Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Volume: 16 Issue:2 March-April
1) Three Isoflavonoid Glycosides from the Rhizomes of Achyranthes bidentata and their Protective Effects on H2O2 Induced H9c2 Cardiomyocytes Injury

A new isoflavonoid glycoside, achyranthoside C (1), along with two known compounds (2 and 3) were isolated from the rhizomes of Achyranthes bidentata. Compounds 1-2 were two rare natural isoflavonoid glycosides with C8 hydroxymethylene derivatization. Their structures were elucidated through comprehensive 1D and 2D NMR, UV, IR, and HRMS analyses. Bioassay results showed all the three compounds had obviously cell-protective effects against H2O2-induced H9c2 cardiomyocytes injury in a concentration -dependent manner.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.257.21.04.2039 Keywords Achyranthes bidentata isoflavonoid glycosides antioxidant activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Chemical Profiling Revealed a Dominant Compound Trans-Anethole and Biological Evaluation of an Edible Plant Clausena harmandiana Containing Essential Oil
300dpi.jpg)
This study we aimed to characterize the chemical and biological properties of the edible plant, Clausena harmandiana (Pierre) Guillaumin. Fresh leaves of this plant were hydrodistilled to obtain the essential oil, which was characterized by GC-MS. Total phenolic content was evaluated by Folin-Ciocalteau assay. Biological activity was assessed by measuring antioxidants, antimicrobial activities, and the inhibitory effects on tyrosinase, collagenase, and a-glucosidase. The primary components were trans-anethole (91.44%), followed by estragole (2.98%) and cis-anethole (2.55%). The essential oil contained the amount of phenolic 20.63 mg GAE/g extract and showed the activity to scavenge DPPH (IC50 18.48 mg/mL), ABTS (IC50 3.97 mg/mL) radicals and also presented the ability to reduce Fe3+-TPTZ complex on FRAP assay (3.74 mg TEAC/g extract). Additionally, the C. harmandiana essential oil exhibited antimicrobial activity against Candida albicans (MIC 6.63 mg/ml, MFC 13.25 mg/mL) and interestingly presented enzymatic inhibitory effects on collagenase (IC50 0.059 mg/mL) and a-glucosidase (IC50 0.677 mg/mL). The remarkable activity of inhibition on a-glucosidase was two times more to acarbose (IC50 1.26 mg/mL).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.259.21.03.2025 Keywords Clausena harmandiana Rutaceae chemical profile biological activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics Profiling of Syzygium grande and Oenanthe javanica and Relationship Between Their Metabolite Compositions and Antimicrobial Activity Against Bacillus species
