Records of Natural Products
Year: 2019 Volume: 13 Issue:6 November-December
1) A New Aporphine Alkaloid from Illigera aromatic
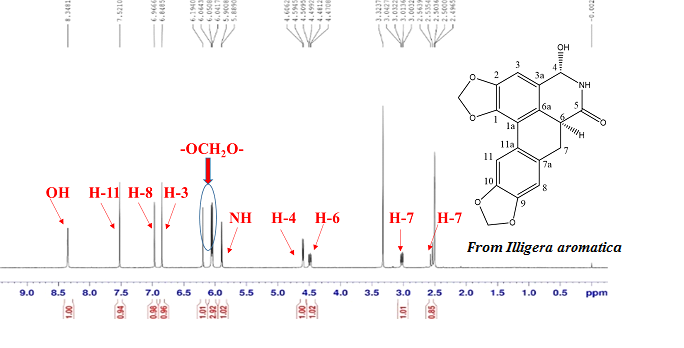
Chemical investigation of the aerial part of Illigera aromatic S.Z. Huang & S.L. Mo has resulted in the isolation and characterization of one new aporphine alkaloid, illigerine B (1), along with three known analogues laurodionine B (2), N-formyl-laurolitsine (3) and illigerine A (4). Their structures were established by spectrometric means and physico-chemical properties. The in vitro cytotoxic activities of compound 1 against Hela, SMMC7721, and Bcap37 cell lines were evaluated. Compound 1 exhibited moderate cytotoxic activity against the three tumor cell types, with IC50 values of 12.40 ± 0.78, 32.61 ± 2.05, and 28.69 ± 1.80 μg/mL. This work shown that aporphine alkaloids might be useful as characteristic markers in chemotaxonomic research of the genus Illigera.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.121.18.11.1033 Keywords Hernandiaceae Illigera aromatic Aporphine alkaloid lligerine B Cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) First Report on Volatile Composition of Tricholoma anatolicum in Comparison with Tricholoma caligatum
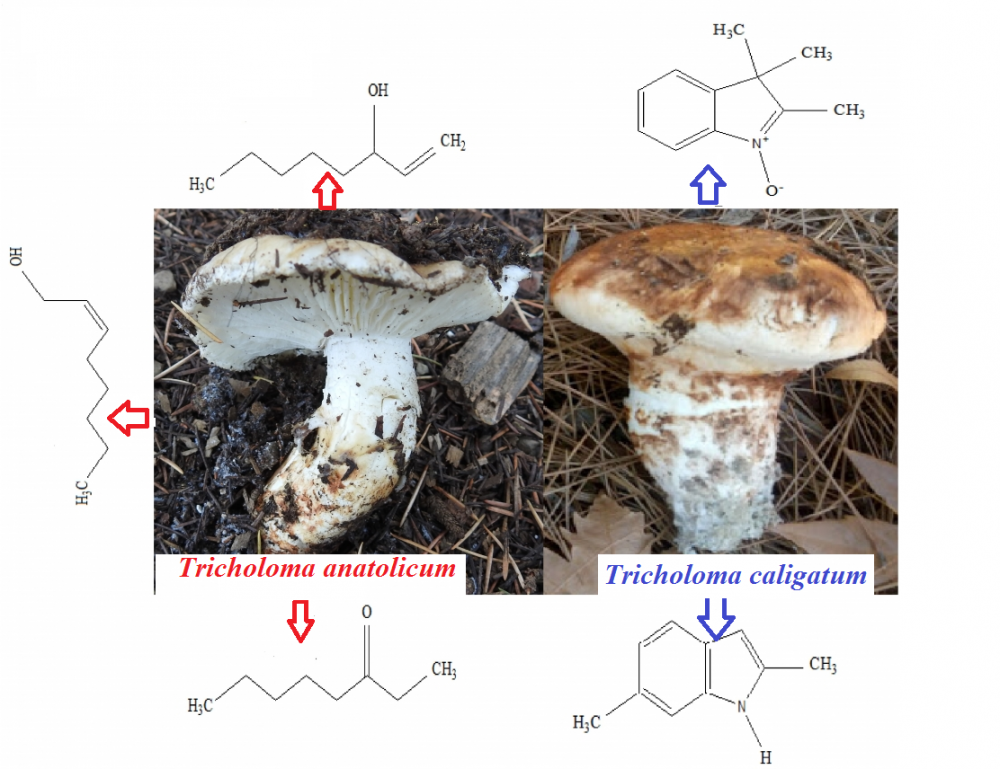
Tricholoma anatolicum collected from Turkey is consumed by public and exported to Japan every year. It was previously identified as Tricholoma caligatum until it was recognized as a new species. In the existing literature, there is no information on the aromatic composition of T. anatolicum. Therefore, in this study it was aimed to identify the volatile composition of T. anatolicum together with T. caligatum. Species identification was confirmed using molecular analyses based on ITS rDNA sequencing. Volatile compounds of both mushroom species were extracted using liquid-liquid extraction method and determined by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-Flame Ionization Detector (GC-MS-FID). In the two Tricholoma species, 31 volatiles were obtained and grouped in seven chemical classes. The amounts of alcohols, volatile acids and esters were found to be higher in T. anatolicum, whereas the amounts of terpenes were detected as higher in T. caligatum. 