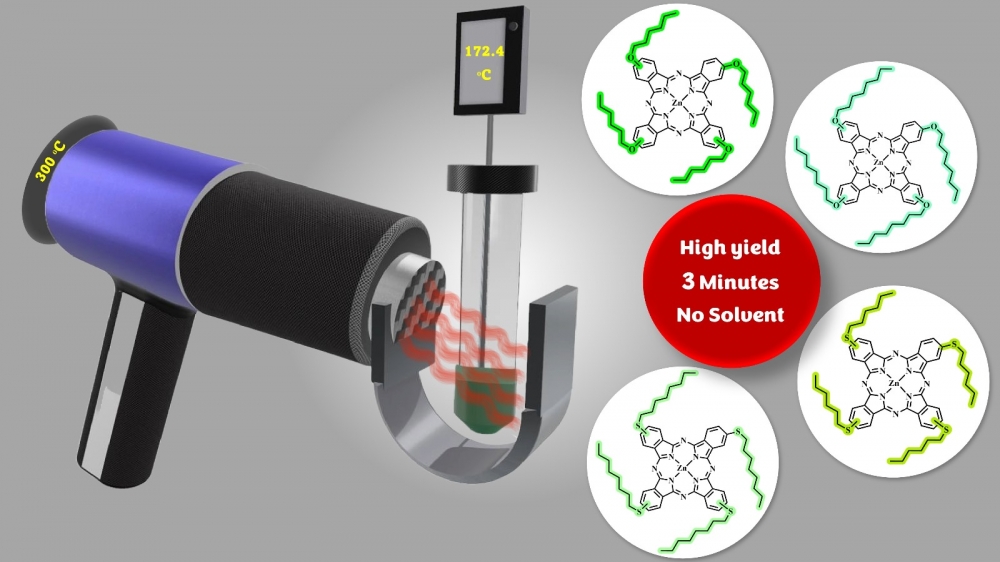
The most common method for metalated or metal-free phthalocyanines involves starting from phthalonitrile derivatives. These conventional reactions are generally carried out in high-boiling-point solvents (such as pentanol, DMF, DMSO, Quinoline, etc.) under reflux where they often have extended reaction times of up to 24 hours. New reaction methods with lower energy in short periods of time have been an issue to solve nowadays. Considering all, we aimed to synthesize substituted zinc phthalocyanine derivatives rapidly and with higher yields, without using any solvents. This study shows new synthesis methods for substituted phthalocyanine derivatives. ZnPc derivatives with different chain lengths functionalized with "O" and "S" donor atoms from the peripheral position have been synthesized in yields ranging from 52-75% in overall 3 minutes. Compared to conventional methods, which typically require extended reaction times and high energy consumption, this innovative approach reduces the reaction time from 18 hours to just 3 minutes and decreases energy consumption from 1.926 kWh to 0.063 kWh. The method achieves high reaction yields, highlighting its potential for sustainable chemical synthesis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/acg.oc.179.24.11.3376 Keywords Solid-state synthesis heat-gun high yield green synthesis alkyl substituted phthalocyanine DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.