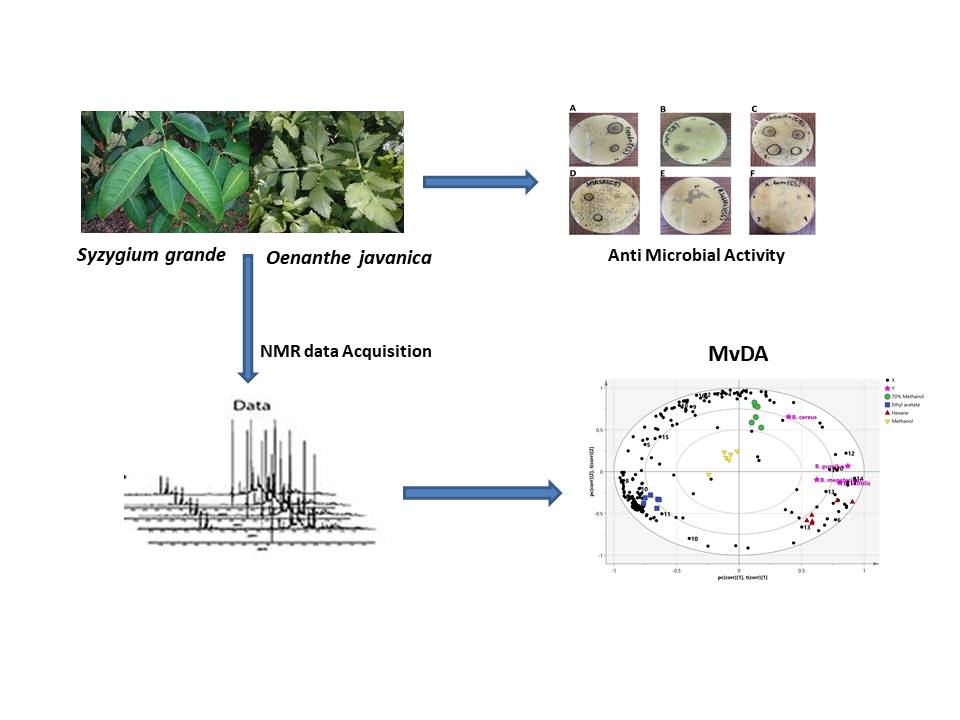
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the variations in the phytochemical compositions and the antimicrobial activities of Syzygium grande and Oenanthe javanica leaf extracts against Bacillus sp. The antibacterial activity of the methanol, 70% methanol, ethyl acetate, and hexane extracts of both plant species were examined in vitro, against various Bacillus species. In addition, the 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) spectroscopy-based metabolomics was employed to gain insights into the correlations between the chemical constituents of the bioactive extract to the biological activity. The hexane extract of S. grande leaves and methanolic extract of O. javanica leaves showed more potent anti-Bacillus activity, among the test extracts. Principal component analysis (PCA) successfully differentiated the extracts on the basis of their metabolite profiles. The results of the Partial Least Square (PLS) analysis showed that the non-polar compounds of the hexane extract of S. grande (alanine, betulin, β-sitosterol, β-caryophyllene, acetic acid and 3-hydroxybutyric acid) were strongly correlated to its anti-Bacillus activity. On the other hand, choline, ellagic acid, and gallic acid, the metabolites present in the methanolic extract of O. javanica, were strongly correlated to its anti-Bacillus activity. On this basis, it was therefore concluded that these conmpounds could be the potential bioactive constituents, contributing to the anti-Bacillus activity of the individual plant species. Further in-depth investigations into the potential utilization of the two plants for useful applications in managing and control of Bacillus sp., will help pave the way towards their valorization.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.258.21.01.1927 Keywords Anti-Bacillus activity Syzygium grande Oenanthe javanica 1H NMR-based metabolomics Multivariate data analysis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Cytotoxic Picrotoxane-type Sesquiterpenoid Lactones from Dendrobium huoshanense