1-Octen-3-ol responsible for the mushroom-like odour was only found in T. anatolicum.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.122.18.12.1095 Keywords Tricholoma anatolicum Tricholoma caligatum Tricholomataceae volatile aroma composition Turkey DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) A New Heliquinomycin Analogue with Immunosuppressive Activity from Streptomyces sp. jys28
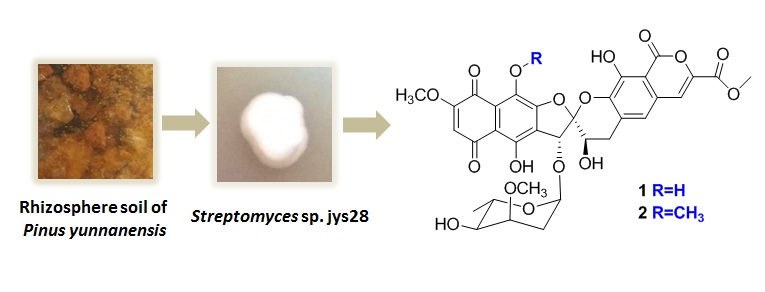
Heliquinomycin (1) and a new analogue 9′-methoxy-heliquinomycin (2) were isolated from the culture broth of Streptomyces sp. jys28. The structure of new analogue was elucidated by comprehensive analyses of HR-ESI-MS and NMR spectroscopic data. Among them, Heliquinomycin (1) showed immunosuppressive and antibacterial activities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.123.18.12.1085 Keywords Heliquinomycin Immunosuppressive activity Antibacterial activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Chemical Compounds from the Twigs and Leaves of Caesalpinia cucullata Roxb

Abstract: A new stilbene dimer, caesalstilbene A (1), along with twelve known compounds were isolated from the twigs and leaves of Caesalpinia cucullata Roxb by means of various chromatographic techniques. Their structures were identified on the basis of NMR spectral analysis and comparing their spectral data with those reported in the literatures. The absolute configuration of 1 was assigned by the comparison of the experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism spectra. Compound 1 was evaluated for their cytotoxicity on HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7 and SW-480 human cancer cell lines, but it was inactive. This is the first report of chemical investigation on Caesalpinia cucullata..
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.124.18.12.1088 Keywords Caesalpinia cucullata Leguminaceae stilbene dimer caesalstilbene A DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
5) Two New Lignans from Lycopodium japonicum Thunb.