Bioassay-guided led to the isolation of five compounds, including a new picrotoxane-type sesquiterpene lactone, aduncin C (1), together with four known ones (2-5) from Dendrobium huoshanense. Their structures were elucidated by means of extensive spectroscopic analysis. Biological evaluation of the isolates against four human cancer cell lines indicated broad-spectrum and cytotoxic activities with IC50 values ranging from 4.08 to 26.75 μM. Among them, α-dihydropicrotoxinin (3) exhibited significant cell proliferation inhibitory activity, especially for HL-60 (IC50 5.81 μM), MCF- 7 (IC50 6.49 μM), SW-480 (IC50 6.80 μM), respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.260.21.04.2048 Keywords Dendrobium huoshanense picrotoxane-type sesquiterpene cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Antileishmanial Derivatives of Humulene from Asteriscus hierochunticus with in silico Tubulin Inhibition Potential
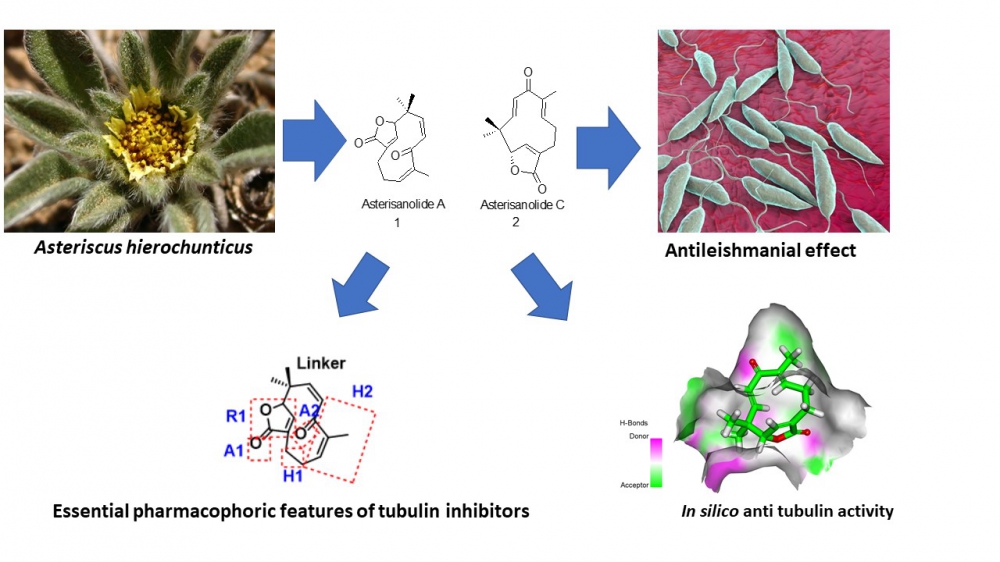
Two humulene derivatives (asteriscunolides A (1) and C (2)) were isolated from the methanolic extract of the whole plant of Asteriscus hierochunticus. Their structures were characterized by IR, 1D, and 2D NMR and HRESIMS data analysis, in addition to comparison with literature. Compounds 1 and 2 exhibited excellent in vitro antileishmanial activities against Leishmania donovani promastigotes with IC50 values of 8.38 and 3.26 µg/mL and against Leishmania donovani axenic amastigotes with IC50 values of 9.41 and 4.69 µg/mL, respectively while Pentamidine (the standard drug) exhibited IC50 values of 4.40 and 29.36, respectively. The isolated compounds possessed good activities against Plasmodium falciparum (D6) and (W2) strains with IC50 values ranging from 3.134 - 4.153 µg/mL. Furthermore, 1 and 2 showed no cytotoxic activity against the transformed human monocytic (THP1) cells. The chemical structures of 1 and 2 showed the essential pharmacophoric features of tubulin inhibitors that act through the colchicine binding site. Accordingly, molecular docking studies against the colchicine binding site of Leishmania tubulin have been preceded. Compounds 1 and 2 showed excellent binding mode with free energies of -5.62 and -5.54 kcal/mol, respectively. Further in silico studies were carried out and expected that 1 and 2 have the likeness to be drugs through exhibiting good ADMET results, no significant affinity against CYP3A4, and general low toxicity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.253.21.01.1945 Keywords Humulene derivatives Asteriscus hierochunticus antileishmanial antimalarial tubulin inhibitor DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
6) Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of Onopordum caricum
Plants are rich sources of biologically and/or pharmacologically active phytochemicals. This study aimed to determine the chemical composition, antioxidant, tyrosinase, anti-cholinesterase, and anti-diabetic activities of ethyl acetate (EtOAc), methanol (MeOH), and water extracts obtained from the aerial parts of Onopordum caricum (Hub.-Mor.), which is an endemic plant species to Turkish flora. As a result of spectrophotometric analysis, the MeOH extract was the richest in total phenolics and flavonoids (46.26 mg GAEs/g and 20.97 mg QEs/g, respectively). In quantitative chromatographic analysis, the MeOH extracts contained considerable amounts of chlorogenic acid, eriodictyol, luteolin 7-O-glucoside, vanillic acid, syringic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, and pinoresinol. Except for the ferrous ion chelating activity assay, MeOH extract showed higher activity than others in all test systems. The activity data exhibited by the MeOH extract in phosphomolybdenum, DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging, CUPRAC, and FRAP tests were 1.46, 1.10, 1.30, 0.87, and 0.76 mg/mL, respectively. The EtOAc extract showed higher activity in all enzyme inhibition assays. The AChE, BChE, α-amylase, α-glucosidase and tyrosinase inhibitory activities of this extract were 0.95, 1.20, 2.37, 1.18 and 1.77 mg/mL, respectively. There was a very high correlation between the extracts' total phenolic and flavonoid contents and their antioxidant activities (phosphomolybdenum, radical scavenging, and reducing power). Since the antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory activity data presented in the current study were found to be higher than the activities of some other Onopordum species in the literature, it was concluded that the plant species in question could be used in the treatment of Alzheimer's, diabetes, hyperpigmentation, and disorders occurred as a result of oxidative stress pressure.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.272.2106.2116 Keywords Onopordum caricum antioxidant activity chemical composition enzyme inhibitory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Chemical Composition and Pesticidal Activity of Alpinia galanga (L.) Willd. Essential Oils in Vietnam
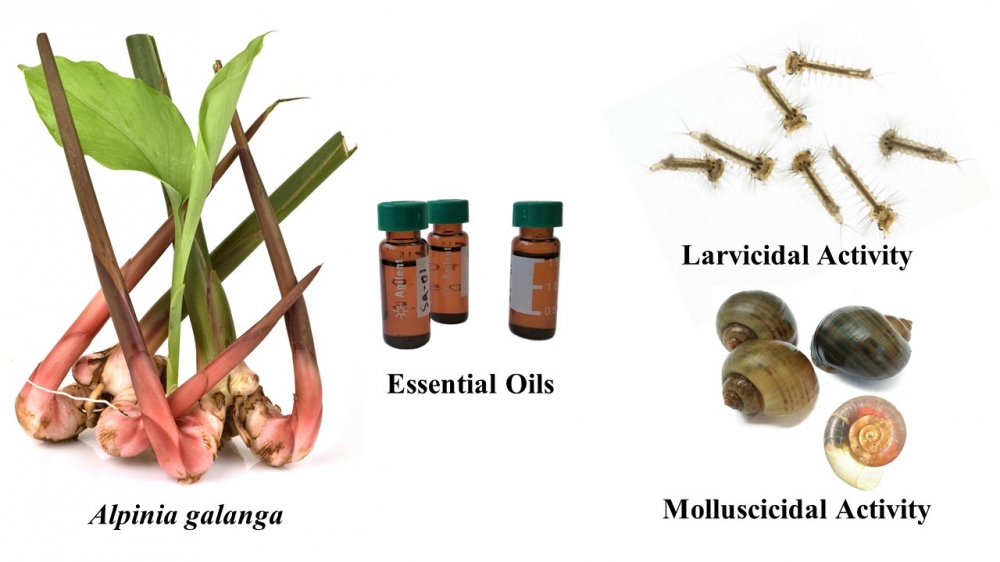