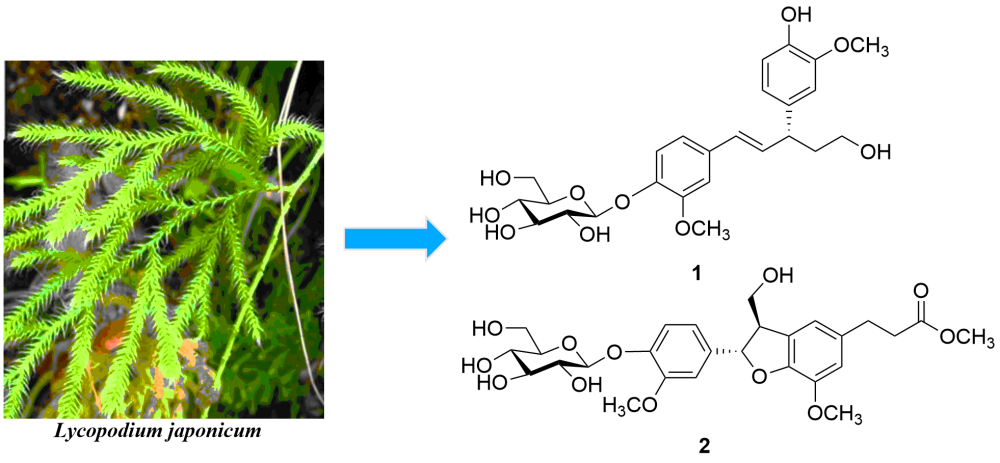
Two new lignans, named lycojaponicumoside A (1) and B (2), together with four known compounds (3˗6) were isolated from the n-BuOH extract of Lycopodium japonicum. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic methods, especially various NMR techniques, HRESIMS and circular dichroism (CD). The absolute configuration of compound 1 was established by the calculation of electronic circular dichroism (ECD) curves. All of the compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities against A549 and HepG2 human cancer cell lines, but those compounds did not exhibit cytotoxicity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.126.19.03.1205 Keywords Lycopodium japonicum lignans ECD calculation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors from the Root Bark Pseudolarix amabilis (Nelson) Rehd. (Pinaceae)

Pseudolarix amabilis (Nelson) Rehd, is a monotypic genus plant belonging to the family Pinaceae. The root bark , known as “Tu-Jin-Pi” has been used for the treatment of skin diseases. During our activity screening, the water-soluble part of the 70% EtOH extract of P. amabilis bark showed excellent inhibitory bioactivities on PTP1B enzyme, leading to the phytochemical isolation of the root bark of P. amabilis. Three oleanane-type compounds (1-3) and seven phenolic compounds (4-10) were isolated, in which oleanolic acid 3-O-β-D-glucuronyl-6′-ethyl ester (1) was identified as a new saponin. The chemical structures of these compounds were elucidated by 1D/2D nuclear magnetic resonance and high resolution mass spectra. In addition, their pharmacological inhibitory bioactivities on PTP1B enzyme were evaluated, and the three oleanane-type compounds 1-3 exhibited inhibitory bioactivities with IC50 values of 1.90 ± 0.37, 19.15 ± 0.10 and 10.44 ± 0.59 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.125.18.12.1132 