Mosquitoes are vectors of numerous pathogenic viruses and freshwater snails are intermediate hosts for several parasitic worms. There is a need for environmentally-benign botanical pesticides to augment or replace synthetic pesticides. In this research, essential oils from the leaves, stems, rhizomes, and roots of Alpinia galanga, an important Vietnamese medicinal plant, have been obtained by hydrodistillation and analyzed by gas chromatographic techniques. The essential oils were screened for mosquito larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus, for molluscicidal activity against Gyraulus convexiusculus and Pomacea canaliculata, and for inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The essential oils showed moderate to good pesticidal activities against these organisms. However, the oils also showed pronounced lethality to a non-target water bug, Diplonychus rusticus.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.263.21.05.2074 Keywords Larvicidal Molluscicidal Aedes Culex Pomacea acetylcholinesterase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Ex-vivo Immune-stimulating Activity of Scutellaria baicalensis and Its Major Flavonoids on Human Immune Cells
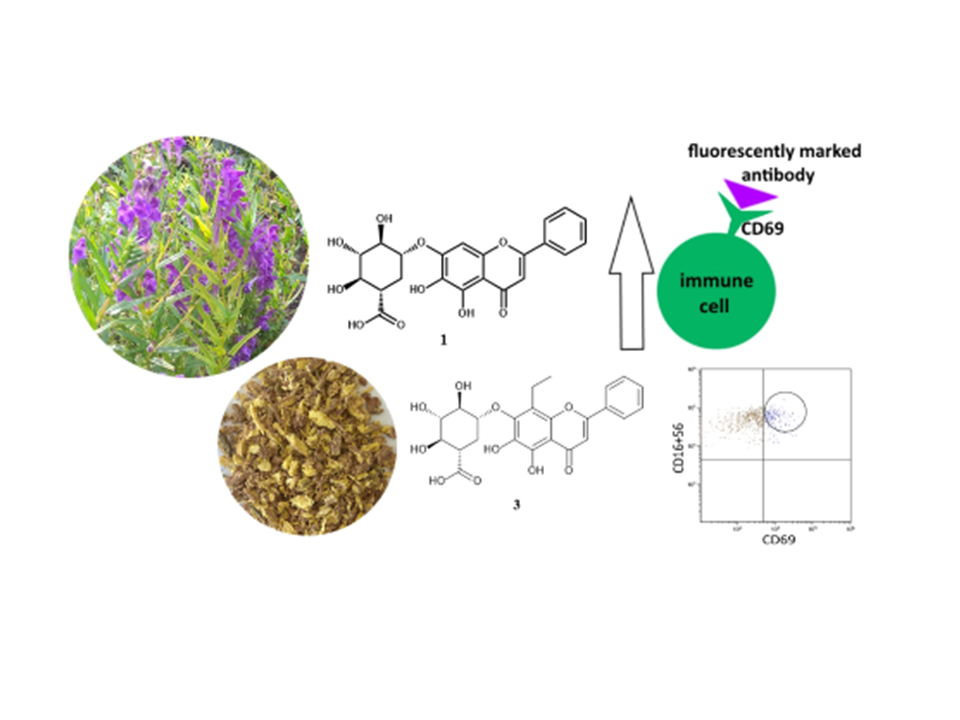
This study investigates the activation of human immune cells (T, B, and NK cells, and granulocytes) by the ethanolic and aqueous extracts of Scutellaria baicalensis root (SBR) and to identify the compounds responsible for such an effect. The cell activation was determined by expression of the cell surface glycoprotein CD69 (cluster of differentiation 69), as measured by flow cytometry. The content of the main flavonoids in SBR extracts was estimated by high performance liquid chromatography with a diode array detector. NK cells were substantially activated by the SBR ethanolic extract (25–200 µg/mL), whereas B cells were activated on a lower scale. NK cells were slightly activated by the SBR aqueous extract (100–200 µg/mL). Wogonoside and baicalin, two major flavonoids present in the SBR extracts, exhibited the highest activation effect on NK cells. The content of baicalin, wogonoside, and baicalein accounted for 201.2, 47.7, and 3.4 mg/g in the ethanolic extract; and for 150.4, 33.6, and 4.6 mg/g in the aqueous extract, respectively. This study shows the immune-stimulating properties of SBR extracts and identifies their active compounds. This data may support the potential utilization of SBR for strengthening the human immune system against bacterial and viral infections.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.264.21.02.1976 Keywords Scutellaria baicalensis Iimune-stimulation flavonoids baicalin baicalein wogonoside DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) In vitro ACE2 and 5-LOX Inhibition of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Essential Oil and its Major Component 1,8-Cineole