Keywords Pseudolarix amabilis PTP1B inhibitors Isolation and identification Oleanane-type compounds Phenolic compounds Oleanolic acid 3-O-β-D-glucuronyl-6′-ethyl ester DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) A New Dimeric Sesquiterpenoid from Chloranthus japonicus
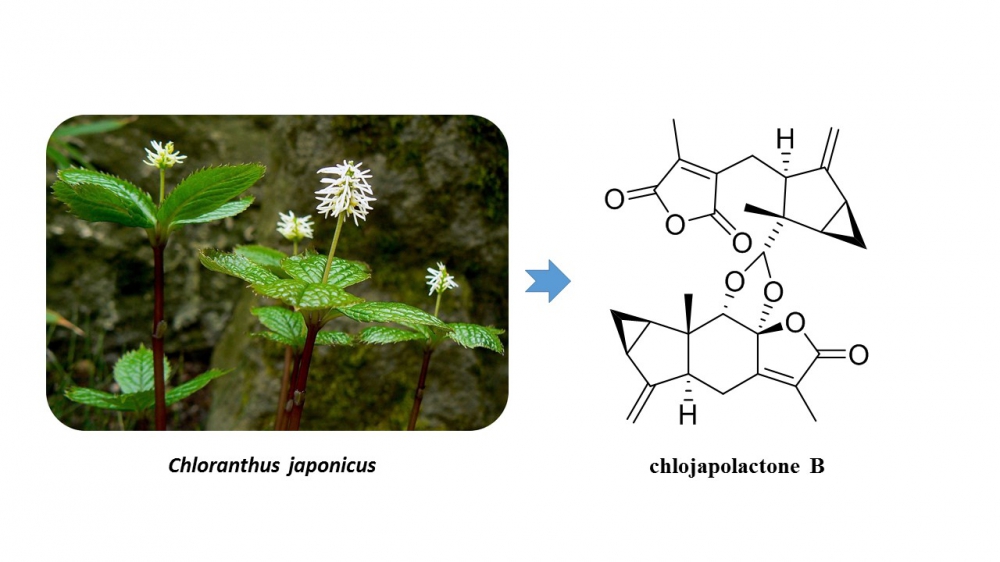
Phytochemical investigation into the whole plants of Chloranthus japonicus Sieb. led to isolation and identification of a new dimeric lindenane sesquiterpenoid, named chlojapolactone B (1), and two new phenolic derivatives (2 and 3). Their chemical structures were elucidated on the basis of HRESIMS and NMR spectroscopic data, and the absolute configuration of 1 was determined using the electronic circular dichroism (ECD) analysis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.127.19.02.1193 Keywords Chloranthus japoni Dimeric sesquiterpenoid Phenolic derivative DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) New Oxoprotoberberine and Aporphine Alkaloids from the Roots of Amoora cucullata with Their Antiproliferative Activites
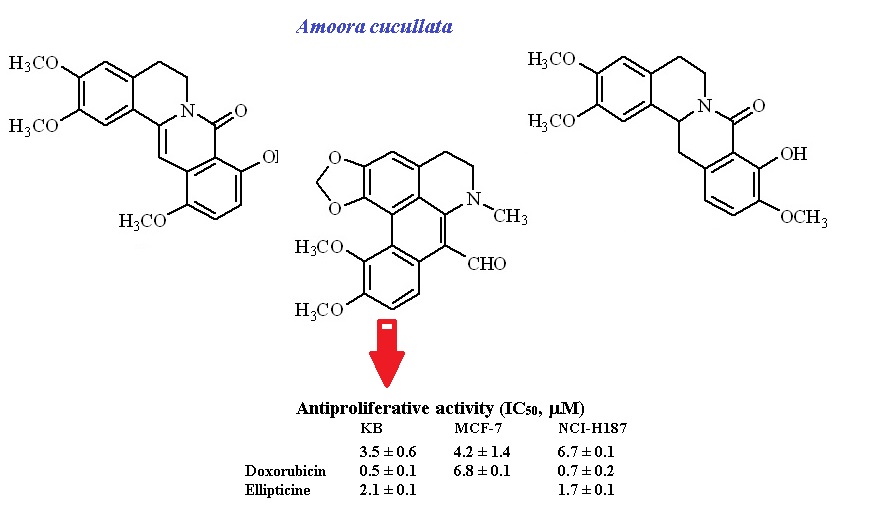
Two new oxoprotoberberine alkaloids, amocurine A and B (1 and 2), a new aporphine alkaloid, amocurine C (3), along with three known compounds (4-6) were isolated from the roots of Amoora cucullata. Their structures were determined by analysis of spectroscopic data. The isolated compounds were evaluated for their antiproliferative activity against three human cancer cell lines (KB, oral cavity; MCF-7, breast cancer; and NCI-H187, small cell lung cancer). Compounds 3 showed the most potent activities against KB and MCF-7 cell lines with IC50 values 3.5 and 4.2 mM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.128.19.02.1181 Keywords Oxoprotoberberine Aporphine Antiproliferative activity Amoora cucullata DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Two New Cholestanol Glycosides from the Roots and Rhizomes of Smilacina henryi
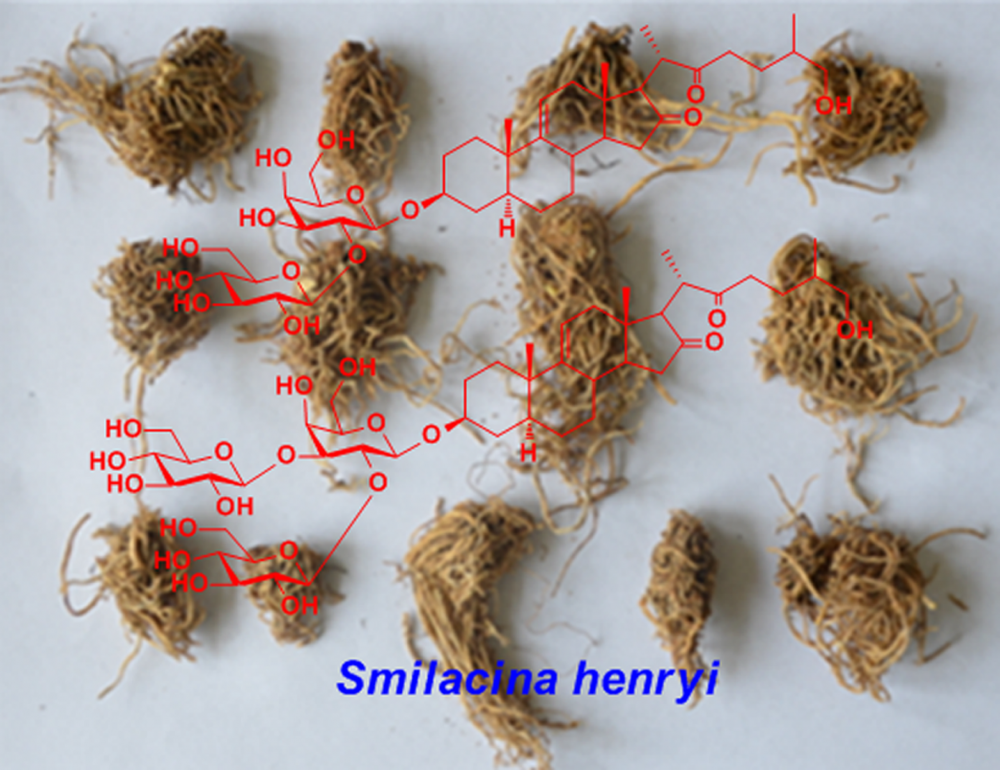
Abstract: Two new cholestanol glycosides (1 and 2) were obtained from the roots and rhizomes of Smilacina henryi. Their structures were determined as 5α-cholest-9(11)-ene-3β, 26-dihydroxy-16, 22-dione 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-galactopyranoside (1), 5α-cholest-9(11)-ene-3β, 26-dihydroxy-16, 22-dione 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)- [β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)]-β-D-galactopyranoside (2), by physicochemical properties and spectroscopic methods. In addition, the isolated glycosides were tested for their cytotoxic activity against human HepG2 tumor cells and compound 2 showed moderate activity with IC50 value of 59.32 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.19.03.1248 Keywords Smilacina henryi cholestanol glycosides structure determination cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Cephalounei A, a New Cephalotaxus Alkaloid from the Powdered Stems of Cephalotaxus fortune Hook. f

A new Cephalotaxus alkaloid, namely Cephalounei A (1), was isolated from the stems of Cephalotaxus fortune Hook. f. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic and mass-spectrometric analyses, including 1D-, 2D-NMR and HRESIMS. The relative and absolute stereochemistry of 1 was determined by a combination of NOESY correlations and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectra, respectively. The cytotoxicity of all compounds were evaluated against five cancer cell lines.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.19.02.1197 Keywords Cephalotaxus alkaloid Cephalounei A ECD DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2019 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.