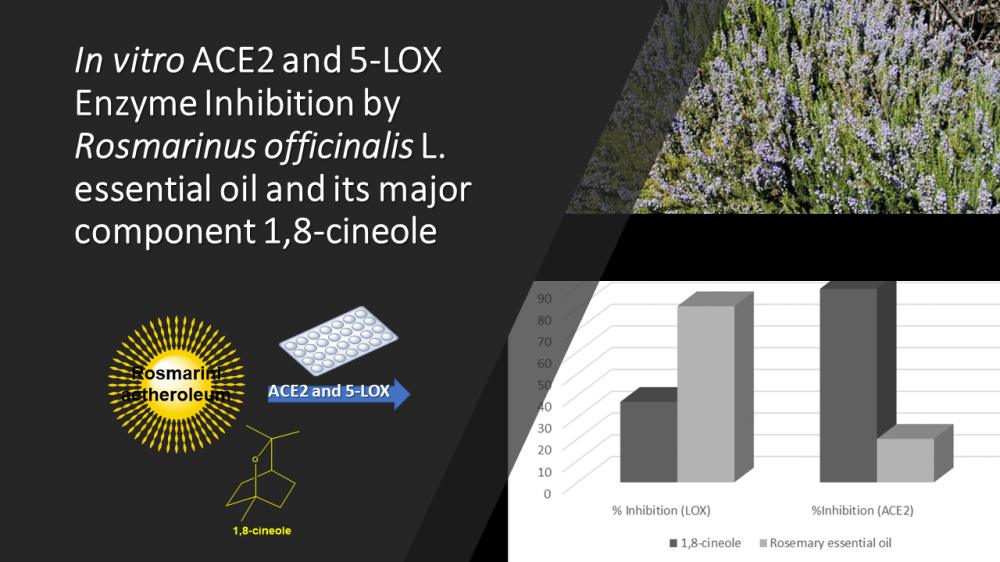
In this present study, Rosmarinus officinalis L. essential oil, and its major component 1,8-cineole was evaluated in vitro for angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), as well as for 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) enzyme inhibitory activity. The essential oil composition was confirmed both by GC-FID and GC/MS, where 1,8-cineole (62.7%), α-pinene (12.6 %), and camphor (8.3 %) were identified as the main constituents. Activity studies were performed at concentrations of 20 µg/mL for essential oil, and 5 µg/mL for the major compound 1,8-cineole, which were compared experimentally with standards. The essential oil was evaluated using a fluorometric multiplate based enzyme inhibition kit, where the ACE2 inhibition of Rosmarinus aetheroleum was 20%, while the 5-LOX inhibition was observed as 81.1%, respectively. In addition, the major constituent 1,8-cineole also showed remarkable ACE2 inhibition with 89.2%, and 5-LOX inhibition with 37.2%, respectively. As a result, the cineole chemotype rosemary essential oil, and its major constituent 1,8-cineol may have antiviral potential applications against coronaviruses due to ACE2 enzyme inhibition with anti-inflammatory effects. Further in vivo studies are needed to confirm the efficacy of essential oils and their constituents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.265.21.05.2080 Keywords Rosmarinus officinalis L. essential oil ACE2 5-LOX 1,8-cineole DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Neoflavonoids from the Heartwood of Dalbergia melanoxylon
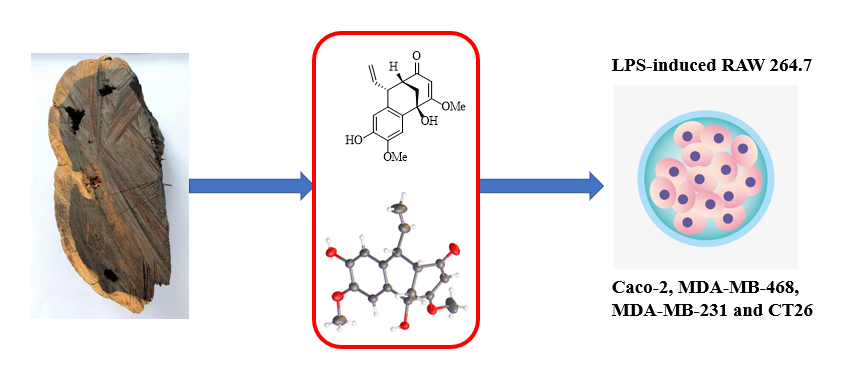
A new neoflavonoid, (1R,8R,9R)-pterolinuse K (1) and six known neoflavonoids (2-7) were obtained from the heartwood of Dalbergia melanoxylon. The structure of the new neoflavonoid was elucidated by extensive NMR investigation, and X-ray crystallographic analysis. Compounds 3 and 6 showed anti-inflammatory activity with IC50 values 23.14 ± 0.30 and 19.46 ± 1.02 μΜ, respectively. Compounds 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 were showed cytotoxicity on Caco-2, MDA-MB-468, MDA-MB-231, CT26 cell lines. Moreover, compounds 2, 4 exhibited the significant activity in MDA-MB-231 cell lines with IC50 values 7.54 ± 1.50 and 7.23 ± 0.40 μΜ, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.267.2105.2071 Keywords Dalbergia melanoxylon neoflavonoids anti-inflammatory activity anti-tumor activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.